|
Helamin
Chemical fouling inhibitors are products that are mixtures of fouling and corrosion inhibitors use in boiler feedwater treatment. Several of these products use aliphatic polyamines to coat the surface of pipes. Helamin Helamin is a boiler feedwater treatment based on amines and polyamines. Helamin is a registered trademark of Helamin Technology Holding SA, Switzerland. Patents have been obtained for Helamin products, and in 2016, the following patents existEP1045045, JP4663046, HK1032080, BR9903614 Chemically, most of the Helamin types are stated by the manufacturer to be a "mixture of polyamines and polycarboxylates in aqueous solution", but some also utilize volatile amines, ammonia, polyelectrolytes, organic polymers, and scavengers of dissolved oxygen. In contrast to the conventional method of the water treatment, its action is based on a preventive protection of the surfaces. Helamin forms a film (i.e., is one of numerous available "filming amines"), which prevents corrosi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boiler Feedwater Treatment
Boiler feedwater is an essential part of boiler operations. The feed water is put into the steam drum from a feed pump. In the steam drum the feed water is then turned into steam from the heat. After the steam is used it is then dumped to the main condenser. From the condenser it is then pumped to the deaerated feed tank. From this tank it then goes back to the steam drum to complete its cycle. The feed water is never open to the atmosphere. This cycle is known as a closed system or Rankine cycle. History of feedwater treatment During the early development of boilers, water treatment was not so much of an issue, as temperatures and pressures were so low that high amounts of scale and rust would not form to such a significant extent, especially if the boiler was “boiler blowdown, blown down”. It was general practice to install zinc plates and/or alkaline chemicals to reduce corrosion within the boiler. Many tests had been performed to determine the cause (and possible protectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boiler Feedwater
Boiler feedwater is an essential part of boiler operations. The feed water is put into the steam drum from a feed pump. In the steam drum the feed water is then turned into steam from the heat. After the steam is used it is then dumped to the main condenser. From the condenser it is then pumped to the deaerated feed tank. From this tank it then goes back to the steam drum to complete its cycle. The feed water is never open to the atmosphere. This cycle is known as a closed system or Rankine cycle. History of feedwater treatment During the early development of boilers, water treatment was not so much of an issue, as temperatures and pressures were so low that high amounts of scale and rust would not form to such a significant extent, especially if the boiler was “ blown down”. It was general practice to install zinc plates and/or alkaline chemicals to reduce corrosion within the boiler. Many tests had been performed to determine the cause (and possible protection) from corrosi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fouling
Fouling is the accumulation of unwanted material on solid surfaces. The fouling materials can consist of either living organisms ( biofouling) or a non-living substance (inorganic or organic). Fouling is usually distinguished from other surface-growth phenomena in that it occurs on a surface of a component, system, or plant performing a defined and useful function and that the fouling process impedes or interferes with this function. Other terms used in the literature to describe fouling include deposit formation, encrustation, crudding, deposition, scaling, scale formation, slagging, and sludge formation. The last six terms have a more narrow meaning than fouling within the scope of the fouling science and technology, and they also have meanings outside of this scope; therefore, they should be used with caution. Fouling phenomena are common and diverse, ranging from fouling of ship hulls, natural surfaces in the marine environment ( marine fouling), fouling of heat-transf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
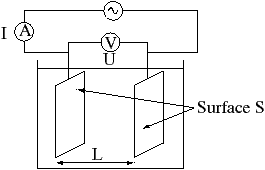
Conductivity (electrolytic)
Conductivity (or specific conductance) of an electrolyte solution is a measure of its ability to conduct electricity. The SI unit of conductivity is Siemens per meter (S/m). Conductivity measurements are used routinely in many industrial and environmental applications as a fast, inexpensive and reliable way of measuring the ionic content in a solution. For example, the measurement of product conductivity is a typical way to monitor and continuously trend the performance of water purification systems. In many cases, conductivity is linked directly to the total dissolved solids (TDS). High quality deionized water has a conductivity of about 0.05 μS/cm at 25 °C, typical drinking water is in the range of 200–800 μS/cm, while sea water is about 50 mS/cm ncorrect according to source(or 50,000 μS/cm). Conductivity is traditionally determined by connecting the electrolyte in a Wheatstone bridge. Dilute solutions follow Kohlrausch's Laws of concentr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Boilers
Steam is a substance containing water in the gas phase, and sometimes also an aerosol of liquid water droplets, or air. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporization. Steam that is saturated or superheated is invisible; however, "steam" often refers to wet steam, the visible mist Mist is a phenomenon caused by small droplets of water suspended in the cold air, usually by condensation. Physically, it is an example of a dispersion. It is most commonly seen where water vapor in warm, moist air meets sudden cooling, such a ... or aerosol of water droplets formed as water vapor condensation, condenses. Water increases in volume by 1,700 times at standard temperature and pressure; this change in volume can be converted into work (physics), mechanical work by steam engines such as reciprocating engine, reciprocating piston type engines and steam turbines, which are a sub-group of steam engines. Piston ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fouling
Fouling is the accumulation of unwanted material on solid surfaces. The fouling materials can consist of either living organisms ( biofouling) or a non-living substance (inorganic or organic). Fouling is usually distinguished from other surface-growth phenomena in that it occurs on a surface of a component, system, or plant performing a defined and useful function and that the fouling process impedes or interferes with this function. Other terms used in the literature to describe fouling include deposit formation, encrustation, crudding, deposition, scaling, scale formation, slagging, and sludge formation. The last six terms have a more narrow meaning than fouling within the scope of the fouling science and technology, and they also have meanings outside of this scope; therefore, they should be used with caution. Fouling phenomena are common and diverse, ranging from fouling of ship hulls, natural surfaces in the marine environment ( marine fouling), fouling of heat-transf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passivation (chemistry)
Passivation, in physical chemistry and engineering, refers to coating a material so it becomes "passive", that is, less readily affected or corroded by the environment. Passivation involves creation of an outer layer of shield material that is applied as a microcoating, created by chemical reaction with the base material, or allowed to build by spontaneous oxidation in the air. As a technique, passivation is the use of a light coat of a protective material, such as metal oxide, to create a shield against corrosion. Passivation of silicon is used during fabrication of microelectronic devices. In electrochemical treatment of water, passivation reduces the effectiveness of the treatment by increasing the circuit resistance, and active measures are typically used to overcome this effect, the most common being polarity reversal, which results in limited rejection of the fouling layer. When exposed to air, many metals naturally form a hard, relatively inert surface layer, usually an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dispersants
A dispersant or a dispersing agent is a substance, typically a surfactant, that is added to a suspension of solid or liquid particles in a liquid (such as a colloid or emulsion) to improve the separation of the particles and to prevent their settling or clumping. Dispersants are widely used to stabilize various industrial and artisanal products, such as paints, ferrofluids, and salad dressings. The plasticizers or superplasticizers, used to improve the workability of pastes like concrete and clay, are typically dispersants. The concept also largely overlaps with that of detergent, used to bring oily contamination into water suspension, and of emulsifier, used to create homogeneous mixtures of immiscible liquids like water and oil. Natural suspensions like milk and latex contain substances that act as dispersants. Applications Automotive Automotive engine oils contain both detergents and dispersants. Metallic-based detergents prevent the accumulation of varnish like deposits ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurofins Scientific
Eurofins Scientific SE is a French group of laboratories headquartered in Luxembourg, providing testing and support services to the pharmaceutical, food, environmental, agriscience and consumer products industriesLe réseau, botte secrète d'Eurofins n° 2965, 26 May 2005 and to governments. Eurofins Group has an international network of more than 900 laboratories across 50 countries and a portfolio of over 200,000 validated analytical methods for characterising the safety, identity, purity, composition, authenticity and origin of products and [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biodegradability
Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process, which differentiates it from composting. Composting is a human-driven process in which biodegradation occurs under a specific set of circumstances. The process of biodegradation is threefold: first an object undergoes biodeterioration, which is the mechanical weakening of its structure; then follows biofragmentation, which is the breakdown of materials by microorganisms; and finally assimilation, which is the incorporation of the old material into new cells. In practice, almost all chemical compounds and materials are subject to biodegradation, the key element being time. Things like vegetables may degrade within days, while glass and some plastics take many millennia to decompose. A standard for biodegradability used by the European Union is that greater than 90% of the original material must be converted into , water and minerals by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conductivity (electrolytic)
Conductivity (or specific conductance) of an electrolyte solution is a measure of its ability to conduct electricity. The SI unit of conductivity is Siemens per meter (S/m). Conductivity measurements are used routinely in many industrial and environmental applications as a fast, inexpensive and reliable way of measuring the ionic content in a solution. For example, the measurement of product conductivity is a typical way to monitor and continuously trend the performance of water purification systems. In many cases, conductivity is linked directly to the total dissolved solids (TDS). High quality deionized water has a conductivity of about 0.05 μS/cm at 25 °C, typical drinking water is in the range of 200–800 μS/cm, while sea water is about 50 mS/cm ncorrect according to source(or 50,000 μS/cm). Conductivity is traditionally determined by connecting the electrolyte in a Wheatstone bridge. Dilute solutions follow Kohlrausch's Laws of concentr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |