|
Heinrich Müller (physiologist)
Heinrich Müller (17 December 1820 – 10 May 1864) was a German anatomist and professor at the University of Würzburg. He is best known for his work in comparative anatomy and his studies involving the eye. He was a native of Castell, Lower Franconia. He was a student at several universities, being influenced by Ignaz Dollinger (1770–1841) in Munich, Friedrich Arnold (1803–1890) in Freiburg, Jakob Henle (1809–1895) in Heidelberg and Carl von Rokitansky (1804–1878) in Vienna. In 1847 he received his habilitation at Würzburg, where from 1858 he served as a full professor of topographical and comparative anatomy. As an instructor, he also taught classes in systematic anatomy, histology and microscopy. In 1851 Müller noticed the red color in rod cells now known as rhodopsin or visual purple, which is a pigment that is present in the rods of the retina. However, Franz Christian Boll (1849–1879) is credited as the discoverer of rhodopsin because he was abl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomist
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine. The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal's body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Purple
Rhodopsin, also known as visual purple, is a protein encoded by the RHO gene and a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). It is the opsin of the rod cells in the retina and a light-sensitive receptor protein that triggers visual phototransduction in rods. Rhodopsin mediates dim light vision and thus is extremely sensitive to light. When rhodopsin is exposed to light, it immediately photobleaches. In humans, it is regenerated fully in about 30 minutes, after which the rods are more sensitive. Defects in the rhodopsin gene cause eye diseases such as retinitis pigmentosa and congenital stationary night blindness. Names Rhodopsin was discovered by Franz Christian Boll in 1876. The name rhodospsin derives from Ancient Greek () for "rose", due to its pinkish color, and () for "sight". It was coined in 1878 by the German physiologist Wilhelm Friedrich Kühne (1837-1900). When George Wald discovered that rhodopsin is a holoprotein, consisting of retinal and an apoprotein, he call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infraorbital Groove
The infraorbital groove (or sulcus) is located in the middle of the posterior part of the orbital surface of the maxilla. Its function is to act as the passage of the infraorbital artery, the infraorbital vein, and the infraorbital nerve. Structure The infraorbital groove begins at the middle of the posterior border of the maxilla (with which it is continuous). This is near the upper edge of the infratemporal surface of the maxilla. It passes forward, and ends in a canal which subdivides into two branches. The infraorbital groove has an average length of 16.7 mm, with a small amount of variation between people. It is similar in men and women. Function The infraorbital groove creates space that allows for passage of the infraorbital artery, the infraorbital vein, and the infraorbital nerve. Clinical significance The infraorbital groove is an important surgical landmark for local anaesthesia of the infraorbital nerve. See also * Infraorbital foramen In human anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
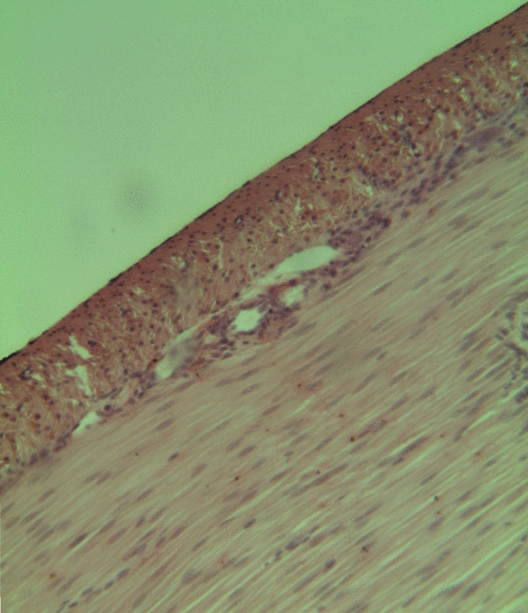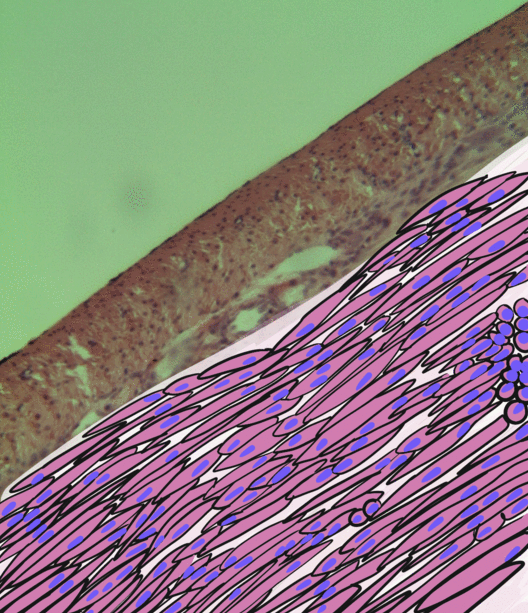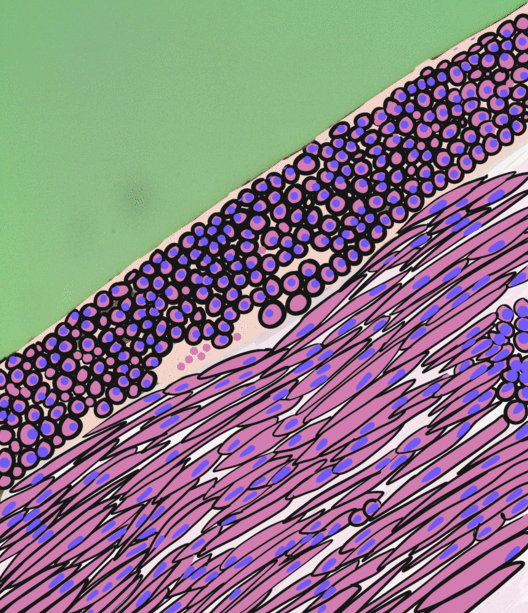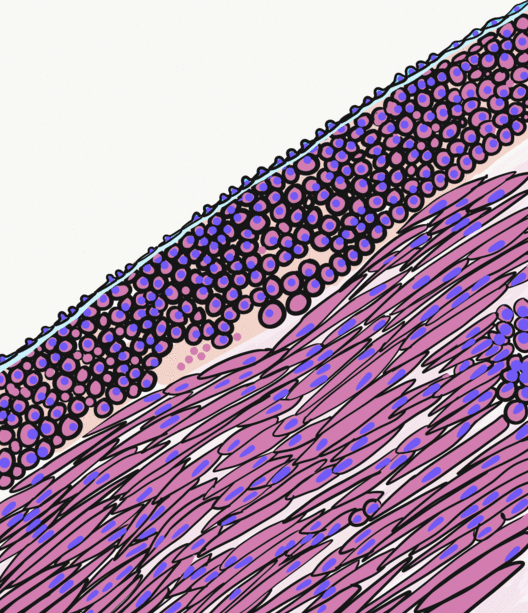
Orbitalis Muscle
The orbitalis muscle is a vestigial or rudimentary nonstriated muscle (smooth muscle) that crosses from the infraorbital groove and sphenomaxillary fissure and is intimately united with the periosteum of the orbit. It was described by Heinrich Müller and is often called Müller's muscle. It lies at the back of the orbit and spans the infraorbital fissure.Gray's Anatomy - 40th Ed/MINOR MUSCLES OF THE EYELIDS It is a thin layer of smooth muscle that bridges the inferior orbital fissure. It is supplied by sympathetic nerves, and its function is unknown. Function The muscle forms an important part of the lateral orbital wall in some animals and can act to change the wall's volume in lower mammals, while in humans it is not known to have any significant function, but its contraction may possibly produce a slight forward protrusion of the eyeball. Several sources have suggested a role in the autonomic regulation of the vascular system due to the pattern of innervation of the orbitali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levator Palpebrae Superioris Muscle
The levator palpebrae superioris ( la, elevating muscle of upper eyelid) is the muscle in the orbit that elevates the upper eyelid. Structure The levator palpebrae superioris originates from inferior surface of the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone, just above the optic foramen. It broadens and decreases in thickness (becomes thinner) and becomes the levator aponeurosis. This portion inserts on the skin of the upper eyelid, as well as the superior tarsal plate. It is a skeletal muscle. The superior tarsal muscle, a smooth muscle, is attached to the levator palpebrae superioris, and inserts on the superior tarsal plate as well. Blood supply The levator palebrae superioris receives its blood supply from branches of the ophthalmic artery, specifically, muscular branches and the supraorbital artery. Blood is drained into the superior ophthalmic vein. Nerve supply The levator palpebrae superioris receives motor innervation from the superior division of the oculomotor nerve. The smoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of smooth muscle cells contracts as a syncytium. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, including the stomach, intestines, bladder and uterus; in the walls of passageways, such as blood, and lymph vessels, and in the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems. In the eyes, the ciliary muscles, a type of smooth muscle, dilate and contract the iris and alter the shape of the lens. In the skin, smooth muscle cells such as those of the arrector pili cause hair to stand erect in response to cold temperature or fear. Structure Gross anatomy Smooth muscle is grouped into two types: single-unit smooth muscle, also known as visceral smooth muscle, and multiunit smooth muscle. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Tarsal Muscle
The superior tarsal muscle is a smooth muscle adjoining the levator palpebrae superioris muscle that helps to raise the upper eyelid. Structure The superior tarsal muscle originates on the underside of levator palpebrae superioris and inserts on the superior tarsal plate of the eyelid. Nerve supply The superior tarsal muscle receives its innervation from the sympathetic nervous system. Postganglionic sympathetic fibers originate in the superior cervical ganglion, and travel via the internal carotid plexus, where small branches communicate with the oculomotor nerve as it passes through the cavernous sinus. The sympathetic fibres continue to the superior division of the oculomotor nerve, where they enter the superior tarsal muscle on its inferior aspect. Function Its role is not fully clear, but may be an accessory muscle to raise the upper eyelid. Clinical significance Damage to some elements of the sympathetic nervous system can inhibit this muscle, causing a drooping ey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Marie Benjamin Rouget
Charles Marie Benjamin Rouget (19 August 1824 – 1904, Paris) was a French physiologist born in Gisors, Eure. He studied at the Collège Sainte-Barbe with medical training at hospitals in Paris. He was later a professor of physiology at the University of Montpellier (1860). From 1879 to 1893, he was a professor of physiology at the Muséum d’Histoire Naturelle in Paris. Rouget is largely remembered for his correlation of physiology to microscopic anatomical structure. He was the first to discover the branching contractile cells on the external wall of the capillaries in amphibians, structures that are now known as " Rouget cells". edited by Benjamin W. Zweifach, Lester Grant, Robert T. McCluskey Also the eponymous "Rouget's muscle" was described by him, which are circula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physiologist
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical and physical functions in a living system. According to the classes of organisms, the field can be divided into medical physiology, animal physiology, plant physiology, cell physiology, and comparative physiology. Central to physiological functioning are biophysical and biochemical processes, homeostatic control mechanisms, and communication between cells. ''Physiological state'' is the condition of normal function. In contrast, ''pathological state'' refers to abnormal conditions, including human diseases. The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for exceptional scientific achievements in physiology related to the field of medicine. Foundations Cells Although there are difference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciliary Muscle
The ciliary muscle is an intrinsic muscle of the eye formed as a ring of smooth muscleSchachar, Ronald A. (2012). "Anatomy and Physiology." (Chapter 4) . in the eye's middle layer, uvea ( vascular layer). It controls accommodation for viewing objects at varying distances and regulates the flow of aqueous humor into Schlemm's canal. It also changes the shape of the lens within the eye but not the size of the pupil which is carried out by the sphincter pupillae muscle and dilator pupillae. Structure Development The ciliary muscle develops from mesenchyme within the choroid and is considered a cranial neural crest derivative.Dudek RW, Fix JD (2004). "Eye" (chapter 9). ''Embryology - Board Review Series'' (3rd edition, illustrated). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 92. , . Books.Google.com. Retrieved on 2010-01-17 from https://books.google.com/books?id=MmoJQWsJteoC. Nerve supply The ciliary muscle receives parasympathetic fibers from the short ciliary nerves that arise fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Von Kölliker
Albert von Kölliker (born Rudolf Albert Kölliker'';'' 6 July 18172 November 1905) was a Swiss anatomist, physiologist, and histologist. Biography Albert Kölliker was born in Zurich, Switzerland. His early education was carried on in Zurich, and he entered the university there in 1836. After two years, however, he moved to the University of Bonn, and later to that of Berlin, becoming a pupil of noted physiologists Johannes Peter Müller and of Friedrich Gustav Jakob Henle. He graduated in philosophy at Zurich in 1841, and in medicine at Heidelberg in 1842. The first academic post which he held was that of prosector of anatomy under Henle, but his tenure of this office was briefin 1844 he returned to Zurich University to occupy a chair as professor extraordinary of physiology and comparative anatomy. His stay here was also brief; in 1847 the University of Würzburg, attracted by his rising fame, offered him the post of professor of physiology and of microscopical and comparativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroglia
Glia, also called glial cells (gliocytes) or neuroglia, are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system that do not produce electrical impulses. They maintain homeostasis, form myelin in the peripheral nervous system, and provide support and protection for neurons. In the central nervous system, glial cells include oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, ependymal cells, and microglia, and in the peripheral nervous system they include Schwann cells and satellite cells. Function They have four main functions: *to surround neurons and hold them in place *to supply nutrients and oxygen to neurons *to insulate one neuron from another *to destroy pathogens and remove dead neurons. They also play a role in neurotransmission and synaptic connections, and in physiological processes such as breathing. While glia were thought to outnumber neurons by a ratio of 10:1, recent studies using newer methods and reappraisal of historical qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |