|
Heic
High Efficiency Image File Format (HEIF) is a container format for storing individual digital images and image sequences. The standard covers multimedia files that can also include other media streams, such as timed text, audio and video. HEIF can store images encoded with multiple coding formats, for example both SDR and HDR images. HEVC is an image and video encoding format and the default image codec used with HEIF. HEIF files containing HEVC-encoded images are also known as HEIC files. Such files require less storage space than the equivalent quality JPEG. HEIF files are a special case of the ISO Base Media File Format (ISOBMFF, ISO/IEC 14496-12), first defined in 2001 as a shared part of MP4 and JPEG 2000. Introduced in 2015, it was developed by the Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) and is defined as Part 12 within the MPEG-H media suite (ISO/IEC 23008-12). HEIF was adopted by Apple in 2017 with the introduction of iOS 11. History The requirements and main use c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AVIF
AV1 Image File Format (AVIF) is an image file format specification for storing images or image sequences compressed with AV1 in the HEIF container format. It competes with HEIC, which uses the same container format built upon ISOBMFF, but HEVC for compression. Version 1.0.0 of the AVIF specification was finalized in February 2019. In a number of tests by Netflix in 2020, AVIF showed better compression efficiency than JPEG as well as better detail preservation, fewer blocking artifacts and less color bleeding around hard edges in composites of natural images, text, and graphics. Features AVIF supports features like: * Multiple color space, including: ** HDR (with PQ or HLG transfer functions and BT.2020 color primaries, as part of BT.2100) ** SDR (with sRGB / BT.709 / BT.601 or with wide color gamut) ** Color space signaling via CICP (ITU-T H.273 and ISO/IEC 23091-2) or ICC profiles * Lossless compression and lossy compression * 8-, 10-, and 12-bit color depths * Monochr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moving Picture Experts Group
The Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) is an alliance of working groups established jointly by ISO and IEC that sets standards for media coding, including compression coding of audio, video, graphics, and genomic data; and transmission and file formats for various applications.John Watkinson, ''The MPEG Handbook'', p. 1 Together with JPEG, MPEG is organized under ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 29 – ''Coding of audio, picture, multimedia and hypermedia information'' (ISO/IEC Joint Technical Committee 1, Subcommittee 29). MPEG formats are used in various multimedia systems. The most well known older MPEG media formats typically use MPEG-1, MPEG-2, and MPEG-4 AVC media coding and MPEG-2 systems transport streams and program streams. Newer systems typically use the MPEG base media file format and dynamic streaming (a.k.a. MPEG-DASH). History MPEG was established in 1988 by the initiative of Dr. Hiroshi Yasuda ( NTT) and Dr. Leonardo Chiariglione (CSELT). Chiariglione was the group' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inter Frame
An inter frame is a frame in a video compression stream which is expressed in terms of one or more neighboring frames. The "inter" part of the term refers to the use of ''Inter frame prediction''. This kind of prediction tries to take advantage from temporal redundancy between neighboring frames enabling higher compression rates. Inter frame prediction An inter coded frame is divided into blocks known as macroblocks. After that, instead of directly encoding the raw pixel values for each block, the encoder will try to find a block similar to the one it is encoding on a previously encoded frame, referred to as a reference frame. This process is done by a block matching algorithm. If the encoder succeeds on its search, the block could be encoded by a vector, known as motion vector, which points to the position of the matching block at the reference frame. The process of motion vector determination is called motion estimation. In most cases the encoder will succeed, but the block fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Compression Picture Types
In the field of video compression a video frame is compressed using different algorithms with different advantages and disadvantages, centered mainly around amount of data compression. These different algorithms for video frames are called picture types or frame types. The three major picture types used in the different video algorithms are I, P and B. They are different in the following characteristics: * I‑frames are the least compressible but don't require other video frames to decode. * P‑frames can use data from previous frames to decompress and are more compressible than I‑frames. * B‑frames can use both previous and forward frames for data reference to get the highest amount of data compression. Summary Three types of ''pictures'' (or frames) are used in video compression: I, P, and B frames. An I‑frame ( Intra-coded picture) is a complete image, like a JPG or BMP image file. A P‑frame (Predicted picture) holds only the changes in the image from the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
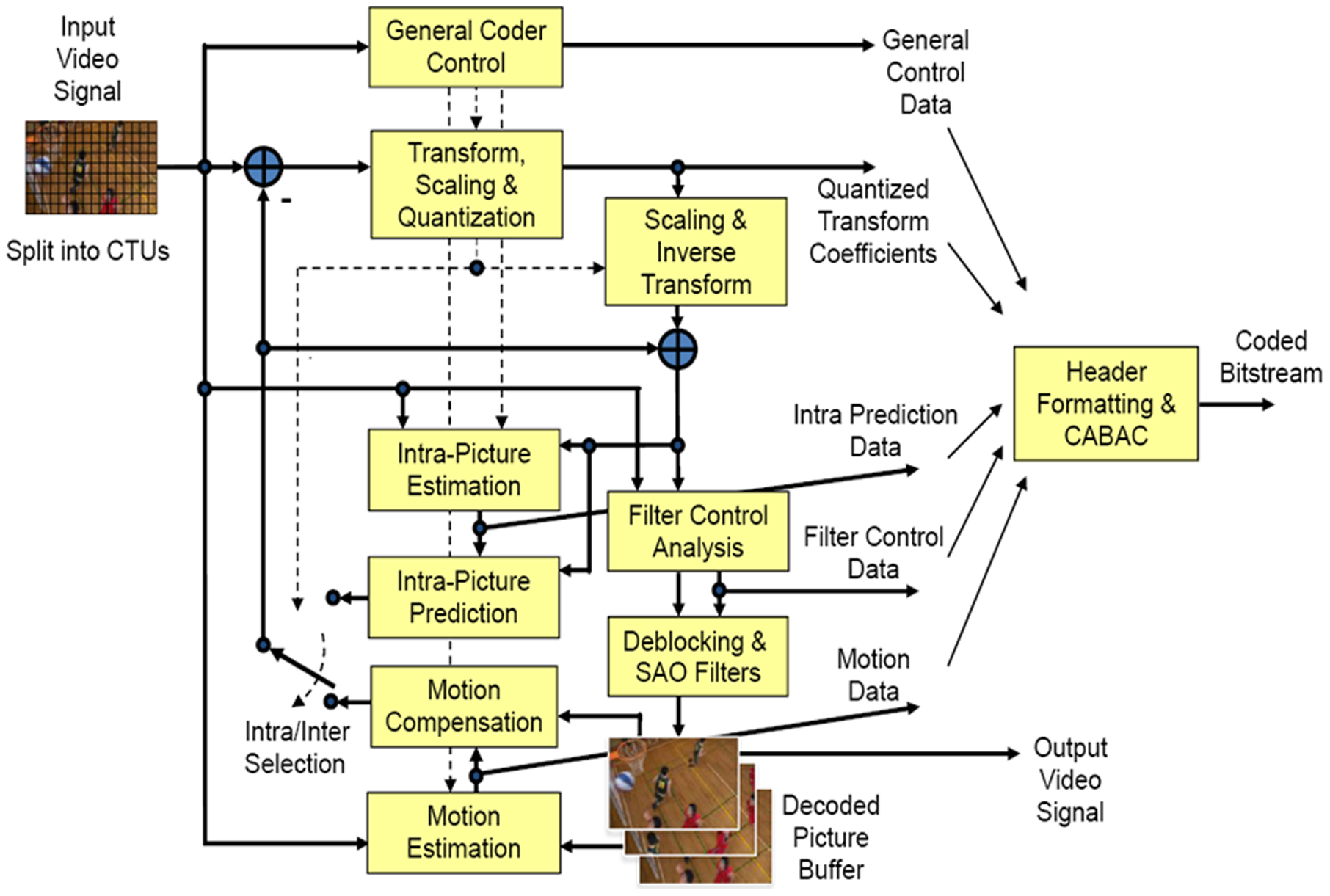
HEVC
High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), also known as H.265 and MPEG-H Part 2, is a video compression standard designed as part of the MPEG-H project as a successor to the widely used Advanced Video Coding (AVC, H.264, or MPEG-4 Part 10). In comparison to AVC, HEVC offers from 25% to 50% better data compression at the same level of video quality, or substantially improved video quality at the same bit rate. It supports resolutions up to 8192×4320, including 8K UHD, and unlike the primarily 8-bit AVC, HEVC's higher fidelity Main 10 profile has been incorporated into nearly all supporting hardware. While AVC uses the integer discrete cosine transform (DCT) with 4×4 and 8×8 block sizes, HEVC uses integer DCT and DST transforms with varied block sizes between 4×4 and 32×32. The High Efficiency Image Format (HEIF) is based on HEVC. , HEVC is used by 43% of video developers, and is the second most widely used video coding format after AVC. Concept In most ways, HEVC is an extensio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPEG-A
MPEG-A is a group of standards for composing MPEG systems formally known as ''ISO/IEC 23000'' - ''Multimedia Application Format'', published since 2007. MPEG-A consists of 20 parts, including: * MPEG-A Part 1: Purpose for multimedia application formats * MPEG-A Part 2: MPEG music player application format * MPEG-A Part 3: MPEG photo player application format * MPEG-A Part 4: Musical slide show application format * MPEG-A Part 5: Media streaming application format * MPEG-A Part 6: Professional archival application format * MPEG-A Part 7: Open access application format * MPEG-A Part 8: Portable video application format * MPEG-A Part 9: Digital Multimedia Broadcasting application format * MPEG-A Part 10: Surveillance application format * MPEG-A Part 11: Stereoscopic video application format * MPEG-A Part 12: Interactive music application format * MPEG-A Part 13: Augmented reality application format * MPEG-A Part 15: Multimedia preservation application format * MPEG-A Part 16: Publish/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filename Extension
A filename extension, file name extension or file extension is a suffix to the name of a computer file (e.g., .txt, .docx, .md). The extension indicates a characteristic of the file contents or its intended use. A filename extension is typically delimited from the rest of the filename with a full stop (period), but in some systems it is separated with spaces. Other extension formats include dashes and/or underscores on early versions of Linux and some versions of IBM AIX. Some file systems implement filename extensions as a feature of the file system itself and may limit the length and format of the extension, while others treat filename extensions as part of the filename without special distinction. Usage Filename extensions may be considered a type of metadata. They are commonly used to imply information about the way data might be stored in the file. The exact definition, giving the criteria for deciding what part of the file name is its extension, belongs to the rules of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensible Metadata Platform
The Extensible Metadata Platform (XMP) is an ISO standard, originally created by Adobe Systems Inc., for the creation, processing and interchange of standardized and custom metadata for digital documents and data sets. XMP standardizes a data model, a serialization format and core properties for the definition and processing of extensible metadata. It also provides guidelines for embedding XMP information into popular image, video and document file formats, such as JPEG and PDF, without breaking their readability by applications that do not support XMP. Therefore, the non-XMP metadata have to be reconciled with the XMP properties. Although metadata can alternatively be stored in a sidecar file, embedding metadata avoids problems that occur when metadata is stored separately. The XMP data model, serialization format and core properties is published by the International Organization for Standardization as ISO 16684-1:2012 standard. Data model The defined XMP data model can be us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
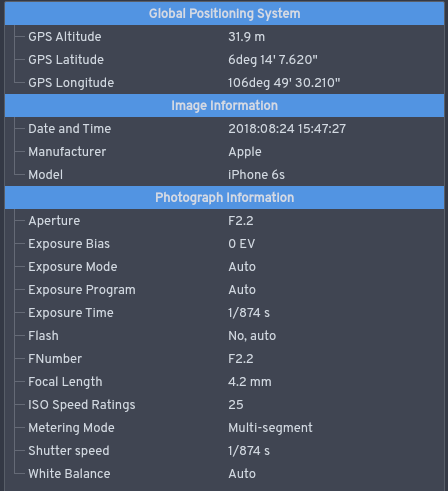
Exif
Exchangeable image file format (officially Exif, according to JEIDA/JEITA/CIPA specifications) is a standard that specifies formats for images, sound, and ancillary tags used by digital cameras (including smartphones), scanners and other systems handling image and sound files recorded by digital cameras. The specification uses the following existing encoding formats with the addition of specific metadata tags: JPEG lossy coding for compressed image files, TIFF Rev. 6.0 (RGB or YCbCr) for uncompressed image files, and RIFF WAV for audio files (linear PCM or ITU-T G.711 μ-law PCM for uncompressed audio data, and IMA-ADPCM for compressed audio data). It does not support JPEG 2000 or GIF encoded images. This standard consists of the Exif image file specification and the Exif audio file specification. Background Exif is supported by almost all camera manufacturers. The metadata tags defined in the Exif standard cover a broad spectrum: * Camera settings: This includes static ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depth Map
In 3D computer graphics and computer vision, a depth map is an image or image channel that contains information relating to the distance of the surfaces of scene objects from a viewpoint. The term is related (and may be analogous) to ''depth buffer'', ''Z-buffer'', ''Z-buffering'', and ''Z-depth''. tp://ftp.futurenet.co.uk/pub/arts/Glossary.pdf Computer Arts / 3D World Glossary Document retrieved 26 January 2011. The "Z" in these latter terms relates to a convention that the central axis of view of a camera is in the direction of the camera's Z axis, and not to the absolute Z axis of a scene. Examples File:Cubic Structure.jpg, Cubic Structure File:Cubic Frame Stucture and Floor Depth Map.jpg, Depth Map: Nearer is darker File:Cubic Structure and Floor Depth Map with Front and Back Delimitation.jpg, Depth Map: Nearer the Focal Plane is darker Two different depth maps can be seen here, together with the original model from which they are derived. The first depth map shows lu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Channel
In computer graphics, alpha compositing or alpha blending is the process of combining one image with a background to create the appearance of partial or full transparency. It is often useful to render picture elements (pixels) in separate passes or layers and then combine the resulting 2D images into a single, final image called the composite. Compositing is used extensively in film when combining computer-rendered image elements with live footage. Alpha blending is also used in 2D computer graphics to put rasterized foreground elements over a background. In order to combine the picture elements of the images correctly, it is necessary to keep an associated ''matte'' for each element in addition to its color. This matte layer contains the coverage information—the shape of the geometry being drawn—making it possible to distinguish between parts of the image where something was drawn and parts that are empty. Although the most basic operation of combining two images is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinemagraph
Cinemagraphs are still photographs in which a minor and repeated movement occurs, forming a video clip. They are published as an animated GIF or in other video formats, and can give the illusion that the viewer is watching an animation. A variation is a ''video snapshot'' (clip composed like a still photo, but instead of a shutter release it is captured using the video recording function with its audio track and perhaps showing minor movement such as the subject's eye blinks). Another variation is an ''audio snapshot'' (still photo linked to an audio file created at the moment of photo capture by certain cameras that offer this proprietary function). Cinemagraphs are made by taking a series of photographs or a video recording, and, using image editing software, compositing the photographs or the video frames into a seamless loop of sequential frames. This is done in such a way that motion in part of the subject between exposures (for example, a person's dangling leg) is perceiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |