|
Hededet
Hededet or Hedjedjet ''(ḥdd.t)'' is a scorpion goddess of the ancient Egyptian religion. She resembles Serket in many ways, but was in later periods merged into Isis. She was depicted with the head of a scorpion, nursing a baby.Richard Wilkinson: ''The Complete Gods and Goddesses of Ancient Egypt''. London, Thames and Hudson, 2003. , p.230 She is mentioned in the ''Book of the Dead The ''Book of the Dead'' ( egy, 𓂋𓏤𓈒𓈒𓈒𓏌𓏤𓉐𓂋𓏏𓂻𓅓𓉔𓂋𓅱𓇳𓏤, ''rw n(y)w prt m hrw(w)'') is an ancient Egyptian funerary text generally written on papyrus and used from the beginning of the New Kingdom ...''. Sources {{Ancient Egyptian religion footer, state=collapsed Egyptian goddesses Isis Animal goddesses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scorpion
Scorpions are predatory arachnids of the order Scorpiones. They have eight legs, and are easily recognized by a pair of grasping pincers and a narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back and always ending with a stinger. The evolutionary history of scorpions goes back 435 million years. They mainly live in deserts but have adapted to a wide range of environmental conditions, and can be found on all continents except Antarctica. There are over 2,500 described species, with 22 extant (living) families recognized to date. Their taxonomy is being revised to account for 21st-century genomic studies. Scorpions primarily prey on insects and other invertebrates, but some species hunt vertebrates. They use their pincers to restrain and kill prey, or to prevent their own predation. The venomous sting is used for offense and defense. During courtship, the male and female grasp each other's pincers and dance while he tries to move her onto his s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egyptian Deities
Ancient Egyptian deities are the God (male deity), gods and goddesses worshipped in ancient Egypt. The beliefs and rituals surrounding these gods formed the core of ancient Egyptian religion, which emerged sometime in prehistoric Egypt, prehistory. Deities represented natural phenomenon, natural forces and phenomena, and the Egyptians supported and appeased them through sacrifice, offerings and rituals so that these forces would continue to function according to ''maat'', or divine order. After the founding of the Egyptian state around 3100 BC, the authority to perform these tasks was controlled by the pharaoh, who claimed to be the gods' representative and managed the Egyptian temple, temples where the rituals were carried out. The gods' complex characteristics were expressed in Egyptian mythology, myths and in intricate relationships between deities: family ties, loose groups and hierarchies, and combinations of separate gods into one. Deities' diverse appearances in art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egyptian Religion
Ancient Egyptian religion was a complex system of polytheistic beliefs and rituals that formed an integral part of ancient Egyptian culture. It centered on the Egyptians' interactions with many deities believed to be present in, and in control of the world. Rituals such as prayer and offerings were provided to the gods to gain their favor. Formal religious practice centered on the pharaohs, the rulers of Egypt, believed to possess divine powers by virtue of their positions. They acted as intermediaries between their people and the gods, and were obligated to sustain the gods through rituals and offerings so that they could maintain Ma'at, the order of the cosmos, and repel Isfet, which was chaos. The state dedicated enormous resources to religious rituals and to the construction of temples. Individuals could interact with the gods for their own purposes, appealing for help through prayer or compelling the gods to act through magic. These practices were distinct from, but closel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serket
Serket ( egy, , italics=no, translit=srqt) is the goddess of healing venomous stings and bites in Egyptian mythology, originally the deification of the scorpion. Her family life is unknown, but she is sometimes credited as the daughter of Neith and Khnum, making her a sister to Sobek and Apep. Scorpion stings lead to paralysis and Serket's name describes this, as it means "(she who) tightens the throat"; however, Serket's name also can be read as meaning "(she who) causes the throat to breathe" and so, as well as being seen as stinging the unrighteous, Serket was seen as one who could cure scorpion stings and the effects of other venoms such as snakebites. In the art of ancient Egypt, Serket was depicted as a scorpion (a symbol found on the earliest artifacts of the culture, such as from Naqada III) or to have the body of a scorpion but the head of a woman or as a woman with a scorpion on her head. Although Serket does not appear to have had any temples, she had a sizable number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isis
Isis (; ''Ēse''; ; Meroitic: ''Wos'' 'a''or ''Wusa''; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎, romanized: ʾs) was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. Isis was first mentioned in the Old Kingdom () as one of the main characters of the Osiris myth, in which she resurrects her slain brother and husband, the divine king Osiris, and produces and protects his heir, Horus. She was believed to help the dead enter the afterlife as she had helped Osiris, and she was considered the divine mother of the pharaoh, who was likened to Horus. Her maternal aid was invoked in healing Spell (paranormal), spells to benefit ordinary people. Originally, she played a limited role in royal rituals and temple rites, although she was more prominent in funerary practices and magical texts. She was usually portrayed in art as a human woman wearing a throne-like hieroglyph on her head. During the New Kingdom (), as she took on traits that originally belo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
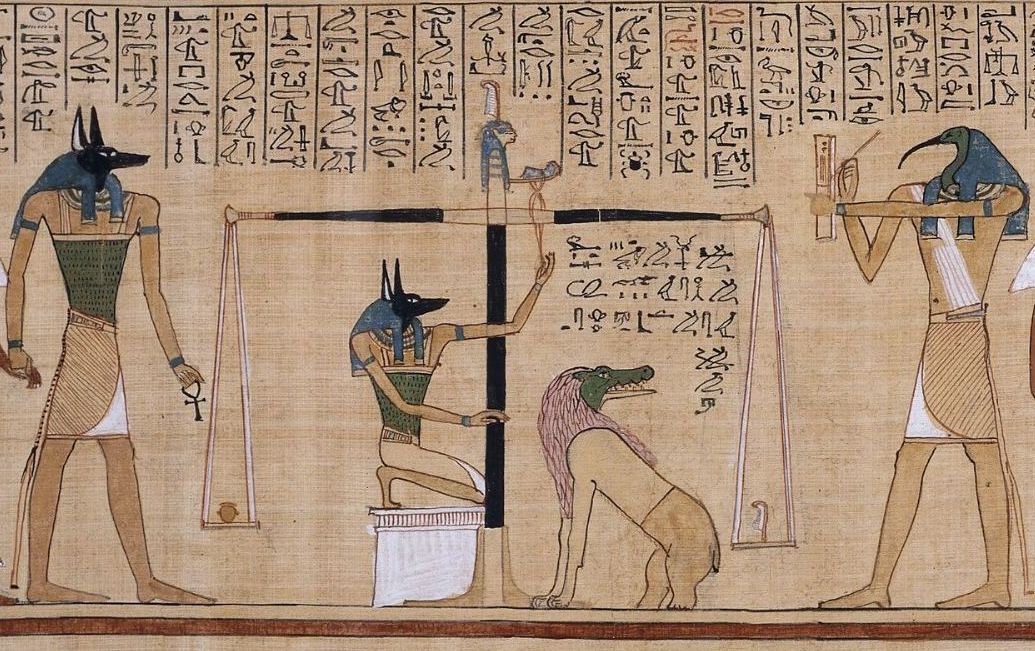
Book Of The Dead
The ''Book of the Dead'' ( egy, 𓂋𓏤𓈒𓈒𓈒𓏌𓏤𓉐𓂋𓏏𓂻𓅓𓉔𓂋𓅱𓇳𓏤, ''rw n(y)w prt m hrw(w)'') is an ancient Egyptian funerary text generally written on papyrus and used from the beginning of the New Kingdom (around 1550 BCE) to around 50 BCE. The original Egyptian name for the text, transliterated ''rw nw prt m hrw'', is translated as ''Book of Coming Forth by Day'' or ''Book of Emerging Forth into the Light''. "Book" is the closest term to describe the loose collection of texts consisting of a number of magic spells intended to assist a dead person's journey through the ''Duat'', or underworld, and into the afterlife and written by many priests over a period of about 1,000 years. Karl Richard Lepsius introduced for these texts the German name ''Todtenbuch'' (modern spelling ''Totenbuch''), translated to English as Book of the Dead. The ''Book of the Dead'', which was placed in the coffin or burial chamber of the deceased, was part of a trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian Goddesses
Ancient Egyptian deities are the gods and goddesses worshipped in ancient Egypt. The beliefs and rituals surrounding these gods formed the core of ancient Egyptian religion, which emerged sometime in prehistory. Deities represented natural forces and phenomena, and the Egyptians supported and appeased them through offerings and rituals so that these forces would continue to function according to ''maat'', or divine order. After the founding of the Egyptian state around 3100 BC, the authority to perform these tasks was controlled by the pharaoh, who claimed to be the gods' representative and managed the temples where the rituals were carried out. The gods' complex characteristics were expressed in myths and in intricate relationships between deities: family ties, loose groups and hierarchies, and combinations of separate gods into one. Deities' diverse appearances in art—as animals, humans, objects, and combinations of different forms—also alluded, through symbolism, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |