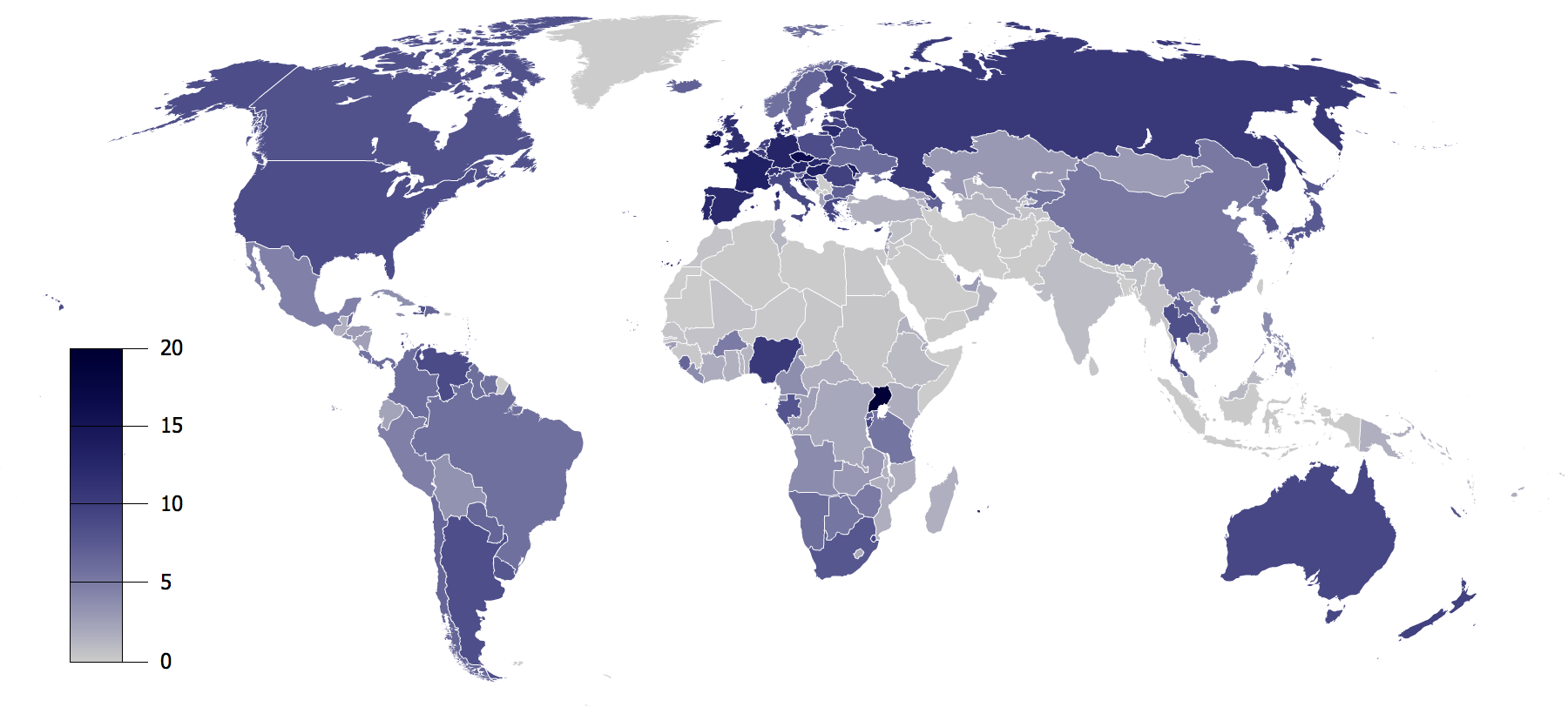
|
Health Effects Of Alcohol
Health effects of alcohol may refer to: * Alcohol and health * Alcohol intoxication * Short-term effects of alcohol consumption * Long-term effects of alcohol consumption * Health effects of wine The health effects of wine are mainly determined by its active ingredient alcohol. Preliminary studies found that drinking small quantities of wine (up to one standard drink per day for women and one to two drinks per day for men), particularl ... {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol And Health
Alcohol (also known as ethanol) has a number of effects on health. Short-term effects of alcohol consumption include intoxication and dehydration. Long-term effects of alcohol include changes in the metabolism of the liver and brain, several types of cancer and alcohol use disorder. Alcohol intoxication affects the brain, causing slurred speech, clumsiness, and delayed reflexes. Alcohol consumption can cause hypoglycemia in diabetics on certain medications, such as insulin or sulfonylurea, by blocking gluconeogenesis. There is an increased risk of developing an alcohol use disorder for teenagers while their brain is still developing. Adolescents who drink have a higher probability of injury including death. Even light and moderate alcohol consumption have negative effects on health, such as by increasing a person's risk of developing several cancers. A 2014 World Health Organization report found that harmful alcohol consumption caused about 3.3 million deaths annually worldwide. N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol Intoxication
Alcohol intoxication, also known as alcohol poisoning, commonly described as drunkenness or inebriation, is the negative behavior and physical effects caused by a recent consumption of alcohol. In addition to the toxicity of ethanol, the main psychoactive component of alcoholic beverages, other physiological symptoms may arise from the activity of acetaldehyde, a metabolite of alcohol. These effects may not arise until hours after ingestion and may contribute to the condition colloquially known as a hangover. Symptoms of intoxication at lower doses may include mild sedation and poor coordination. At higher doses, there may be slurred speech, trouble walking, and vomiting. Extreme doses may result in a respiratory depression, coma, or death. Complications may include seizures, aspiration pneumonia, injuries including suicide, and low blood sugar. Alcohol intoxication can lead to alcohol-related crime with perpetrators more likely to be intoxicated than victims. Alcohol intox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short-term Effects Of Alcohol Consumption
The short-term effects of alcohol (more specifically ethanol) consumption range from a decrease in anxiety and motor skills and euphoria at lower doses to intoxication (drunkenness), to stupor, unconsciousness, anterograde amnesia (memory "blackouts"), and central nervous system depression at higher doses. Cell membranes are highly permeable to alcohol, so once alcohol is in the bloodstream, it can diffuse into nearly every cell in the body. The concentration of alcohol in blood is measured via blood alcohol content (BAC). The amount and circumstances of consumption play a large role in determining the extent of intoxication; for example, eating a heavy meal before alcohol consumption causes alcohol to absorb more slowly. The amount of alcohol consumed largely determines the extent of hangovers, although hydration also plays a role. After excessive drinking, stupor and unconsciousness can both occur. Extreme levels of consumption can cause alcohol poisoning and death; in fact, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long-term Effects Of Alcohol Consumption
The long-term heavy consumption of alcohol (alcohol use disorder) can cause severe detrimental effects. Health effects associated with alcohol intake in large amounts include an increased risk of developing an alcohol use disorder, malnutrition, chronic pancreatitis, erectile dysfunction, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, gastritis, stomach ulcers, alcoholic liver disease, certain types of dementia, and several types of cancer. In addition, damage to the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system (e.g., painful peripheral neuropathy) can occur from chronic heavy alcohol consumption. There is also an increased risk for accidental injuries, for example, those sustained in traffic accidents and falls. Studies show that individuals with heavy substance use have a much higher risk of having other disorders. A cross-sectional observational study found evidence that people who used substances had the highest risk for five of the disorders studied. However, even light and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Effects Of Wine
The health effects of wine are mainly determined by its active ingredient alcohol. Preliminary studies found that drinking small quantities of wine (up to one standard drink per day for women and one to two drinks per day for men), particularly of red wine, may be associated with a decreased risk of cardiovascular diseases, cognitive decline, stroke, diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, and early death. Other studies found no such effects. Drinking more than the standard drink amount increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, stroke, and cancer. Mixed results are also observed in light drinking and cancer mortality. Risk is greater in young people due to binge drinking, which may result in violence or accidents. About 88,000 deaths in the United States are estimated to be due to alcohol each year. Alcoholism reduces a person's life expectancy by around ten years and excessive alcohol use is the third leading cause of early death ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |