|
Head Shadow
A head shadow (or acoustic shadow) is a region of reduced amplitude of a sound because it is obstructed by the head. It is an example of diffraction. Sound may have to travel through and around the head in order to reach an ear. The obstruction caused by the head can account for attenuation (reduced amplitude) of overall intensity as well as cause a filtering effect. The filtering effects of head shadowing are an essential element of sound localisation—the brain weighs the relative amplitude, timbre, and phase of a sound heard by the two ears and uses the difference to interpret directional information. The shadowed ear, the ear further from the sound source, receives sound slightly later (up to approximately 0.7 ms later) than the unshadowed ear, and the timbre, or frequency spectrum, of the shadowed sound wave is different because of the obstruction of the head. The head shadow causes particular difficulty in sound localisation in people suffering from unilateral hearing loss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of amplitude (see below), which are all functions of the magnitude of the differences between the variable's extreme values. In older texts, the phase of a periodic function is sometimes called the amplitude. Definitions Peak amplitude & semi-amplitude For symmetric periodic waves, like sine waves, square waves or triangle waves ''peak amplitude'' and ''semi amplitude'' are the same. Peak amplitude In audio system measurements, telecommunications and others where the measurand is a signal that swings above and below a reference value but is not sinusoidal, peak amplitude is often used. If the reference is zero, this is the maximum absolute value of the signal; if the reference is a mean value (DC component), the peak amplitude is the maximu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave, through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid. In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the brain. Only acoustic waves that have frequencies lying between about 20 Hz and 20 kHz, the audio frequency range, elicit an auditory percept in humans. In air at atmospheric pressure, these represent sound waves with wavelengths of to . Sound waves above 20 kHz are known as ultrasound and are not audible to humans. Sound waves below 20 Hz are known as infrasound. Different animal species have varying hearing ranges. Acoustics Acoustics is the interdisciplinary science that deals with the study of mechanical waves in gasses, liquids, and solids including vibration, sound, ultrasound, and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an ''acoustician'', while someone working in the field of acoustica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffraction
Diffraction is defined as the interference or bending of waves around the corners of an obstacle or through an aperture into the region of geometrical shadow of the obstacle/aperture. The diffracting object or aperture effectively becomes a secondary source of the propagating wave. Italian scientist Francesco Maria Grimaldi coined the word ''diffraction'' and was the first to record accurate observations of the phenomenon in 1660. In classical physics, the diffraction phenomenon is described by the Huygens–Fresnel principle that treats each point in a propagating wavefront as a collection of individual spherical wavelets. The characteristic bending pattern is most pronounced when a wave from a coherent source (such as a laser) encounters a slit/aperture that is comparable in size to its wavelength, as shown in the inserted image. This is due to the addition, or interference, of different points on the wavefront (or, equivalently, each wavelet) that travel by paths of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoustic Attenuation
Acoustic attenuation is a measure of the energy loss of sound propagation in media. Most media have viscosity and are therefore not ideal media. When sound propagates in such media, there is always thermal consumption of energy caused by viscosity. This effect can be quantified through the Stokes's law of sound attenuation. Sound attenuation may also be a result of heat conductivity in the media as has been shown by G. Kirchhoff in 1868. The Stokes-Kirchhoff attenuation formula takes into account both viscosity and thermal conductivity effects. For heterogeneous media, besides media viscosity, acoustic scattering is another main reason for removal of acoustic energy. Acoustic attenuation in a lossy medium plays an important role in many scientific researches and engineering fields, such as medical ultrasonography, vibration and noise reduction. Power-law frequency-dependent acoustic attenuation Many experimental and field measurements show that the acoustic attenuation coeffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
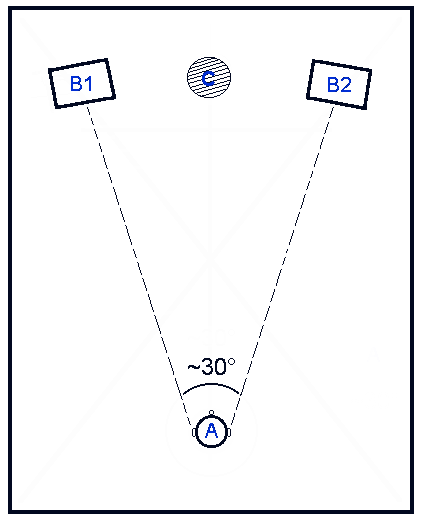
Sound Localisation
Sound localization is a listener's ability to identify the location or origin of a detected sound in direction and distance. The sound localization mechanisms of the mammalian auditory system have been extensively studied. The auditory system uses several cues for sound source localization, including time difference and level difference (or intensity difference) between the ears, and spectral information. These cues are also used by other animals, such as birds and reptiles, but there may be differences in usage, and there are also localization cues which are absent in the human auditory system, such as the effects of ear movements. Animals with the ability to localize sound have a clear evolutionary advantage. How sound reaches the brain Sound is the perceptual result of mechanical vibrations traveling through a medium such as air or water. Through the mechanisms of compression and rarefaction, sound waves travel through the air, bounce off the pinna and concha of the exter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timbre
In music, timbre ( ), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics), is the perceived sound quality of a musical note, sound or musical tone, tone. Timbre distinguishes different types of sound production, such as choir voices and musical instruments. It also enables listeners to distinguish different instruments in the same category (e.g., an oboe and a clarinet, both Woodwind instrument, woodwind instruments). In simple terms, timbre is what makes a particular musical instrument or human voice have a different sound from another, even when they play or sing the same note. For instance, it is the difference in sound between a guitar and a piano playing the same note at the same volume. Both instruments can sound equally tuned in relation to each other as they play the same note, and while playing at the same amplitude level each instrument will still sound distinctively with its own unique tone color. Experienced musicians are able to distinguish between diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase (waves)
In physics and mathematics, the phase of a periodic function F of some real variable t (such as time) is an angle-like quantity representing the fraction of the cycle covered up to t. It is denoted \phi(t) and expressed in such a scale that it varies by one full turn as the variable t goes through each period (and F(t) goes through each complete cycle). It may be measured in any angular unit such as degrees or radians, thus increasing by 360° or 2\pi as the variable t completes a full period. This convention is especially appropriate for a sinusoidal function, since its value at any argument t then can be expressed as \phi(t), the sine of the phase, multiplied by some factor (the amplitude of the sinusoid). (The cosine may be used instead of sine, depending on where one considers each period to start.) Usually, whole turns are ignored when expressing the phase; so that \phi(t) is also a periodic function, with the same period as F, that repeatedly scans the same range of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millisecond
A millisecond (from '' milli-'' and second; symbol: ms) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one thousandth (0.001 or 10−3 or 1/1000) of a second and to 1000 microseconds. A unit of 10 milliseconds may be called a centisecond, and one of 100 milliseconds a decisecond, but these names are rarely used. To help compare orders of magnitude of different times, this page lists times between 10−3 seconds and 100 seconds (1 millisecond and one second). ''See also'' times of other orders of magnitude. Examples The Apollo Guidance Computer used metric units internally, with centiseconds used for time calculation and measurement. *1 millisecond (1 ms) – cycle time for frequency 1 kHz; duration of light for typical photo flash strobe; time taken for sound wave to travel about 34 cm; repetition interval of GPS C/A PN code *1 millisecond - time taken for light to travel 204.19 km in a single mode fiber optic cable for a wavelength o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Spectrum
The power spectrum S_(f) of a time series x(t) describes the distribution of power into frequency components composing that signal. According to Fourier analysis, any physical signal can be decomposed into a number of discrete frequencies, or a spectrum of frequencies over a continuous range. The statistical average of a certain signal or sort of signal (including noise) as analyzed in terms of its frequency content, is called its spectrum. When the energy of the signal is concentrated around a finite time interval, especially if its total energy is finite, one may compute the energy spectral density. More commonly used is the power spectral density (or simply power spectrum), which applies to signals existing over ''all'' time, or over a time period large enough (especially in relation to the duration of a measurement) that it could as well have been over an infinite time interval. The power spectral density (PSD) then refers to the spectral energy distribution that would b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unilateral Hearing Loss
Unilateral hearing loss (UHL) is a type of hearing impairment where there is normal hearing in one ear and impaired hearing in the other ear. Signs and symptoms Patients with unilateral hearing loss have difficulty: * Hearing conversation on their impaired side * Localizing sound * Understanding speech in the presence of background noise * In interpersonal interaction in social settings * Focusing on individual sound sources in large, open environments * Heavy impairment of the auditory Figure–ground perception In quiet conditions, speech discrimination is no worse than normal hearing in those with partial deafness; however, in noisy environments speech discrimination is almost always severe. The prevalence is 3–8.3% of the population. Individuals who are diagnosed with Single Sided Deafness have difficulties with sound localization and speech in noise discrimination. Children with SSD are more likely to experience developmental delays- school, speech, behavioral problems. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hearing Aid
A hearing aid is a device designed to improve hearing by making sound audible to a person with hearing loss. Hearing aids are classified as medical devices in most countries, and regulated by the respective regulations. Small audio amplifiers such as personal sound amplification products (PSAPs) or other plain sound reinforcing systems cannot be sold as "hearing aids". Early devices, such as ear trumpets or ear horns, were passive Amplifier, amplification cones designed to gather sound energy and direct it into the ear canal. Modern devices are computerised electroacoustic systems that transform environmental sound to make it audible, according to audiometry, audiometrical and cognitive rules. Modern devices also utilize sophisticated digital signal processing to try and improve speech intelligibility and comfort for the user. Such Digital signal processing, signal processing includes feedback management, wide dynamic range compression, directionality, frequency lowering, and noi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interaural Intensity Difference
Sound localization is a listener's ability to identify the location or origin of a detected sound in direction and distance. The sound localization mechanisms of the mammalian auditory system have been extensively studied. The auditory system uses several cues for sound source localization, including time difference and level difference (or intensity difference) between the ears, and spectral information. These cues are also used by other animals, such as birds and reptiles, but there may be differences in usage, and there are also localization cues which are absent in the human auditory system, such as the effects of ear movements. Animals with the ability to localize sound have a clear evolutionary advantage. How sound reaches the brain Sound is the perceptual result of mechanical vibrations traveling through a medium such as air or water. Through the mechanisms of compression and rarefaction, sound waves travel through the air, bounce off the pinna and concha of the exter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

