|
Head-coupled Perspective
Head-coupled perspective is a 2.5D, technique to show 3D imagery on 2D devices. The perspective (graphical), perspective of the scene on the screen is based on the position of the user’s eyes, simulating a 3D environment. When the user moves their head, the perspective of the scene changes, creating the effect of looking through a window to the scene instead of looking at a flat graphical projection, projection of a scene. See also * 3D rendering * 3D computer graphics * Perspective (visual) * Eye tracking * Video tracking * Amazon Fire Phone's Dynamic Perspective References External links http://iihm.imag.fr/francone/i3D/Paper on using head coupled perspective on mobile devicesEarly research on head coupled perspectiveA system based on head coupled perspective to give the illusion of a 3D virtual world all around a user {{Tech-stub Stereoscopy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
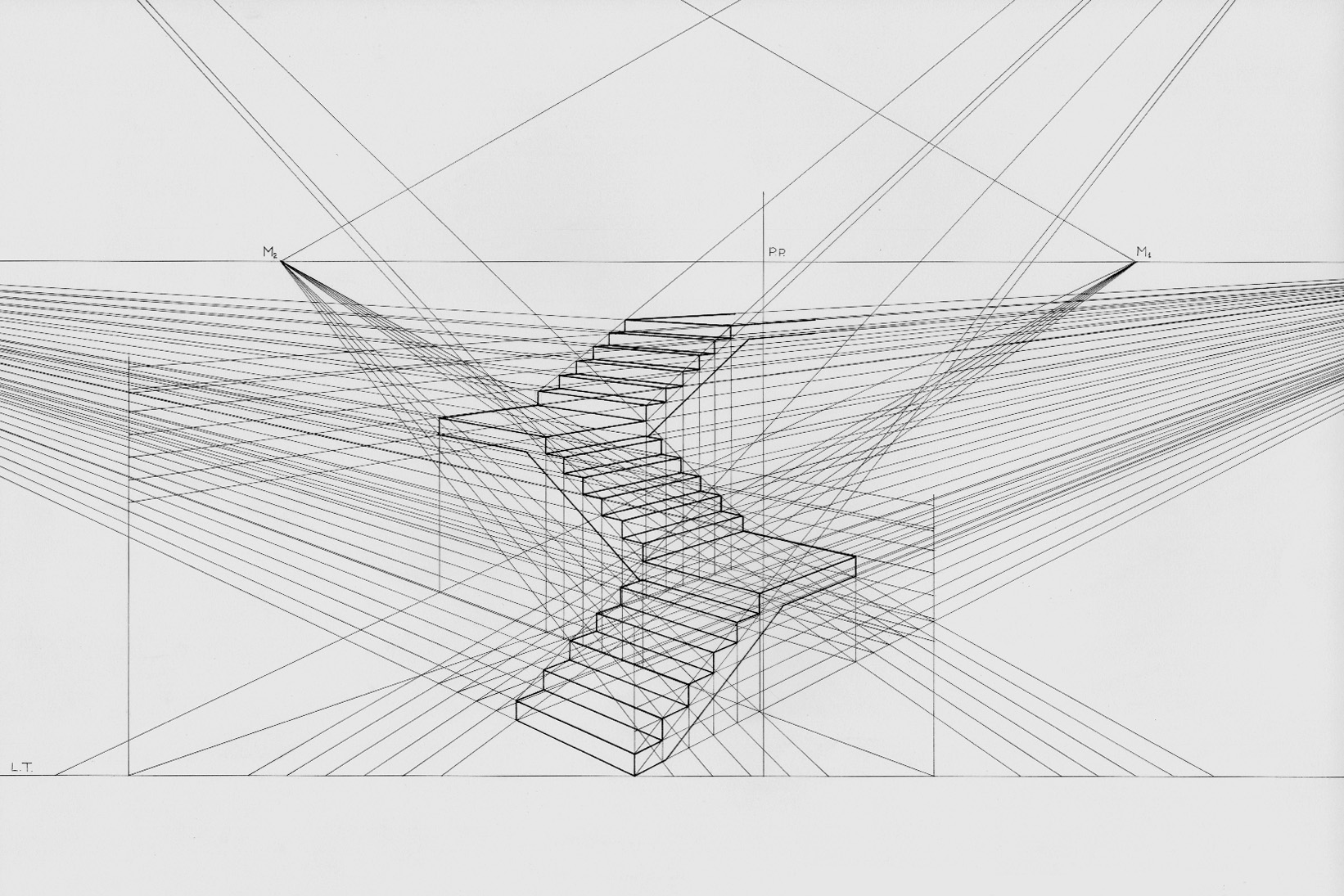
Perspective (graphical)
Linear or point-projection perspective (from la, perspicere 'to see through') is one of two types of 3D projection, graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, generally on a flat surface, of an image as it is seen by the eye. Perspective drawing is useful for representing a three-dimensional scene in a two-dimensional medium, like paper. The most characteristic features of linear perspective are that objects appear smaller as their distance from the observer increases, and that they are subject to ''foreshortening'', meaning that an object's dimensions along the line of sight appear shorter than its dimensions across the line of sight. All objects will recede to points in the distance, usually along the horizon line, but also above and below the horizon line depending on the view used. Italian Renaissance painters and architects including Masaccio, Paolo Uccello, Piero della Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphical Projection
A 3D projection (or graphical projection) is a design technique used to display a three-dimensional (3D) object on a two-dimensional (2D) surface. These projections rely on visual perspective and aspect analysis to project a complex object for viewing capability on a simpler plane. 3D projections use the primary qualities of an object's basic shape to create a map of points, that are then connected to one another to create a visual element. The result is a graphic that contains conceptual properties to interpret that the figure or image as not actually flat (2D), but rather, as a solid object (3D) being viewed on a 2D display. 3D objects are largely displayed on two-dimensional mediums (i.e. paper and computer monitors). As such, graphical projections are a commonly used design element; notably, in engineering drawing, drafting, and computer graphics. Projections can be calculated through employment of mathematical analysis and formulae, or by using various geometric and op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Rendering
3D rendering is the 3D computer graphics process of converting 3D modeling, 3D models into 2D computer graphics, 2D images on a computer. 3D renders may include photorealistic rendering, photorealistic effects or non-photorealistic rendering, non-photorealistic styles. Rendering methods Rendering (computer graphics), Rendering is the final process of creating the actual 2D image or animation from the prepared scene. This can be compared to taking a photo or filming the scene after the setup is finished in real life. Several different, and often specialized, rendering methods have been developed. These range from the distinctly non-realistic Wire frame model, wireframe rendering through polygon-based rendering, to more advanced techniques such as: scanline rendering, Ray tracing (graphics), ray tracing, or Radiosity (computer graphics), radiosity. Rendering may take from fractions of a second to days for a single image/frame. In general, different methods are better suited for e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Computer Graphics
3D computer graphics, or “3D graphics,” sometimes called CGI, 3D-CGI or three-dimensional computer graphics are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data (often Cartesian) that is stored in the computer for the purposes of performing calculations and rendering digital images, usually 2D images but sometimes 3D images. The resulting images may be stored for viewing later (possibly as an animation) or displayed in real time. 3D computer graphics, contrary to what the name suggests, are most often displayed on two-dimensional displays. Unlike 3D film and similar techniques, the result is two-dimensional, without visual depth. More often, 3D graphics are being displayed on 3D displays, like in virtual reality systems. 3D graphics stand in contrast to 2D computer graphics which typically use completely different methods and formats for creation and rendering. 3D computer graphics rely on many of the same algorithms as 2D computer vector gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perspective (visual)
Linear or point-projection perspective (from la, perspicere 'to see through') is one of two types of graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, generally on a flat surface, of an image as it is seen by the eye. Perspective drawing is useful for representing a three-dimensional scene in a two-dimensional medium, like paper. The most characteristic features of linear perspective are that objects appear smaller as their distance from the observer increases, and that they are subject to ''foreshortening'', meaning that an object's dimensions along the line of sight appear shorter than its dimensions across the line of sight. All objects will recede to points in the distance, usually along the horizon line, but also above and below the horizon line depending on the view used. Italian Renaissance painters and architects including Masaccio, Paolo Uccello, Piero della Francesca and Luca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Tracking
Eye tracking is the process of measuring either the point of gaze (where one is looking) or the motion of an eye relative to the head. An eye tracker is a device for measuring eye positions and eye movement. Eye trackers are used in research on the visual system, in psychology, in psycholinguistics, marketing, as an input device for human-computer interaction, and in product design. Eye trackers are also being increasingly used for rehabilitative and assistive applications (related,for instance, to control of wheel chairs, robotic arms and prostheses). There are a number of methods for measuring eye movement. The most popular variant uses video images from which the eye position is extracted. Other methods use search coils or are based on the electrooculogram. History In the 1800s, studies of eye movement were made using direct observations. For example, Louis Émile Javal observed in 1879 that reading does not involve a smooth sweeping of the eyes along the text, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Tracking
Video tracking is the process of locating a moving object (or multiple objects) over time using a camera. It has a variety of uses, some of which are: human-computer interaction, security and surveillance, video communication and compression, augmented reality, traffic control, medical imaging and video editing. Video tracking can be a time-consuming process due to the amount of data that is contained in video. Adding further to the complexity is the possible need to use object recognition techniques for tracking, a challenging problem in its own right. Objective The objective of video tracking is to associate target objects in consecutive video frames. The association can be especially difficult when the objects are moving fast relative to the frame rate. Another situation that increases the complexity of the problem is when the tracked object changes orientation over time. For these situations video tracking systems usually employ a motion model which describes how the image o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire Phone
The Fire Phone was a 3D-enabled smartphone developed by Amazon and manufactured by Foxconn. It was announced on June 18, 2014, and marked Amazon's first foray into the smartphone market, following the success of the Kindle Fire. It was available for pre-order on the day it was announced. In the United States, it launched as an AT&T exclusive on July 25. The phone was notable for its hallmark feature "Dynamic Perspective": using four front-facing cameras and the gyroscope to track the user's movements, the OS adjusts the UI so it gives the impression of depth and 3D. Other notable Amazon services on the phone included X-Ray, used for identifying and finding information about media; Mayday, the 24-hour customer service tool; and Firefly, a tool which automatically recognized text, sounds, and objects, then offers a way to buy recognized items through Amazon's online store. The phone received mixed reviews. Critics praised the Dynamic Perspective, Firefly and, to a lesser extent, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Perspective
Dynamics (from Greek δυναμικός ''dynamikos'' "powerful", from δύναμις ''dynamis'' " power") or dynamic may refer to: Physics and engineering * Dynamics (mechanics) ** Aerodynamics, the study of the motion of air ** Analytical dynamics, the motion of bodies as induced by external forces ** Brownian dynamics, the occurrence of Langevin dynamics in the motion of particles in solution ** File dynamics, stochastic motion of particles in a channel ** Flight dynamics, the science of aircraft and spacecraft design ** Fluid dynamics or ''hydrodynamics'', the study of fluid flow *** Computational fluid dynamics, a way of studying fluid dynamics using numerical methods ** Fractional dynamics, dynamics with integrations and differentiations of fractional orders ** Molecular dynamics, the study of motion on the molecular level ** Langevin dynamics, a mathematical model for stochastic dynamics ** Orbital dynamics, the study of the motion of rockets and spacecraft ** Quant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Footnotes
A note is a string of text placed at the bottom of a page in a book or document or at the end of a chapter, volume, or the whole text. The note can provide an author's comments on the main text or citations of a reference work in support of the text. Footnotes are notes at the foot of the page while endnotes are collected under a separate heading at the end of a chapter, volume, or entire work. Unlike footnotes, endnotes have the advantage of not affecting the layout of the main text, but may cause inconvenience to readers who have to move back and forth between the main text and the endnotes. In some editions of the Bible, notes are placed in a narrow column in the middle of each page between two columns of biblical text. Numbering and symbols In English, a footnote or endnote is normally flagged by a superscripted number immediately following that portion of the text the note references, each such footnote being numbered sequentially. Occasionally, a number between brack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |