|
HbE
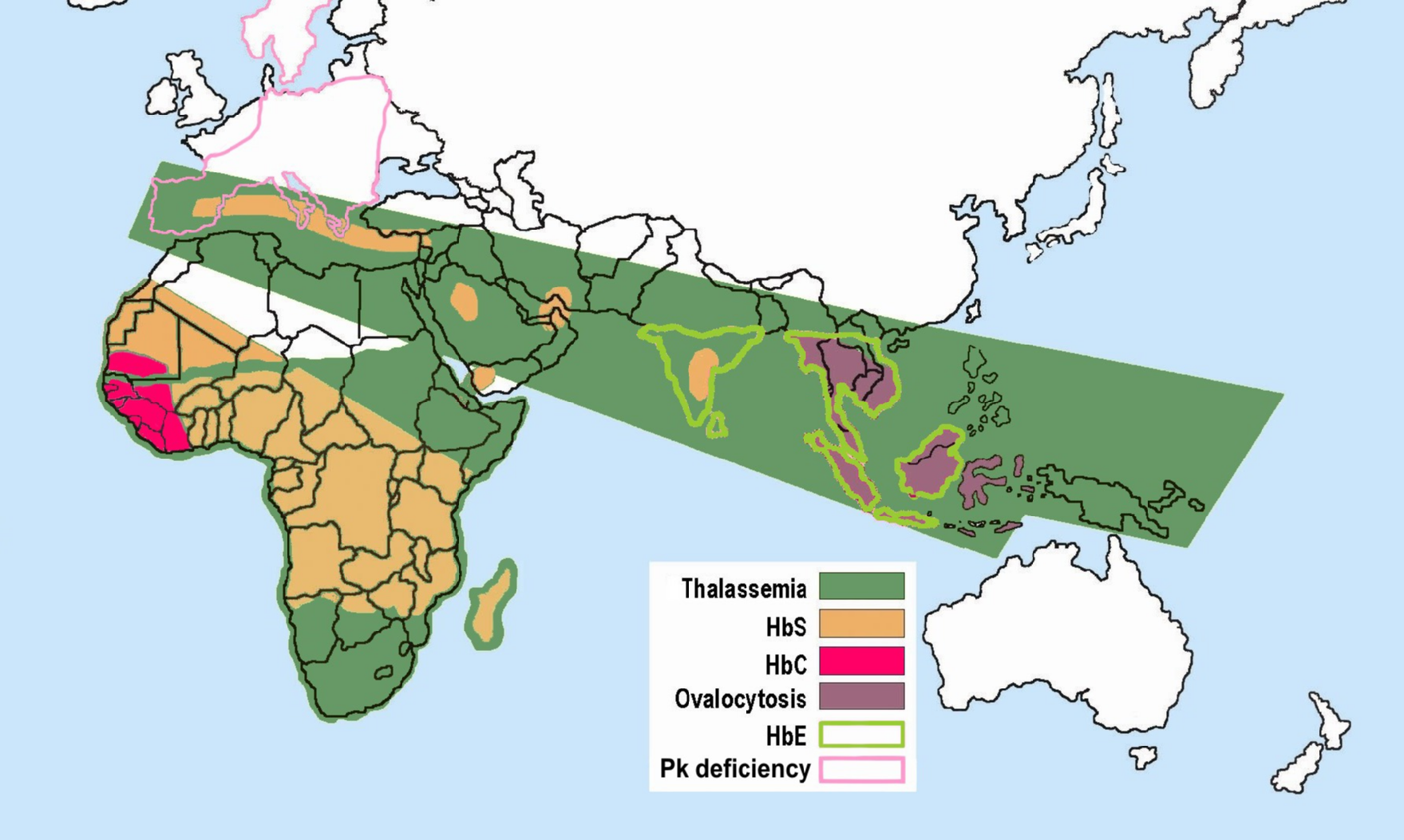
Hemoglobin E (HbE) is an abnormal hemoglobin with a single point mutation in the β chain. At position 26 there is a change in the amino acid, from glutamic acid to lysine (E26K). Hemoglobin E is very common among people of Southeast Asian, Northeast Indian, Sri Lankan and Bangladeshi descent. The βE mutation affects β-gene expression creating an alternate splicing site in the mRNA at codons 25-27 of the β-globin gene. Through this mechanism, there is a mild deficiency in normal β mRNA and production of small amounts of anomalous β mRNA. The reduced synthesis of β chain may cause β-thalassemia. Also, this hemoglobin variant has a weak union between α- and β-globin, causing instability when there is a high amount of oxidant. HbE can be detected on electrophoresis. Hemoglobin E disease (EE) Hemoglobin E disease results when the offspring inherits the gene for HbE from both parents. At birth, babies homozygous for the hemoglobin E allele do not present symptoms because they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HbE BetaThalassemia Trait
Hemoglobin E (HbE) is an abnormal hemoglobin with a single point mutation in the β chain. At position 26 there is a change in the amino acid, from glutamic acid to lysine (E26K). Hemoglobin E is very common among people of Southeast Asian, Northeast Indian, Sri Lankan and Bangladeshi descent. The βE mutation affects β-gene expression creating an alternate splicing site in the mRNA at codons 25-27 of the β-globin gene. Through this mechanism, there is a mild deficiency in normal β mRNA and production of small amounts of anomalous β mRNA. The reduced synthesis of β chain may cause β-thalassemia. Also, this hemoglobin variant has a weak union between α- and β-globin, causing instability when there is a high amount of oxidant. HbE can be detected on electrophoresis. Hemoglobin E disease (EE) Hemoglobin E disease results when the offspring inherits the gene for HbE from both parents. At birth, babies homozygous for the hemoglobin E allele do not present symptoms because they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virginia Minnich
Virginia Minnich (1910–1996) was an American molecular biologist and hematology researcher known for discovering hemoglobin E, an abnormal form of hemoglobin that can cause blood disorders, and for working out the glutathione synthesis pathway. She was a noted blood morphologist and teacher and helped set up hematology laboratories around the world. She was the first person without a PhD or MD to be appointed a Professor of Medicine at Washington University School of Medicine. Early life and education Minnich was born on January 24, 1910, in Zanesville, Ohio, and raised on her family's farm. She suffered severe burns at the age of four when her dress caught fire from a gas stove and she underwent close to thirty operations to correct the resultant disfigurement. Despite the surgeries, she was left with considerable scarring to her face, neck, and upper body that led some colleagues to discourage her from jobs requiring much human interaction. She had wanted to become a nurse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematology
Hematology ( always spelled haematology in British English) is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to blood. It involves treating diseases that affect the production of blood and its components, such as blood cells, hemoglobin, blood proteins, bone marrow, platelets, blood vessels, spleen, and the mechanism of coagulation. Such diseases might include hemophilia, blood clots (thrombus), other bleeding disorders, and blood cancers such as leukemia, multiple myeloma, and lymphoma. The laboratory analysis of blood is frequently performed by a medical technologist or medical laboratory scientist. Specialization Physicians specialized in hematology are known as hematologists or haematologists. Their routine work mainly includes the care and treatment of patients with hematological diseases, although some may also work at the hematology laboratory viewing blood films and bone marrow slides under the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygosity
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism. Most eukaryotes have two matching sets of chromosomes; that is, they are diploid. Diploid organisms have the same loci on each of their two sets of homologous chromosomes except that the sequences at these loci may differ between the two chromosomes in a matching pair and that a few chromosomes may be mismatched as part of a chromosomal sex-determination system. If both alleles of a diploid organism are the same, the organism is homozygous at that locus. If they are different, the organism is heterozygous at that locus. If one allele is missing, it is hemizygous, and, if both alleles are missing, it is nullizygous. The DNA sequence of a gene often varies from one individual to another. These gene variants are called alleles. While some gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vedda
The Vedda ( si, වැද්දා , ta, வேடர் (''Vēḍar'')), or Wanniyalaeto, are a minority indigenous group of people in Sri Lanka who, among other sub-communities such as Coast Veddas, Anuradhapura Veddas and Bintenne Veddas, are accorded indigenous status. The Vedda minority in Sri Lanka may become completely assimilated. Most speak Sinhala instead of their indigenous languages, which are nearing extinction. It has been hypothesized that the Vedda were probably the earliest inhabitants of Sri Lanka and have lived on the island since before the arrival of other ethnic groups in India. The Ratnapura District, which is part of the Sabaragamuwa Province, is known to have been inhabited by the Veddas in the distant past. This has been shown by scholars like Nandadeva Wijesekera. The very name ''Sabaragamuwa'' is believed to have meant the village of the ''Sabaras'' or "forest barbarians". Place-names such as ''Vedda-gala'' (Vedda Rock), ''Vedda-ela'' (Vedda Canal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinhalese People
Sinhalese people ( si, සිංහල ජනතාව, Sinhala Janathāva) are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group native to the island of Sri Lanka. They were historically known as Hela people ( si, හෙළ). They constitute about 75% of the Sri Lankan population and number more than 16.2 million. The Sinhalese identity is based on language, cultural heritage and nationality. The Sinhalese people speak Sinhala, an insular Indo-Aryan language, and are predominantly Theravada Buddhists, although a minority of Sinhalese follow branches of Christianity and other religions. Since 1815, they were broadly divided into two respective groups: The 'Up-country Sinhalese' in the central mountainous regions, and the 'Low-country Sinhalese' in the coastal regions; although both groups speak the same language, they are distinguished as they observe different cultural customs. According to the Mahavamsa and the Dipavamsa, a third–fifth century treatise written in Pali by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Rochester Medical Center
The University of Rochester Medical Center (URMC), now known as UR Medicine, is located in Rochester, New York, is one of the main campuses of the University of Rochester and comprises the university's primary medical education, research and patient care facilities. Schools and facilities URMC is one of the largest facilities for medical treatment and research in Upstate New York and includes a regional Prenatal Center, Trauma Center, Burn Center, Cancer Center, an Epilepsy Center, Psychiatric/Behavioral Health Emergency and treatment departments, Liver Transplant Center and Cardiac Transplant Center and also includes a major AIDS Treatment Center and an NIH-designated AIDS Vaccine Evaluation Unit. A large portion of the university's biomedical research is conducted in the Arthur Kornberg Medical Research Building and the Aab Institute of Biomedical Sciences. In January 2008, the University of Rochester announced a $500 million strategic plan geared toward expansion in research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mainland Southeast Asia
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west and the Pacific Ocean to the east. It includes the countries of Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand and Vietnam, with peninsular Malaysia sometimes also being included. The term Indochina (originally Indo-China) was coined in the early nineteenth century, emphasizing the historical cultural influence of Indian and Chinese civilizations on the area. The term was later adopted as the name of the colony of French Indochina (today's Cambodia, Laos, and Vietnam). Today, the term, Mainland Southeast Asia, in contrast to Maritime Southeast Asia, is more commonly referenced. Terminology The origins of the name Indo-China are usually attributed jointly to the Danish-French geographer Conrad Malte-Brun, who referred to the area as in 1804, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Blood Cell Abnormalities
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to Orange (colour), orange and opposite Violet (color), violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondary color (made from magenta and yellow) in the CMYK color model, and is the complementary color of cyan. Reds range from the brilliant yellow-tinged Scarlet (color), scarlet and Vermilion, vermillion to bluish-red crimson, and vary in shade from the pale red pink to the dark red burgundy (color), burgundy. Red pigment made from ochre was one of the first colors used in prehistoric art. The Ancient Egyptians and Mayan civilization, Mayans colored their faces red in ceremonies; Roman Empire, Roman generals had their bodies colored red to celebrate victories. It was also an important color in China, where it was used to color early pottery and later the gates and walls of palaces. In the Renaissance, the brillian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin ten to fifteen days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria. Malaria is caused by single-celled microorganisms of the ''Plasmodium'' group. It is spread exclusively through bites of infected ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. The mosquito bite introduces the parasites from the mosquito's saliva into a person's blood. The parasites travel to the liver where they mature and reproduce. Five species of ''Plasmodium'' can infect and be spread by h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaundice
Jaundice, also known as icterus, is a yellowish or greenish pigmentation of the skin and sclera due to high bilirubin levels. Jaundice in adults is typically a sign indicating the presence of underlying diseases involving abnormal heme metabolism, liver dysfunction, or biliary-tract obstruction. The prevalence of jaundice in adults is rare, while jaundice in babies is common, with an estimated 80% affected during their first week of life. The most commonly associated symptoms of jaundice are itchiness, pale feces, and dark urine. Normal levels of bilirubin in blood are below 1.0 mg/ dl (17 μmol/ L), while levels over 2–3 mg/dl (34–51 μmol/L) typically result in jaundice. High blood bilirubin is divided into two types – unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin. Causes of jaundice vary from relatively benign to potentially fatal. High unconjugated bilirubin may be due to excess red blood cell breakdown, large bruises, genetic conditions s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatomegaly
Hepatomegaly is the condition of having an enlarged liver. It is a non-specific medical sign having many causes, which can broadly be broken down into infection, hepatic tumours, or metabolic disorder. Often, hepatomegaly will present as an abdominal mass. Depending on the cause, it may sometimes present along with jaundice. Signs and symptoms The individual may experience many symptoms, including weight loss, poor appetite and lethargy (jaundice and bruising may also be present). Causes Among the causes of hepatomegaly are the following: Infective Mechanism The mechanism of hepatomegaly consists of vascular swelling, inflammation (due to the various causes that are infectious in origin) and deposition of (1) non-hepatic cells or (2) increased cell contents (such due to iron in hemochromatosis or hemosiderosis and fat in fatty liver disease). Diagnosis Suspicion of hepatomegaly indicates a thorough medical history and physical examination, wherein the latter typically incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |