|
Hathigumpha Inscription
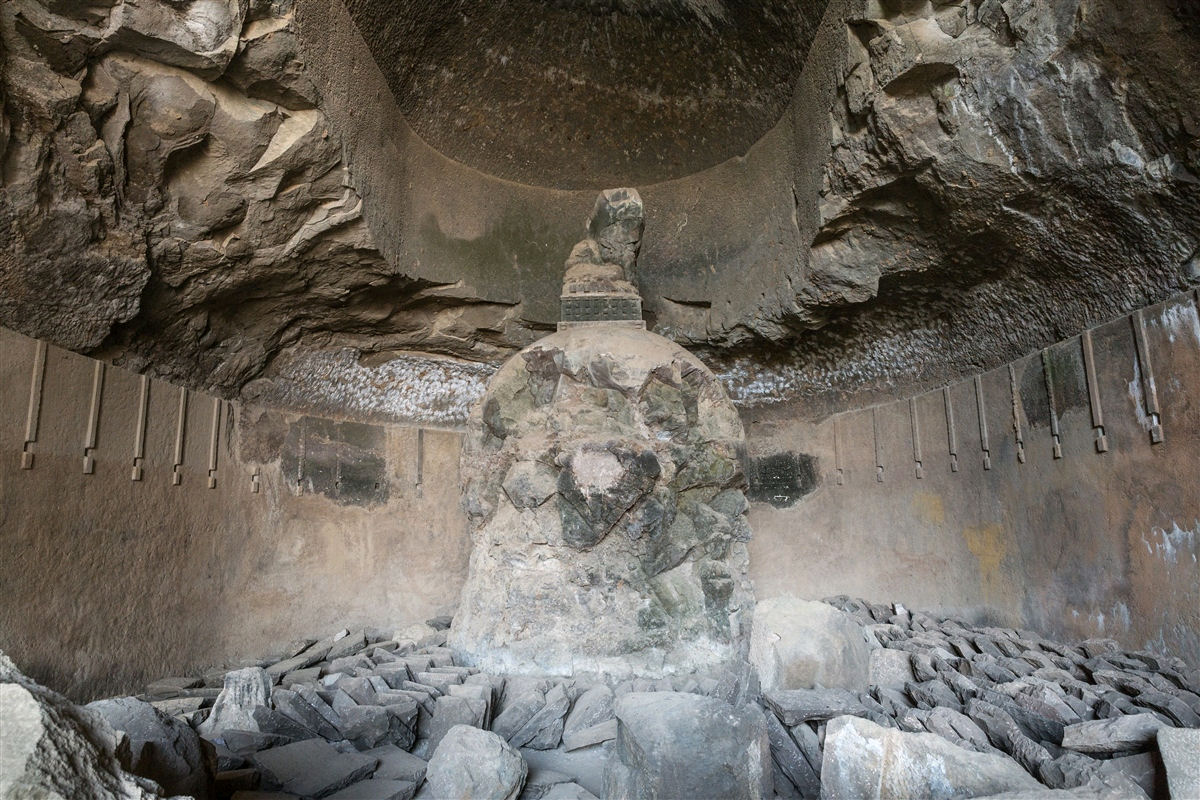
The Hathigumpha Inscription is a seventeen line inscription in Prakrit language incised in Brahmi script in a cavern called Hathigumpha in Udayagiri hills, near Bhubaneswar in Odisha, India. Dated between 2nd-century BCE and 1st-century CE, it was inscribed by the Jain king Kharavela of Kalinga kingdom. The Hathigumpha Inscription, among other things, presents a biographical sketch of a king in the eastern region of ancient India (now part of and near Odisha). It also includes the religious values, public infrastructure projects, military expeditions and its purpose, and socio-cultural information. Paleographically, the inscription dates from mid-1st century BCE to early 1st century CE. Location and history The Hathigumpha inscription () of Kharavela is found at Udayagiri, about west of Bhubaneswar international airport. The Udayagiri hills host many ancient rock-cut caves such as the Rani Gumpha. Among these, to the west of Rani Gumpha, is a cavern called Hathigumpha on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Udayagiri And Khandagiri Caves
Udayagiri and Khandagiri Caves, formerly called Kattaka Caves or Cuttack caves, are partly natural and partly artificial caves of archaeological, historical and religious importance near the city of Bhubaneswar in Odisha, India. The caves are situated on two adjacent hills, Udayagiri and Khandagiri mentioned as ''Kumari Parvata'' in the Hathigumpha inscription. They have a number of finely and ornately carved caves built during the 1st century BCE. It is believed that most of these caves were carved out as residential blocks for Jaina monks during the reign of King Kharavela. Udayagiri means "Sunrise Hill" and has 18 caves while Khandagiri has 15 caves. The caves of Udayagiri and Khandagiri, called ''lena'' or ''leṇa'' in the inscriptions, were dug out mostly during the reign of Kharavela for the abode of Jaina ascetics. The most important of this group is Ranigumpha in Udayagiri which is a double storeyed monastery. Other important caves include Hathi Gumpha, Ananta Gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dineshchandra Sircar
Dineshchandra Sircar (1907–1985), also known as D. C. Sircar or D. C. Sarkar, was an epigraphist, historian, numismatist and folklorist, known particularly in India and Bangladesh for his work deciphering inscriptions. He was the Chief Epigraphist of the Archaeological Survey of India (1949–1962), Carmichael Professor of Ancient Indian History and Culture at the University of Calcutta (1962–1972) and the General President of the Indian History Congress. In 1972, Sircar was awarded the Sir William Jones Memorial Plaque. Early life and education Sircar was born to a family of Ayurvedic physicians at Krishnanagar. He graduated with Honours in Sanskrit in 1929 and obtained a First Class in his MA Examination in 1931 in Ancient Indian History and Culture with specialisation in Epigraphy and Numismatics from the University of Calcutta. Selected bibliography He authors more than forty books both in Bengali and English. Some of his best-known books include: * ''পা� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demetrius I Of Bactria
Demetrius I Anicetus ( grc, Δημήτριος Ἀνίκητος, Dēmētrios Anikētos, "the unconquered"), also called Damaytra was a Greco-Bactrian and later Indo-Greek king (Yona in Pali language, "Yavana" in Sanskrit) (reigned c. 200–167 BC), who ruled areas from Bactria to ancient northwestern India. He was the son of the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom's ruler Euthydemus I and succeeded him around 200 BC, after which he conquered extensive areas in what is now southern Afghanistan, Iran and Pakistan and India. He was never defeated in battle and was posthumously referred to as "the Unconquered" (''Aniketos'') on the pedigree coins of his successor Agathocles. Demetrius I may have been the initiator of the Yavana era, starting in 186–185 BC, which was used for several centuries thereafter. "Demetrius" was the name of at least two and probably three Bactrian kings. The much debated Demetrius II was a possible relative, whereas Demetrius III (), is known only from numismatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathura, Uttar Pradesh
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located approximately north of Agra, and south-east of Delhi; about from the town of Vrindavan, and from Govardhan. In ancient times, Mathura was an economic hub, located at the junction of important caravan routes. The 2011 Census of India estimated the population of Mathura at 441,894. In Hinduism, Mathura is birthplace of Krishna, which is located at the Krishna Janmasthan Temple Complex. It is one of the Sapta Puri, the seven cities considered holy by Hindus, also called Mokshyadayni Tirth. The Kesava Deo Temple was built in ancient times on the site of Krishna's birthplace (an underground prison). Mathura was the capital of the kingdom of Surasena, ruled by Kansa, the maternal uncle of Krishna. Mathura is part of the Lord Krishna circuit (Mathura,Vrindavan, Barsana, Govardhan, Kurukshetra, Dwarka and Bhalka). Janmashtami is grandly celebrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yavana
The word Yona in Pali and the Prakrits, and the analogue Yavana in Sanskrit and Yavanar in Tamil, were words used in Ancient India to designate Greek speakers. "Yona" and "Yavana" are transliterations of the Greek word for " Ionians" ( grc, Ἴωνες < Ἰάoνες < *Ἰάϝoνες), who were probably the first Greeks to be known in the East. Both terms appear in ancient literature. ''Yavana'' appears, for instance, in the '''', while ''Yona'' appears in texts such as the n chronicle '' Mahavamsa''. The Yona are me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hathigumpha Inscription (2020) Yavana Dimita Detail
The Hathigumpha Inscription (pronounced: ɦɑːt̪ʰiːgumpʰɑː) is a seventeen line inscription in a Prakrit language incised in Brahmi script in a cavern called Hathigumpha in Udayagiri hills, near Bhubaneswar in Odisha, India. Dated between the second century BCE and the first century CE, it was inscribed by the Jain king Kharavela of the Kalinga kingdom. The Hathigumpha Inscription presents, among other topics, a biographical sketch of a king in the eastern region of ancient India (now part of and near Odisha). It also includes information on religious values, public infrastructure projects, military expeditions and their purposes, society and culture. Paleographically, the inscription dates from the middle of the first century BCE to the early first century CE. Location and history The Hathigumpha inscription () of Kharavela is found at Udayagiri, about west of Bhubaneswar international airport. The Udayagiri hills host many ancient rock-cut caves such as the Rani Gum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hathigumpha Inscription (2020) Satakani Detail
The Hathigumpha Inscription (pronounced: ɦɑːt̪ʰiːgumpʰɑː) is a seventeen line inscription in a Prakrit language incised in Brahmi script in a cavern called Hathigumpha in Udayagiri hills, near Bhubaneswar in Odisha, India. Dated between the second century BCE and the first century CE, it was inscribed by the Jain king Kharavela of the Kalinga kingdom. The Hathigumpha Inscription presents, among other topics, a biographical sketch of a king in the eastern region of ancient India (now part of and near Odisha). It also includes information on religious values, public infrastructure projects, military expeditions and their purposes, society and culture. Paleographically, the inscription dates from the middle of the first century BCE to the early first century CE. Location and history The Hathigumpha inscription () of Kharavela is found at Udayagiri, about west of Bhubaneswar international airport. The Udayagiri hills host many ancient rock-cut caves such as the Rani Gum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kondana Caves
The Kondana Caves are located in the small village of Kondana, 33 km north of Lonavala and 16 km northwest of Karla Caves. This cave group has 16 Buddhist caves. The caves were excavated in first century B.C. The construction on wooden pattern is notable. One can reach the cave by descending from Rajmachi village. The cave only one inscription on the front of the Chaitya, which gives information about donors. Description About 14 km from the Karjat station, on Central Railway, and at the base of the old hill fort of Rajmachi, is the Kondane group of caves, first brought to notice in the 19th century by Vishnu Sastri, and soon after visited by Mr. Law, then collector of Thana. They are in the face of a steep scarp, and quite hidden from view by the thick forest in front of them. Water trickles down over the face of the rock above them during a considerable part even of the dry season, and has greatly injured them. So much so indeed that it is now difficult to determ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasik Caves
The Nasik Caves, or Trirashmi Leni (''Trirashmi'' being the name of the hills in which the caves are located, ''Leni'' being a Marathi word for caves), are a group of 23 caves carved between the 1st century BCE and the 3rd century CE, though additional sculptures were added up to about the 6th century, reflecting changes in Buddhist devotional practices.Michell, 384 The Buddhist sculptures are a significant group of early examples of Indian rock-cut architecture initially representing the Early Buddhist schools tradition. Most of the caves are viharas except for Cave 18 which is a chaitya of the 1st century BCE. The style of some of the elaborate pillars or columns, for example in caves 3 and 10, is an important example of the development of the form. The location of the caves is a holy Buddhist site and is located about 8 km south of the centre of Nashik (or Nasik), Maharashtra, India. The Pandavleni name sometimes given to the Nasik Caves has nothing to do with the P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhaja Caves
Bhaja Caves is a group of 22 rock-cut caves dating back to the 2nd century BC located in the city of Pune, India. The caves are 400 feet above the village of Bhaja, on an important ancient trade route running from the Arabian Sea eastward into the Deccan Plateau (the division between North India and South India). The inscriptions and the cave temple are protected as a Monument of National Importance, by the Archaeological Survey of India per Notification No. 2407-A. It belongs to the Early Buddhist schools in Maharashtra. The caves have a number of stupas, one of their significant features. The most prominent excavation is its chaitya (or ''chaityagrha'' - Cave XII), a good example of the early development of this form from wooden architecture, with a vaulted horseshoe ceiling. Its vihara (Cave XVIII) has a pillared verandah in front and is adorned with unique reliefs. These caves are notable for their indications of the awareness of wooden architecture. The carvings prove that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satakarni
Satakarni (also called Sātakarnī I, Brahmi script: 𑀲𑀸𑀢𑀓𑀡𑀺, ''Sātakaṇi'') was the third of the Satavahana kings, who ruled the Deccan region of India. His reign is generally dated to 70-60 BCE, although some authors have claimed 187-177 BCE, and most recently dated to 88-42 BCE. It was thought there were "two Satakarnis" (Satakarni I and Satakarni II), however, Andrew Ollett argues that there is only one Satakarni, as the alleged first Satakarni is assigned ten years, and the second, fifty years by other scholars, but the only dated inscription of this king is Candankheda seal from his reign's year 30, around 60 BCE, and he ruled ca. 88-42 BCE. Biography According to the Puranas, the Satavahana king Simuka was succeeded by his brother Krishna (also known as Kanha). According to ''Matsya Purana'', Krishna was succeeded by Mallakarni, but according to other Puranas, he was succeeded by Satakarni. The Nanaghat cave inscription of Satakarni lists his family m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satavahana
The Satavahanas (''Sādavāhana'' or ''Sātavāhana'', IAST: ), also referred to as the Andhras in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty based in the Deccan region. Most modern scholars believe that the Satavahana rule began in the late second century BCE and lasted until the early third century CE, although some assign the beginning of their rule to as early as the 3rd century BCE based on the Puranas, but uncorroborated by archaeological evidence. The Satavahana kingdom mainly comprised the present-day Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Maharashtra. At different times, their rule extended to parts of modern Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Karnataka. The dynasty had different capital cities at different times, including Pratishthana (Paithan) and Amaravati ( Dharanikota). The origin of the dynasty is uncertain, but according to the Puranas, their first king overthrew the Kanva dynasty. In the post- Maurya era, the Satavahanas established peace in the Deccan region and re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_Satakani_detail.jpg)



