|
Hasta Vinyasas
Hasta Vinyasas ( sa, हास्त विन्यास; ; IAST:) are a set of yoga vinyasas which primarily involve movement of the arms. The Hasta Vinyasas are: Parshvabhaga (Lateral Side Movement), Purvabhaga (Frontal Stretch), Prasarana (Sweeping Movement), Elbow Movement, Hands on Shoulder Blades Movements, Hands-Lock Behind Movements, Prishtanjali (Back Salute), and Shoulder Rotations. Etymology Hasta Vinyasa is derived from sa, हास्त Hāsta, "formed with the hands", and sa, विन्यास Vinyāsa, "movement". Below is a table of the Sanskrit etymology of the Hasta Vinyasas. Description As vinyasas which have Tadasana as their base, the Hasta Vinyasas improve balance, and calm the mind (which also helps to produce a steady body) and ready a practitioner for asana practice. Simultaneously the movement of the Hasta Vinyasas help invigorate the body and prepare it for other asana practice. When performing these vinyasas, all bandhas may be eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IAST
The International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration (IAST) is a transliteration scheme that allows the lossless romanisation of Indic scripts as employed by Sanskrit and related Indic languages. It is based on a scheme that emerged during the nineteenth century from suggestions by Charles Trevelyan, William Jones, Monier Monier-Williams and other scholars, and formalised by the Transliteration Committee of the Geneva Oriental Congress, in September 1894. IAST makes it possible for the reader to read the Indic text unambiguously, exactly as if it were in the original Indic script. It is this faithfulness to the original scripts that accounts for its continuing popularity amongst scholars. Usage Scholars commonly use IAST in publications that cite textual material in Sanskrit, Pāḷi and other classical Indian languages. IAST is also used for major e-text repositories such as SARIT, Muktabodha, GRETIL, and sanskritdocuments.org. The IAST scheme represents more than a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoga Hast Vinyasas - YOGAnDHARMA - Prasarana
Yoga (; sa, योग, lit=yoke' or 'union ) is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices or disciplines which originated in ancient India and aim to control (yoke) and still the mind, recognizing a detached witness-consciousness untouched by the mind ('' Chitta'') and mundane suffering (''Duḥkha''). There is a wide variety of schools of yoga, practices, and goals in Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism,Stuart Ray Sarbacker, ''Samādhi: The Numinous and Cessative in Indo-Tibetan Yoga''. SUNY Press, 2005, pp. 1–2.Tattvarthasutra .1 see Manu Doshi (2007) Translation of Tattvarthasutra, Ahmedabad: Shrut Ratnakar p. 102. and traditional and modern yoga is practiced worldwide. Two general theories exist on the origins of yoga. The linear model holds that yoga originated in the Vedic period, as reflected in the Vedic textual corpus, and influenced Buddhism; according to author Edward Fitzpatrick Crangle, this model is mainly supported by Hindu scholars. According ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinyasa Krama Yoga
Tirumalai Krishnamacharya Venkata Desikachar (21 June 1938 – 8 August 2016), better known as T. K. V. Desikachar, was a yoga teacher, son of the pioneer of modern yoga as exercise, Tirumalai Krishnamacharya. The style that he taught was initially called Viniyoga although he later abandoned that name and asked for the methods he taught to be called "yoga" without special qualification. Biography Desikachar was born in Mysore, son of the pioneer of modern yoga Tirumalai Krishnamacharya, under whom he studied. He moved to Madras (now Chennai) in the early 1960s. He had trained as an engineer, but, inspired by his father's teachings, he studied under his father in the 1960s, and from the 1970s he taught in many parts of the world. He published many books, especially the 1995 ''The Heart of Yoga''. During his thirty years of study, Desikachar learned the practice and application of yoga techniques and texts, for therapeutic, exercise, and spiritual purposes. Desikachar developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoga Hast Vinyasas - YOGAnDHARMA - Both Shoulder Rotations
Yoga (; sa, योग, lit=yoke' or 'union ) is a group of Asana, physical, mental, and Spirituality#Asian traditions, spiritual practices or disciplines which originated in History of India, ancient India and aim to control (yoke) and Śūnyatā, still the mind, Jnana, recognizing a detached Purusha, witness-consciousness untouched by the mind (''Chit (consciousness), Chitta'') and mundane suffering (''Duḥkha''). There is a wide variety of schools of yoga, practices, and goals in Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism,Stuart Ray Sarbacker, ''Samādhi: The Numinous and Cessative in Indo-Tibetan Yoga''. SUNY Press, 2005, pp. 1–2.Tattvarthasutra [6.1], see Manu Doshi (2007) Translation of Tattvarthasutra, Ahmedabad: Shrut Ratnakar p. 102. and traditional and modern yoga is practiced worldwide. Two general theories exist on the origins of yoga. The linear model holds that yoga originated in the Vedic period, as reflected in the Vedas, Vedic textual corpus, and influenced Buddhism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasta Vinyasas
Hasta Vinyasas ( sa, हास्त विन्यास; ; IAST:) are a set of yoga vinyasas which primarily involve movement of the arms. The Hasta Vinyasas are: Parshvabhaga (Lateral Side Movement), Purvabhaga (Frontal Stretch), Prasarana (Sweeping Movement), Elbow Movement, Hands on Shoulder Blades Movements, Hands-Lock Behind Movements, Prishtanjali (Back Salute), and Shoulder Rotations. Etymology Hasta Vinyasa is derived from sa, हास्त Hāsta, "formed with the hands", and sa, विन्यास Vinyāsa, "movement". Below is a table of the Sanskrit etymology of the Hasta Vinyasas. Description As vinyasas which have Tadasana as their base, the Hasta Vinyasas improve balance, and calm the mind (which also helps to produce a steady body) and ready a practitioner for asana practice. Simultaneously the movement of the Hasta Vinyasas help invigorate the body and prepare it for other asana practice. When performing these vinyasas, all bandhas may be eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uttanasana
Uttanasana ( sa, उत्तानासन; ) or Standing Forward Bend, with variants such as Padahastasana where the toes are grasped, is a standing forward bending asana in modern yoga as exercise. Etymology and origins The name comes from the Sanskrit words उत्तान ''uttāna'', "intense stretch"; and आसन; ''āsana'', "posture" or "seat". The pose is a modern one, first seen in the 20th century. A pose with the name Uttānāsana is illustrated in the 19th century ''Sritattvanidhi'' but it is quite different from the modern pose (lying on the back, with elbows touching the knees and the hands behind the neck). The modern pose is described in Krishnamacharya's 1934 ''Yoga Makaranda'', and in the works of his pupils, B. K. S. Iyengar's 1966 ''Light on Yoga'' and Pattabhi Jois's Ashtanga Vinyasa Yoga. Theos Bernard however illustrates the related pose "Padhahasthasana" (sic) in his 1944 report of his experience of hatha yoga on the border of India and Tibet, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
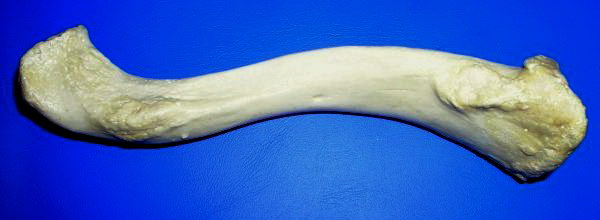
Clavicles
The clavicle, or collarbone, is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately 6 inches (15 cm) long that serves as a strut between the shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on the left and one on the right. The clavicle is the only long bone in the body that lies horizontally. Together with the shoulder blade, it makes up the shoulder girdle. It is a palpable bone and, in people who have less fat in this region, the location of the bone is clearly visible. It receives its name from the Latin ''clavicula'' ("little key"), because the bone rotates along its axis like a key when the shoulder is abducted. The clavicle is the most commonly fractured bone. It can easily be fractured by impacts to the shoulder from the force of falling on outstretched arms or by a direct hit. Structure The collarbone is a thin doubly curved long bone that connects the arm to the trunk of the body. Located directly above the first rib, it acts as a strut to keep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pectoral Muscles
Pectoral muscles (colloquially referred to as "pecs") are the muscles that connect the front of the human chest with the bones of the upper arm and shoulder. This region contains four muscles that provide movements to the upper limbs or ribs. Pectoralis major is a thick, fan-shaped or triangular convergent muscle, which makes up the bulk of the chest muscle. It lies under the breast. It serves to flex, extend, and rotate the humerus, the long bone of the upper arm. Pectoralis minor is a thin, triangular muscle located beneath the pectoralis major. It attaches to the ribs, and serves to stabilize the scapula, the large bone of the shoulder. The pectoral fascia is a thin layer of tissue over the pectoralis major, extending toward the latissimus dorsi muscle on the back. Along with the pectoralis major and pectoralis minor, the subclavius muscle forms the axilla or armpit. The subclavius moves the shoulder downward and forward. Serratus anterior is another muscle on the front of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercostal Muscles
Intercostal muscles are many different groups of muscles that run between the ribs, and help form and move the chest wall. The intercostal muscles are mainly involved in the mechanical aspect of breathing by helping expand and shrink the size of the chest cavity. Structure There are three principal layers; # External intercostal muscles also known as intercostalis externus aid in quiet and forced inhalation. They originate on ribs 1–11 and have their insertion on ribs 2–12. The external intercostals are responsible for the elevation of the ribs and bending them more open, thus expanding the transverse dimensions of the thoracic cavity. The muscle fibers are directed downwards, forwards and medially in the anterior part. # Internal intercostal muscles also known as intercostalis internus aid in forced expiration (quiet expiration is a passive process). They originate on ribs 2–12 and have their insertions on ribs 1–11.Their fibers pass anterior and supe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adduction
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urdhva Baddhanguliyasana
Tadasana ( sa , ताड़ासन, translit=Tāḍāsana), Mountain pose or Samasthiti ( sa, समस्थिति; IAST: ''samasthitiḥ'') is a standing asana in modern yoga as exercise; it is not described in medieval hatha yoga texts. It is the basis for several other standing asanas. Etymology and origins Tāḍāsana is from the Sanskrit words ताड ''tāḍa'', "mountain" and आसन ''āsana'' meaning "posture" or "seat". Samasthitiḥ is from सम ''sama'' meaning "equal", level", or "balanced"; and स्थिति ''sthiti'', "standing". The pose was unknown in hatha yoga until the 20th century ''Light on Yoga'', but it appears in the 1896 ''Vyayama Dipika'', a manual of gymnastics, as part of the "very old" sequence of ''danda'' (Sanskrit for "staff" or "stick") exercises. Norman Sjoman suggests that it was among the poses adopted into modern yoga as exercise in Mysore by Krishnamacharya to form the "primary foundation" for his vinyasas with flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |