|
Harold Sonny White (NASA Scientist)
Harold G. "Sonny" White (born October 8, 1965) is a mechanical engineer, aerospace engineer, and applied physicist who is known for proposing new Alcubierre drive concepts and promoting advanced propulsion projects. Educational White obtained a B.S. degree in mechanical engineering from University of South Alabama, an M.S. degree in mechanical engineering from Wichita State University in 1999, and a Ph.D. degree in Physics from Rice University in 2008.Icarus Interstellar"Dr. Harold 'Sonny' White", ''Project Icarus''. Alcubierre "warp" drive White attracted the attention of the press when he began presenting his ideas at space conventions and publishing proposals for Alcubierre drive concepts. In 2011, he released a paper titled ''Warp Field Mechanics 101'' that outlined an updated concept of Miguel Alcubierre's faster-than-light propulsion concept, including methods to prove the feasibility of the project. Alcubierre's concept had been considered infeasible be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Nationality Law
United States nationality law details the conditions in which a person holds United States nationality. In the United States, nationality is typically obtained through provisions in the U.S. constitution, U.S. Constitution, various laws, and international agreements. Citizenship is a right, not a privilege. While the domestic documents often use citizenship and nationality interchangeably, nationality refers to the legal means in which a person obtains a national identity and formal membership in a nation and citizenship refers to the relationship held by nationals who are also citizens. Individuals born in any of the 50 U.S. states, the District of Columbia or almost any inhabited Territories of the United States, territory are Natural-born-citizen clause, natural-born United States citizens. The sole exception is American Samoa, where individuals are typically non-citizen U.S. nationals at birth. Foreign nationals living in any state or qualified territory may naturalize aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torus
In geometry, a torus (plural tori, colloquially donut or doughnut) is a surface of revolution generated by revolving a circle in three-dimensional space about an axis that is coplanar with the circle. If the axis of revolution does not touch the circle, the surface has a ring shape and is called a torus of revolution. If the axis of revolution is tangent to the circle, the surface is a horn torus. If the axis of revolution passes twice through the circle, the surface is a spindle torus. If the axis of revolution passes through the center of the circle, the surface is a degenerate torus, a double-covered sphere. If the revolved curve is not a circle, the surface is called a ''toroid'', as in a square toroid. Real-world objects that approximate a torus of revolution include swim rings, inner tubes and ringette rings. Eyeglass lenses that combine spherical and cylindrical correction are toric lenses. A torus should not be confused with a '' solid torus'', which is formed by r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation Of Energy
In physics and chemistry, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant; it is said to be ''conserved'' over time. This law, first proposed and tested by Émilie du Châtelet, means that energy can neither be created nor destroyed; rather, it can only be transformed or transferred from one form to another. For instance, chemical energy is converted to kinetic energy when a stick of dynamite explodes. If one adds up all forms of energy that were released in the explosion, such as the kinetic energy and potential energy of the pieces, as well as heat and sound, one will get the exact decrease of chemical energy in the combustion of the dynamite. Classically, conservation of energy was distinct from conservation of mass. However, special relativity shows that mass is related to energy and vice versa by ''E = mc2'', and science now takes the view that mass-energy as a whole is conserved. Theoretically, this implies that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Momentum
In Newtonian mechanics, momentum (more specifically linear momentum or translational momentum) is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. It is a vector quantity, possessing a magnitude and a direction. If is an object's mass and is its velocity (also a vector quantity), then the object's momentum is : \mathbf = m \mathbf. In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of measurement of momentum is the kilogram metre per second (kg⋅m/s), which is equivalent to the newton-second. Newton's second law of motion states that the rate of change of a body's momentum is equal to the net force acting on it. Momentum depends on the frame of reference, but in any inertial frame it is a ''conserved'' quantity, meaning that if a closed system is not affected by external forces, its total linear momentum does not change. Momentum is also conserved in special relativity (with a modified formula) and, in a modified form, in electrodynamics, quantum mechanics, quan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laws Of Physics
Scientific laws or laws of science are statements, based on repeated experiments or observations, that describe or predict a range of natural phenomena. The term ''law'' has diverse usage in many cases (approximate, accurate, broad, or narrow) across all fields of natural science (physics, chemistry, astronomy, geoscience, biology). Laws are developed from data and can be further developed through mathematics; in all cases they are directly or indirectly based on empirical evidence. It is generally understood that they implicitly reflect, though they do not explicitly assert, causal relationships fundamental to reality, and are discovered rather than invented. Scientific laws summarize the results of experiments or observations, usually within a certain range of application. In general, the accuracy of a law does not change when a new theory of the relevant phenomenon is worked out, but rather the scope of the law's application, since the mathematics or statement representing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EM Drive
The EmDrive is a concept for a thruster for spacecraft, first written about in 2001. It is purported to generate thrust by reflecting microwaves inside the device, in a way that would violate the law of conservation of momentum and other laws of physics. The concept has been referred to at times as a resonant cavity thruster or as the latest Impossible Drive. There is no official design for this device. Neither person who claims to have invented it has committed to an explanation for how it could operate as a thruster or what elements define it, making it hard to say definitively whether a given object is an example of an EmDrive. However, over the years, prototypes based on its public descriptions have been constructed and tested. In 2016, Harold White's group at NASA observed a small apparent thrust from one such test, however subsequent studies suggested this was a measurement error caused by thermal gradients. In 2021, Martin Tajmar's group at the Dresden University of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Physical Journal C
The ''European Physical Journal C'' (''EPJ C'') is a biweekly peer-reviewed, open access scientific journal covering theoretical and experimental physics. It is part of the SCOAP3 initiative. See also * ''European Physical Journal The ''European Physical Journal'' (or ''EPJ'') is a joint publication of EDP Sciences, Springer Science+Business Media, and the Società Italiana di Fisica. It arose in 1998 as a merger and continuation of ''Acta Physica Hungarica'', '' Anales d ...'' References Physics journals Springer Science+Business Media academic journals Publications established in 1998 English-language journals Semi-monthly journals EDP Sciences academic journals Particle physics journals {{physics-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Rifle Coffee Company
Black Rifle Coffee Company (BRCC) is a coffee company based in Salt Lake City, Utah, United States. It gained national attention in 2017, when it employed about 50 people, after pledging to hire 10,000 veterans to protest Starbucks's pledge to hire 10,000 refugees. History The company was founded in December 2014 by former Green Beret Evan Hafer. He began by selling a small volume of his "Freedom Roast" coffee through a friend's apparel website. The coffee sold well, so Hafer launched his own brand and website through which to sell his coffee and branded accessories. The company specializes in its online, direct-to-consumer coffee subscription service, which had over 100,000 subscribers as of 2020. In addition to online sales, Black Rifle Coffee Company has physical coffee shops in Utah, Texas, Oklahoma and Georgia. The coffee is also distributed at some firing ranges, 5.11 Tactical stores, and Bass Pro Shops. BRCC has produced a number of sometimes controversial social me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
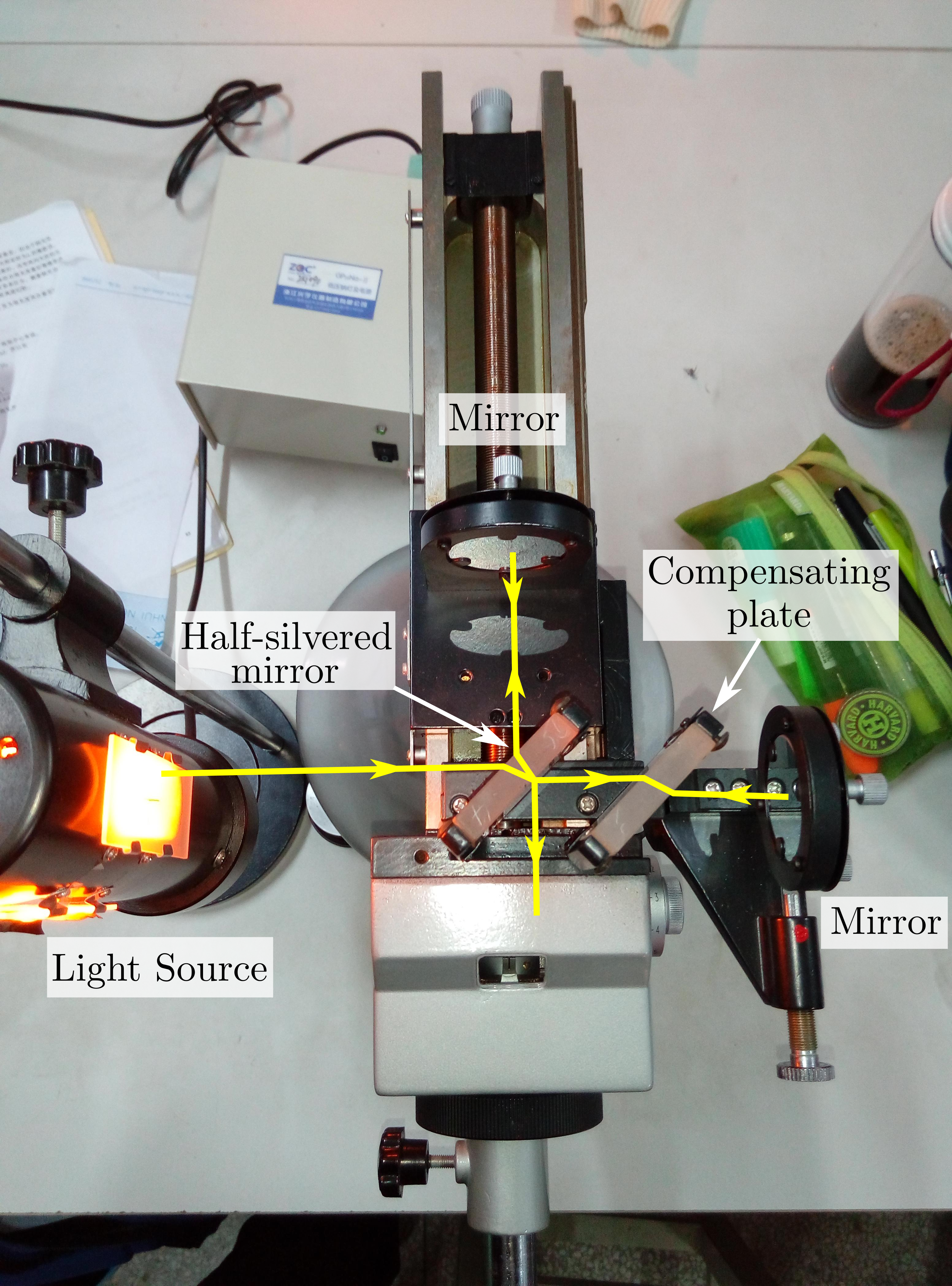
Michelson Interferometer
The Michelson interferometer is a common configuration for optical interferometry and was invented by the 19/20th-century American physicist Albert Abraham Michelson. Using a beam splitter, a light source is split into two arms. Each of those light beams is reflected back toward the beamsplitter which then combines their amplitudes using the superposition principle. The resulting interference pattern that is not directed back toward the source is typically directed to some type of photoelectric detector or camera. For different applications of the interferometer, the two light paths can be with different lengths or incorporate optical elements or even materials under test. The Michelson interferometer (among other interferometer configurations) is employed in many scientific experiments and became well known for its use by Michelson and Edward Morley in the famous Michelson–Morley experiment (1887) in a configuration which would have detected the Earth's motion through the sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Propulsion Physics Laboratory
The Advanced Propulsion Physics Laboratory or "Eagleworks Laboratories" at NASA's Johnson Space Center is a small research group investigating a variety of theories regarding new forms of spacecraft propulsion. The principal investigator is Dr. Harold G. White. The group is developing the White–Juday warp-field interferometer in the hope of observing small disturbances of spacetime and also testing small prototypes of thrusters that do not use reaction mass, with currently inconclusive results. The proposed principle of operation of these quantum vacuum plasma thrusters, such as the RF resonant cavity thruster ('EM Drive'), has been shown to be inconsistent with known laws of physics, including conservation of momentum and conservation of energy. No plausible theory of operation for such drives has been proposed. Purpose The Advanced Propulsion Physics Laboratory is enabled by section 2.3.7 of the NASA Technology Roadmap TA 2: In Space Propulsion Technologies: The lab' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferometer
Interferometry is a technique which uses the ''interference'' of superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy (and its applications to chemistry), quantum mechanics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, remote sensing, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, velocimetry, optometry, and making holograms. Interferometers are devices that extract information from interference. They are widely used in science and industry for the measurement of microscopic displacements, refractive index changes and surface irregularities. In the case with most interferometers, light from a single source is split into two beams that travel in different optical paths, which are then combined again to produce in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and one of the most prestigious and highly ranked universities in the world. The university is composed of ten academic faculties plus Harvard Radcliffe Institute. The Faculty of Arts and Sciences offers study in a wide range of undergraduate and graduate academic disciplines, and other faculties offer only graduate degrees, including professional degrees. Harvard has three main campuses: the Cambridge campus centered on Harvard Yard; an adjoining campus immediately across Charles River in the Allston neighborhood of Boston; and the medical campus in Boston's Longwood Medical Area. Harvard's endowment is valued at $50.9 billion, making it the wealthiest academic institution in the world. Endowment inco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)