|
Harnes
Harnes () is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Hauts-de-France region of France. Geography Harnes is an ex-coalmining and light industrial town situated some northeast of Lens, at the junction of the D162e and the D39. The Lens canal forms much of the southern border of the town and the A21 autoroute passes by a few yards from the canal. History First recorded as Hamas, the town was known as Harnis until, in the 12th century, when its present spelling was used. It’s possible that the name comes from the Flemish "Hearn" meaning “Marsh”. The town was settled during the Gallo-Roman period, as archaeological finds have proved. In the municipal museum of Harnes, one can see the "treasure of Harnes": Coins, building materials, urns, vases, spears, iron objects and bones as well as some Samian ware (red glazed pottery) decorated with eagles, lions, sphinxes etc. In 1304, Harnes was looted and burned by the Flemish. Under the Counts of Burgundy, from 1384 to 14 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communauté D'agglomération De Lens – Liévin
The Communauté d'agglomération de Lens – Liévin is the ''communauté d'agglomération'', an intercommunal structure, centred on the cities of Lens and Liévin. It is located in the Pas-de-Calais department, in the Hauts-de-France region, northern France. It was created in January 2000.CA de Lens - Liévin (N° SIREN : 246200364) BANATIC, accessed 6 April 2022. It adopted the name Communaupole on June 25, 2004. Its area is 239.4 km2. Its population was 241,703 in 2018, of which 31,606 in Lens and 30,423 in Liévin.Comparateur de territoire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loanhead
Loanhead is a town in Midlothian, Scotland, in a commuter belt to the south of Edinburgh, and close to Roslin, Bonnyrigg and Dalkeith. The town was built on coal and oil shale mining, and the paper industries. History Loanhead was a tiny village by about 1599, when it was included on a map of the Lothians. It was granted a charter allowing a weekly market and annual fair in 1669. Coal was mined profitably in the area for Sir John Clerk of Penicuik by 1685. The Springfield paper mill, in the valley of the River North Esk to the south of the town, commenced in 1742, while Polton mill followed in 1750. By 1754 Loanhead was a medium-sized settlement. The limestone industry was a source of employment by the late eighteenth century, the works being at Burdiehouse, about a mile to the northwest. The coal industry continued to expand and by 1874 the town was linked to the railway. Shale was mined between Loanhead and Burdiehouse in the late nineteenth century, from 1880 under the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of France
The () is a level of administrative division in the French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipalities in the United States and Canada, ' in Germany, ' in Italy, or ' in Spain. The United Kingdom's equivalent are civil parishes, although some areas, particularly urban areas, are unparished. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the municipal arrondi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falkenstein, Saxony
Falkenstein is a town in the Vogtlandkreis district, in Saxony, Germany. It is situated 4 km southwest of Auerbach, and 17 km east of Plauen. Population Development Historical Population (ab 31 December 1960): : Datasource: Statistisches Landesamt Sachsen Sons and daughters of the city * Otto Lindner (1893–1983), writer * Gottfried Weimann (1907–1990), javelin thrower * Helmut Rauca (1908–1983), perpetrator of the Holocaust, born in the district of Trieb * Wolfgang Männel (1937–2006), economist * Ulrich Eisenfeld (born 1939), painter * Bernd Eisenfeld Bernd Eisenfeld (9 January 1941 – 12 June 2010), also known by the pseudonym Fred Werner, was an opponent of the East German dictatorship who became a writer and an historian. Early years Bernd Eisenfeld and his twin brother Peter were born i ... (1941–2010), historian and GDR opposition leader * Gabriele Eckart (born 1954), writer References Vogtlandkreis {{Vogtlandkreis-geo-st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gmina Chrzanów, Lesser Poland Voivodeship
Gmina Chrzanów is an urban-rural gmina (administrative district) in Chrzanów County, Lesser Poland Voivodeship, in southern Poland. Its seat is the town of Chrzanów, which lies approximately west of the regional capital Kraków. Overview The gmina covers an area of , and as of 2006 its total population is 49,752 (out of which the population of Chrzanów amounts to 39,797, and the population of the rural part of the gmina is 9,955). The gmina contains part of the protected area called Tenczynek Landscape Park. Villages Apart from the town of Chrzanów, Gmina Chrzanów contains the villages and settlements of Balin, Luszowice, Płaza and Pogorzyce. Neighbouring gminas Gmina Chrzanów is bordered by the city of Jaworzno and by the gminas of Alwernia, Babice, Libiąż and Trzebinia Trzebinia (; yi, טשעבין ''Tchebin'') is a town in Chrzanów County, Lesser Poland, Poland with an Orlen oil refinery and a major rail junction of the Kraków - Katowice line, with co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within city limits,Barcelona: Población por municipios y sexo – Instituto Nacional de Estadística. (National Statistics Institute) its urban area extends to numerous neighbouring municipalities within the and is home to around 4.8 million people, making it the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Turbine
A wind turbine is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind into electrical energy. Hundreds of thousands of large turbines, in installations known as wind farms, now generate over 650 gigawatts of power, with 60 GW added each year. Wind turbines are an increasingly important source of intermittent renewable energy, and are used in many countries to lower energy costs and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. One study claimed that, wind had the "lowest relative greenhouse gas emissions, the least water consumption demands and the most favorable social impacts" compared to photovoltaic, hydro, geothermal, coal and gas energy sources. Smaller wind turbines are used for applications such as battery charging for auxiliary power for boats or caravans, and to power traffic warning signs. Larger turbines can contribute to a domestic power supply while selling unused power back to the utility supplier via the electrical grid. Wind turbines are manufactured in a wide range of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
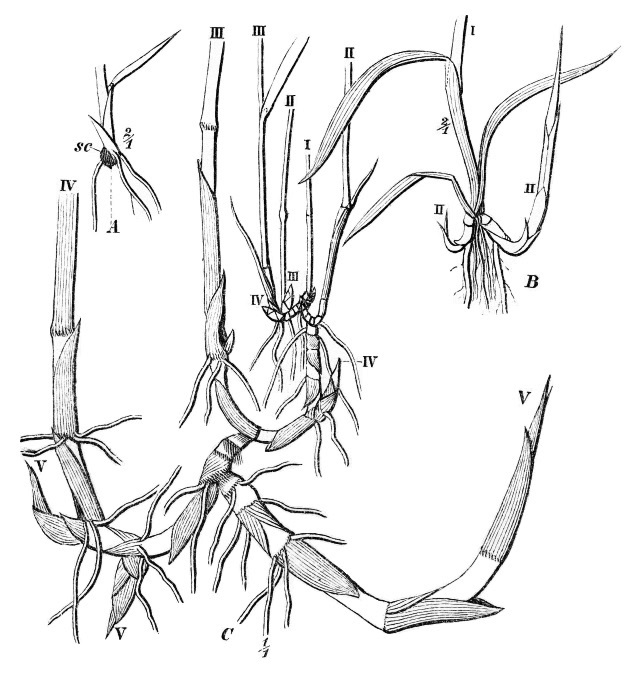
Schoenoplectus
''Schoenoplectus'' (club-rush ld World species bulrush or tule ew World species is a genus of plants in the sedges with a cosmopolitan distribution. Note that the name bulrush is also applied to species in the unrelated genus ''Typha'' as well as to other sedges. The genus ''Schoenoplectus'' was formerly considered part of ''Scirpus'', but recent phylogenetic data shows that they are not closely related. Species Species accepted: *''Schoenoplectus acutus'' ( Muhl. ex J.M.Bigelow) Á.Löve & D.Löve – Tule – Canada, much of the United States; northern and central Mexico as far south as Michoacán; Clipperton Island. *''Schoenoplectus americanus'' (Pers.) Volkart ex Schinz & R. Keller – Chairmaker's bulrush, Olney's bulrush – Much of Western Hemisphere from Alaska to Argentina including West Indies; also New Zealand *''Schoenoplectus annamicus'' (Raymond) T.Koyama – Vietnam *''Schoenoplectus californicus'' ( C.A.Mey.) Steud. – California bulrush, giant bulrush ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iris (plant)
''Iris'' is a flowering plant genus of 310 accepted species with showy flowers. As well as being the scientific name, ''iris'' is also widely used as a common name for all ''Iris'' species, as well as some belonging to other closely related genera. A common name for some species is 'flags', while the plants of the subgenus '' Scorpiris'' are widely known as 'junos', particularly in horticulture. It is a popular garden flower. The often-segregated, monotypic genera '' Belamcanda'' (blackberry lily, ''I. domestica''), '' Hermodactylus'' (snake's head iris, ''I. tuberosa''), and ''Pardanthopsis'' (vesper iris, '' I. dichotoma'') are currently included in ''Iris''. Three Iris varieties are used in the Iris flower data set outlined by Ronald Fisher in his 1936 paper ''The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems'' as an example of linear discriminant analysis. Description Irises are perennial plants, growing from creeping rhizomes (rhizomatous irises) or, in drier cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phragmites
''Phragmites'' () is a genus of four species of large perennial reed grasses found in wetlands throughout temperate and tropical regions of the world. Taxonomy The World Checklist of Selected Plant Families, maintained by Kew Garden in London, accepts the following four species: * ''Phragmites australis'' ( Cav.) Trin. ex Steud. – cosmopolitan * ''Phragmites japonicus'' Steud. – Japan, Korea, Ryukyu Islands, Russian Far East * ''Phragmites karka'' ( Retz.) Trin. ex Steud. – tropical Africa, southern Asia, Australia, some Pacific Islands, invasive in New Zealand * ''Phragmites mauritianus'' Kunth – central + southern Africa, Madagascar, Mauritius The cosmopolitan common reed has the generally accepted botanical name ''Phragmites australis''. (Cav.) Trin. ex Steud. About 130 other synonyms have been proposed. Examples include ''Phragmites communis'' Trin., ''Arundo phragmites'' L., and ''Phragmites vulgaris'' (Lam.) Crép. (illegitimate name). Wildlife in reed beds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
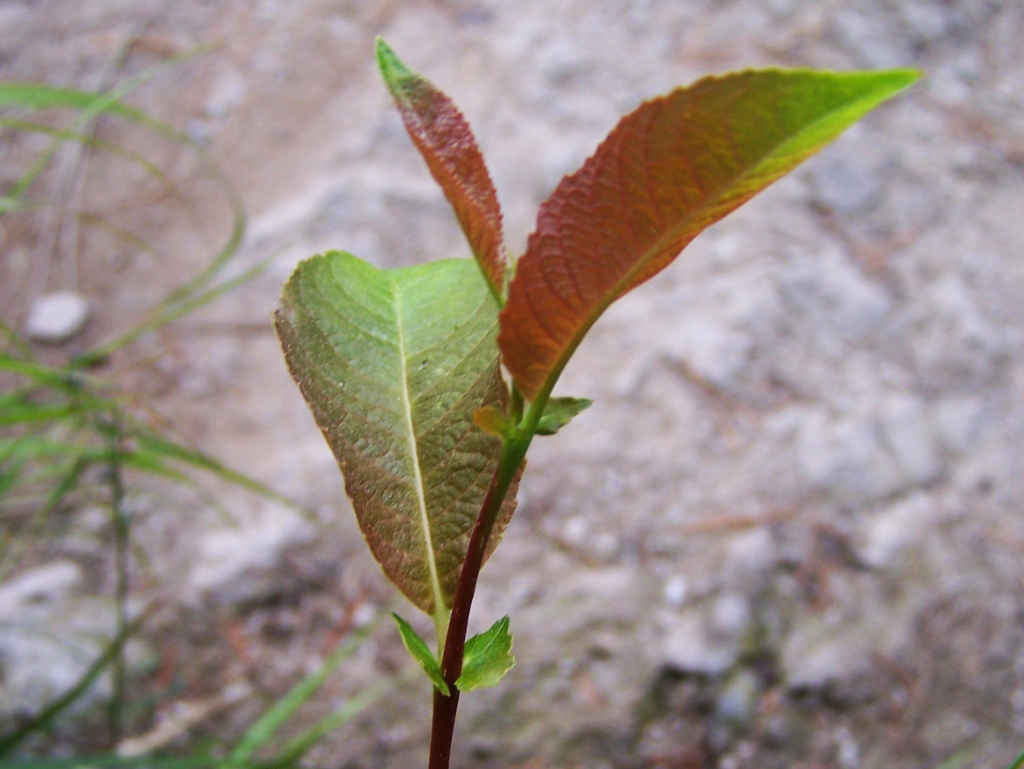
Willow
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, from the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 400 speciesMabberley, D.J. 1997. The Plant Book, Cambridge University Press #2: Cambridge. of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist soils in cold and temperate regions. Most species are known as willow, but some narrow-leaved shrub species are called osier, and some broader-leaved species are referred to as sallow (from Old English ''sealh'', related to the Latin word ''salix'', willow). Some willows (particularly arctic and alpine species) are low-growing or creeping shrubs; for example, the dwarf willow (''Salix herbacea'') rarely exceeds in height, though it spreads widely across the ground. Description Willows all have abundant watery bark sap, which is heavily charged with salicylic acid, soft, usually pliant, tough wood, slender branches, and large, fibrous, often stoloniferous roots. The roots are remarkable for their toughness, size, and tenacity to live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coppice
Coppicing is a traditional method of woodland management which exploits the capacity of many species of trees to put out new shoots from their stump or roots if cut down. In a coppiced wood, which is called a copse, young tree stems are repeatedly cut down to near ground level, resulting in a stool. New growth emerges, and after a number of years, the coppiced tree is harvested, and the cycle begins anew. Pollarding is a similar process carried out at a higher level on the tree in order to prevent grazing animals from eating new shoots. ''Daisugi'' (台杉, where ''sugi'' refers to Japanese cedar), is a similar Japanese technique. Many silviculture practices involve cutting and regrowth; coppicing has been of significance in many parts of lowland temperate Europe. The widespread and long-term practice of coppicing as a landscape-scale industry is something that remains of special importance in southern England. Many of the English language terms referenced in this article are pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)