|
Happy Path
In the context of software or information modeling, a happy path (sometimes called happy flow) is a default scenario featuring no exceptional or error conditions. For example, the happy path for a function validating credit card numbers would be where none of the validation rules raise an error, thus letting execution continue successfully to the end, generating a positive response. Process steps for a happy path are also used in the context of a use case. In contrast to the happy path, process steps for alternate flow and exception flow may also be documented. Happy path test is a well-defined test case using known input, which executes without exception and produces an expected output. Happy path testing can show that a system meets its functional requirements but it doesn't guarantee a graceful handling of error conditions or aid in finding hidden bugs. Happy day (or sunny day) scenario and golden path are slang synonyms for happy path. In use case analysis, there is only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Scenario (computing)
In computing, a scenario (, ; loaned (), ) is a narrative of foreseeable interactions of user roles (known in the Unified Modeling Language as 'actors') and the technical system, which usually includes computer hardware and software. A scenario has a goal, which is usually functional. A scenario describes one way that a system is used, or is envisaged to be used, in the context of an activity in a defined time-frame. The time-frame for a scenario could be (for example) a single transaction; a business operation; a day or other period; or the whole operational life of a system. Similarly the scope of a scenario could be (for example) a single system or a piece of equipment; an equipped team or a department; or an entire organization. Scenarios are frequently used as part of the system development process. They are typically produced by usability or marketing specialists, often working in concert with end users and developers. Scenarios are written in plain language, with mini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Exception Handling
In computing and computer programming, exception handling is the process of responding to the occurrence of ''exceptions'' – anomalous or exceptional conditions requiring special processing – during the execution of a program. In general, an exception breaks the normal flow of execution and executes a pre-registered ''exception handler''; the details of how this is done depend on whether it is a hardware or software exception and how the software exception is implemented. Exceptions are defined by different layers of a computer system, and the typical layers are CPU-defined interrupts, operating system (OS)-defined signals, programming language-defined exceptions. Each layer requires different ways of exception handling although they may be interrelated, e.g. a CPU interrupt could be turned into an OS signal. Some exceptions, especially hardware ones, may be handled so gracefully that execution can resume where it was interrupted. Definition The definition of an excep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Validation Rule
Validation may refer to: * Data validation, in computer science, ensuring that data inserted into an application satisfies defined formats and other input criteria * Emotional validation, in interpersonal communication is the recognition, the affirmation, the acceptance of the existence of expressed emotions, and the communication, the acknowledgement, of this recognition with the emoter(s) (the one(s) who express the emotions). * Forecast verification, validating and verifying prognostic output from a numerical model * Regression validation, in statistics, determining whether the outputs of a regression model are adequate * Social validation, compliance in a social activity to fit in and be part of the majority * Statistical model validation, determining whether the outputs of a statistical model are acceptable * Validation (drug manufacture), documenting that a process or system meets its predetermined specifications and quality attributes * Validation (gang membership), a fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Use Case
In both software and systems engineering, a use case is a structured description of a system’s behavior as it responds to requests from external actors, aiming to achieve a specific goal. It is used to define and validate functional requirements A use case is a list of actions or event steps typically defining the interactions between a role (known in the Unified Modeling Language (UML) as an ''actor'') and a system to achieve a goal. The actor can be a human or another external system. In systems engineering, use cases are used at a higher level than within software engineering, often representing missions or stakeholder goals. The detailed requirements may then be captured in the Systems Modeling Language (SysML) or as contractual statements. Differences between Systems and Software Engineering Use Cases In software engineering, the use case defines potential scenarios of the software in response to an external request (such as user input). In systems engineering, a use c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Test Case
In software engineering, a test case is a specification of the inputs, execution conditions, testing procedure, and expected results that define a single test to be executed to achieve a particular software testing objective, such as to exercise a particular program path or to verify compliance with a specific requirement. Test cases underlie testing that is methodical rather than haphazard. A battery of test cases can be built to produce the desired coverage of the software being tested. Formally defined test cases allow the same tests to be run repeatedly against successive versions of the software, allowing for effective and consistent regression testing. Formal test cases In order to fully test that all the requirements of an application are met, there must be at least two test cases for each requirement: one positive test and one negative test. If a requirement has sub-requirements, each sub-requirement must have at least two test cases. Keeping track of the link between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Functional Requirement
In software engineering and systems engineering, a functional requirement defines a function of a system or its component, where a function is described as a summary (or specification or statement) of behavior between inputs and outputs. Functional requirements may involve calculations, technical details, data manipulation and processing, and other specific functionality that define what a system is supposed to accomplish. Behavioral requirements describe all the cases where the system uses the functional requirements, these are captured in use cases. Functional requirements are supported by non-functional requirements (also known as "quality requirements"), which impose constraints on the design or implementation (such as performance requirements, security, or reliability). Generally, functional requirements are expressed in the form "system must do ," while non-functional requirements take the form "system shall be ." The plan for implementing functional requirements is detailed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Software Bug
A software bug is a design defect ( bug) in computer software. A computer program with many or serious bugs may be described as ''buggy''. The effects of a software bug range from minor (such as a misspelled word in the user interface) to severe (such as frequent crashing). In 2002, a study commissioned by the US Department of Commerce's National Institute of Standards and Technology concluded that "software bugs, or errors, are so prevalent and so detrimental that they cost the US economy an estimated $59 billion annually, or about 0.6 percent of the gross domestic product". Since the 1950s, some computer systems have been designed to detect or auto-correct various software errors during operations. History Terminology ''Mistake metamorphism'' (from Greek ''meta'' = "change", ''morph'' = "form") refers to the evolution of a defect in the final stage of software deployment. Transformation of a ''mistake'' committed by an analyst in the early stages of the softw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
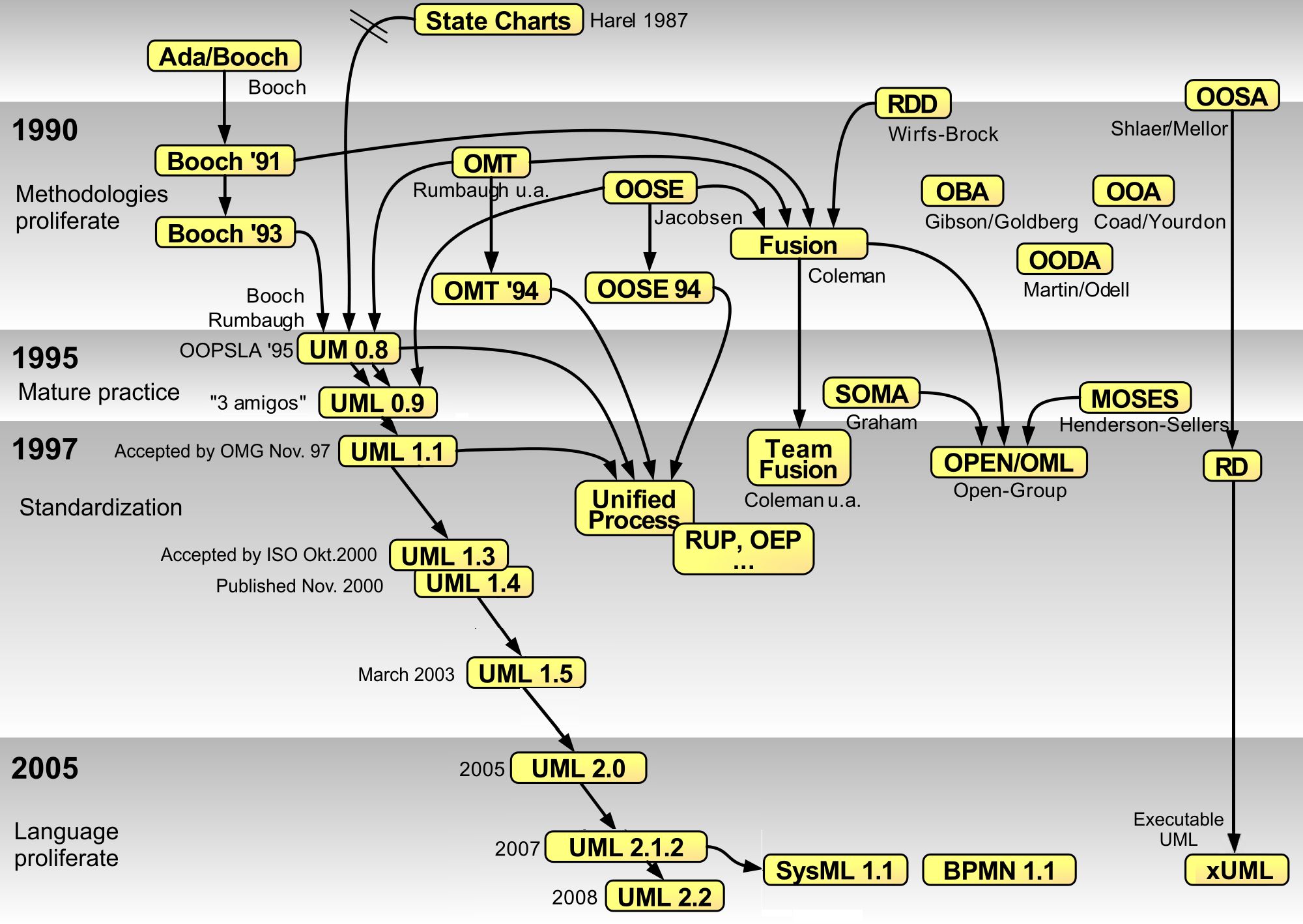
Unified Modeling Language
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose visual modeling language that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system. UML provides a standard notation for many types of diagrams which can be roughly divided into three main groups: behavior diagrams, interaction diagrams, and structure diagrams. The creation of UML was originally motivated by the desire to standardize the disparate notational systems and approaches to software design. It was developed at Rational Software in 1994–1995, with further development led by them through 1996. In 1997, UML was adopted as a standard by the Object Management Group (OMG) and has been managed by this organization ever since. In 2005, UML was also published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as the ISO/IEC 19501 standard. Since then the standard has been periodically revised to cover the latest revision of UML. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Edge Case
An edge case is a problem or situation that occurs only at an extreme (maximum or minimum) operating parameter. For example, a stereo speaker might noticeably distort audio when played at maximum volume, even in the absence of any other extreme setting or condition. An edge case can be expected or unexpected. In engineering, the process of planning for and gracefully addressing edge cases can be a significant task, and yet this task may be overlooked or underestimated. Some common causes of edge cases are: * Unpredictable user behavior * Evolution of use cases (e.g. user behavior may change over time) * Limited test coverage * Product complexity (for instance, in distributed systems or microservice architectures) * Resource limitations (e.g. limited processing power, computer memory, or computer storage) * Other external causes Some basic examples of edge cases include: * A long username in an app overflows and displays incorrectly * A booking system does not handle reservati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Corner Case
In engineering, a corner case (or pathological case) involves a problem or situation that occurs only outside normal operating parameters—specifically one that manifests itself when multiple environmental variables or conditions are simultaneously at extreme levels, even though each parameter is within the specified range for that parameter. For example, a loudspeaker might distort audio, but only when played at maximum volume, maximum bass, and in a high-humidity environment. Or a computer server may be unreliable, but only with the maximum complement of 64 processors, 512 GB of memory, and 10,000 signed-on users. The investigation of corner cases is of extreme importance as it can provide engineers with valuable insight into how corner case effects can be mitigated. In the case where automotive radar fails, corner case investigation can possibly tell engineers and investigators alike what may have occurred. Corner cases form part of an engineer's lexicon—especially an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Use Case
In both software and systems engineering, a use case is a structured description of a system’s behavior as it responds to requests from external actors, aiming to achieve a specific goal. It is used to define and validate functional requirements A use case is a list of actions or event steps typically defining the interactions between a role (known in the Unified Modeling Language (UML) as an ''actor'') and a system to achieve a goal. The actor can be a human or another external system. In systems engineering, use cases are used at a higher level than within software engineering, often representing missions or stakeholder goals. The detailed requirements may then be captured in the Systems Modeling Language (SysML) or as contractual statements. Differences between Systems and Software Engineering Use Cases In software engineering, the use case defines potential scenarios of the software in response to an external request (such as user input). In systems engineering, a use c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |