|
Haplogroup E1b (Y-DNA)
In human population genetics, haplogroups define the major lineages of direct paternal (male) lines back to a shared common ancestor in Africa. Haplogroup E-P177, has 2 known branches, E-P2, which is the most common, and E-P75. Distribution The Americas E-P177 was not present in the Americas before European colonization. Subclade distribution E-P177* So far there are no attested exemplars of E-M177*. E-P2 The E-P177 lineage is dominated in modern populations by subclade E-P2 (aka E-PN2), which is by far the most frequent. E-P75 Another subclade, E-P75, was announced in and confirmed as a sibling to E-P177 in . Associated SNPs E-P177 is defined by the P177 SNP alone. Phylogenetics Phylogenetic history Prior to 2002, there were in academic literature at least seven naming systems for the Y-Chromosome Phylogenetic tree. This led to considerable confusion. In 2002, the major research groups came together and formed the Y-Chromosome Consortium (YCC). They publish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup E-P147 (Y-DNA)
In human genetics, Haplogroup E-P147 is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. Haplogroup E-P147, along with the less common Haplogroup E-M75, is one of the two main branches of the older Haplogroup E-M96. The E-P147 clade is commonly observed throughout Africa and is divided into two subclades: the less common E-M33 & the more common E-P177. Origin Distribution The Polymorphism P147 was first discovered in 2008 and contains the vast majority of men who belong to E-M96. The two branches of this lineage have different distributions, while the less common branch, E-M33, has more of a West African distribution, the more common branch, E-P177, can be found widely distributed with high frequency throughout Africa and to a lesser extent in the Middle East and Europe Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup E-M81 (Y-DNA)
E-Z827, also known as E1b1b1b, is a major human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is the parent lineage to the E-Z830 and E-L19 subclades, and defines their common phylogeny. The former is predominantly found in the Middle East; the latter is most frequently observed in North Africa. E-Z827 is also found at lower frequencies in Europe, and in isolated parts of Southeast Africa. Subclades of E-Z827 and Distribution Family Tree The following phylogeny is based on the YCC 2008 tree and subsequent published research as summarized by ISOGG. *E-Z827 (Z827) - E1b1b1bISOGG 2015 **E-V257/L19 (L19, V257) - E1b1b1b1 ***E-PF2431 (PF2431) ****E-PF2438 *****E-Y10561 ******E-FGC18981 *******E-FGC38527 *******E-Y35933 *******E-FGC18960 ********E-Y33020 ********E-FGC18958 *****E-PF2440 ******E-PF2471 *******E-BY9805 ***E-M81 (M81) ****E-M81* ****E-PF2546 *****E-PF2546* *****E-CTS12227 ******E-MZ11 *******E-MZ12 *****E-A929 ******E-Z5009 *******E-Z5009* *******E-Z5010 *******E-Z5013 ********E-Z5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Genealogy
Genetic genealogy is the use of genealogical DNA tests, i.e., DNA profiling and DNA testing, in combination with traditional genealogical methods, to infer genetic relationships between individuals. This application of genetics came to be used by family historians in the 21st century, as DNA tests became affordable. The tests have been promoted by amateur groups, such as surname study groups or regional genealogical groups, as well as research projects such as the Genographic Project. As of 2019, about 30 million people had been tested. As the field developed, the aims of practitioners broadened, with many seeking knowledge of their ancestry beyond the recent centuries, for which traditional pedigrees can be constructed. History The investigation of surnames in genetics can be said to go back to George Darwin, a son of Charles Darwin and Charles' first cousin Emma Darwin. In 1875, George Darwin used surnames to estimate the frequency of first-cousin marriages and calculated t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
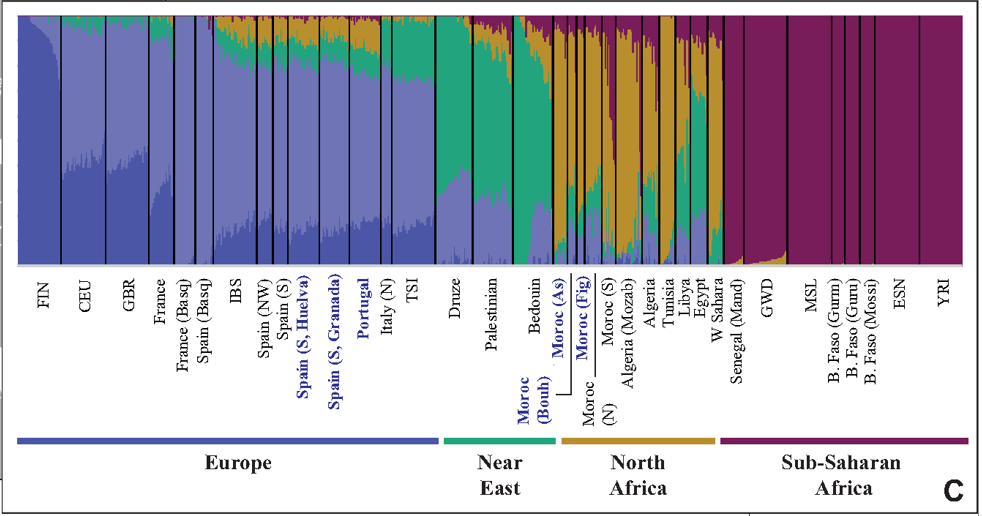
African Admixture In Europe
African admixture in Europe refers to the presence of human genotypes attributable to periods of human population dispersals out of Africa in the genetic history of Europe. for example, certain Y-DNA and mtDNA lineages are thought to have spread from Northeastern Africa to the Near East during the later Pleistocene, and from there to Europe with the Neolithic Revolution. More recent African admixtureprimarily Berber admixture from North Africais associated with historic migrations through the Mediterranean Sea and the Muslim conquests of the Early Middle Ages. This admixture can be found primarily in western-southern Iberian peninsula and Southern Italy and the main islands, with the highest incidence being in Sicily. Neolithic The change from hunting and gathering to agriculture during the Neolithic Revolution was a watershed in world history. The societies that first made the change to agriculture are believed to have lived in the Middle East around 10,000 BCE. Agriculture was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
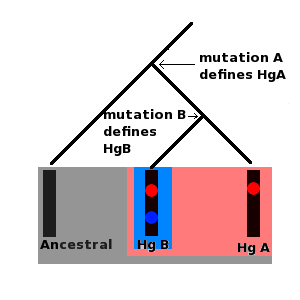
Subclade
In genetics, a subclade is a subgroup of a haplogroup. Naming convention Although human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and Y chromosome DNA (Y-DNA) haplogroups and subclades are named in a similar manner, their names belong to completely separate systems. mtDNA mtDNA haplogroups are defined by the presence of a series of single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers in the hypervariable regions and the coding region of mitochondrial DNA. They are named with the capital letters A through Z, with further subclades named using numbers and lower case letters. Y-DNA Y-DNA haplogroups are defined by the presence of a series of SNP markers on the Y chromosome. Subclades are defined by a ''terminal SNP'', the SNP furthest down in the Y chromosome phylogenetic tree. Human Y-DNA The Y Chromosome Consortium (YCC) developed a system of naming major human Y-DNA haplogroups with the capital letters A through T, with further subclades named using numbers and lower case letters (YCC longhand nomenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup E-M329 (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup E-M329, also known as E1b1a2, is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. E-M329 is mostly found in East Africa. Origin Trombetta et al. (2011) suggested an origin in East Africa: The new topology here reported has important implications as to the origins of the haplogroup E-P2. Using the principle of the phylogeographic parsimony, the resolution of the E-M215 trifurcation in favor of a common ancestor of E-M2 and E-M329 strongly supports the hypothesis that haplogroup E-P2 originated in eastern Africa, as previously suggested, and that chromosomes E-M2, so frequently observed in sub-Saharan Africa, trace their descent to a common ancestor present in eastern Africa. Distribution E-M329 is mostly found in East Africa. E-M329 is frequent in Southwestern Ethiopia, especially among Omotic-speaking populations. Semino et al. (2004) found 2 cases of E-M329 in Ethiopian Oromo, out of 2400 individuals, including 78 Oromo. Cadenas et al. (2007) found one case of E-M329, out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup E-M215 (Y-DNA)
E-M215, also known as E1b1b and formerly E3b, is a major human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is a division of the macro-haplogroup E-M96, which is defined by the single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) mutation M215. In other words, it is one of the major patrilineality, patrilineages of humanity, linking from father-to-son back to a common male-line ancestor ("Y-chromosomal Adam"). It is a subject of discussion and study in genetics as well as genetic genealogy, archaeology, and historical linguistics. The E-M215 haplogroup has two ancient branches that contain all the known modern E-M215, E-M35 and E-M281 subclades. Of the latter two E-M215 subhaplogroups, the only branch that has been confirmed in a native population outside of Ethiopia is E-M35. E-M35 in turn has two known branches, Haplogroup E-V68, E-V68 and Haplogroup E-Z827, E-Z827, which contain by far the majority of all modern E-M215 subclade bearers. The E-V257 and E-V68 subclades each respectively their highest freque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup E-V38 (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup E-V38 is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is primarily distributed in Sub Saharan Africa. E-V38 has two basal branches, E-M329 (formerly E1b1c or E1b1*) and E-M2 (formerly E3a & E1b1a). The E-M329 subclade is today almost exclusively found in Ethiopia. E-M2 is the predominant subclade in Western Africa, Central Africa, Southern Africa and the region of African Great Lakes, and occurs at only moderate frequencies in some parts of North Africa, West Asia and Southern Europe. Origins The discovery of two SNPs (V38 and V100) by Trombetta et al. (2011) significantly redefined the E-V38 phylogenetic tree. This led the authors to suggest that E-V38 may have originated in East Africa. V38 joins the West African-affiliated E-M2 and the northern East African-affiliated E-M329 with an earlier common ancestor who, like E-P2, may have also originated in East Africa. The downstreams SNP E-M180 may have originated on the moist south-central Saharan savannah/grassland of North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amateur
An amateur () is generally considered a person who pursues an avocation independent from their source of income. Amateurs and their pursuits are also described as popular, informal, autodidacticism, self-taught, user-generated, do it yourself, DIY, and hobbyist. History Historically, the amateur was considered to be the ideal balance between pure intent, open mind, and the interest or passion for a subject. That ideology spanned many different fields of interest. It may have its roots in the ancient Greek philosophy of Amateur sports, amateur athletes competing in the Olympic Games, Olympics. The ancient Greek citizens spent most of their time in other pursuits, but competed according to their natural talents and abilities. The "gentleman amateur" was a phenomenon among the gentry of United Kingdom, Great Britain from the 17th century until the 20th century. With the start of the Age of Enlightenment, Age of Reason, with people thinking more about how the world works around th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houston, Texas
Houston (; ) is the most populous city in Texas, the most populous city in the Southern United States, the fourth-most populous city in the United States, and the sixth-most populous city in North America, with a population of 2,304,580 in 2020. Located in Southeast Texas near Galveston Bay and the Gulf of Mexico, it is the seat and largest city of Harris County and the principal city of the Greater Houston metropolitan area, which is the fifth-most populous metropolitan statistical area in the United States and the second-most populous in Texas after Dallas–Fort Worth. Houston is the southeast anchor of the greater megaregion known as the Texas Triangle. Comprising a land area of , Houston is the ninth-most expansive city in the United States (including consolidated city-counties). It is the largest city in the United States by total area whose government is not consolidated with a county, parish, or borough. Though primarily in Harris County, small portions of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup E-M136 (Y-DNA)
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup (haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a single-nucleotide polymorphism mutation. More specifically, a haplogroup is a combination of alleles at different chromosomal regions that are closely linked and that tend to be inherited together. As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup (or paragroup). As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a nested hierarchy, in which each set (hapl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup E-M34 (Y-DNA)
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup (haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a single-nucleotide polymorphism mutation. More specifically, a haplogroup is a combination of alleles at different chromosomal regions that are closely linked and that tend to be inherited together. As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup (or paragroup). As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a nested hierarchy, in which each set (hapl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |