|
Hammerstone Corporation
In archaeology, a hammerstone is a hard cobble used to strike off lithic flakes from a lump of tool stone during the process of lithic reduction. The hammerstone is a rather universal stone tool which appeared early in most regions of the world including Europe, India and North America. This technology was of major importance to prehistoric cultures before the age of metalworking. Materials A hammerstone is made of a material such as sandstone, limestone or quartzite, is often ovoid in shape (to fit the human hand better), and develops telltale battering marks on one or both ends. In archaeological recovery, hammerstones are often found in association with other stone tool artifacts, debitage and/or objects of the hammer such as ore. The modern use of hammerstones is now mostly limited to flintknappers and others who wish to develop a better understanding of how stone tools were made. Usage Hammerstones are or were used to produce flakes and hand axes as wel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flintknapper
Knapping is the shaping of flint, chert, obsidian, or other conchoidal fracturing stone through the process of lithic reduction to manufacture stone tools, strikers for flintlock firearms, or to produce flat-faced stones for building or facing walls, and flushwork decoration. The original Germanic term ''knopp'' meant to strike, shape, or work, so it could theoretically have referred equally well to making statues or dice. Modern usage is more specific, referring almost exclusively to the hand-tool pressure-flaking process pictured. It is distinguished from the more general verb "chip" (to break up into small pieces, or unintentionally break off a piece of something) and is different from "carve" (removing only part of a face), and "cleave" (breaking along a natural plane). Method Flintknapping or knapping is done in a variety of ways depending on the purpose of the final product. For stone tools and flintlock strikers, chert is worked using a fabricator such as a hamme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcolithic
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper" and ''líthos'', "stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin '' aeneus'' "of copper"), is an archaeological period characterized by regular human manipulation of copper, but prior to the discovery of bronze alloys. Modern researchers consider the period as a subset of the broader Neolithic, but earlier scholars defined it as a transitional period between the Neolithic and the Bronze Age. The archaeological site of Belovode, on Rudnik mountain in Serbia, has the world's oldest securely dated evidence of copper smelting at high temperature, from (7000 BP). The transition from Copper Age to Bronze Age in Europe occurred between the late 5th and the late In the Ancient Near East the Copper Age covered about the same period, beginning in the late and lasting for about a millennium before it gave rise to the Early Bronze Age. Terminology The multiple names result from m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malachite
Malachite is a copper carbonate hydroxide mineral, with the formula Cu2CO3(OH)2. This opaque, green-banded mineral crystallizes in the monoclinic crystal system, and most often forms botryoidal, fibrous, or stalagmitic masses, in fractures and deep, underground spaces, where the water table and hydrothermal fluids provide the means for chemical precipitation. Individual crystals are rare, but occur as slender to acicular prisms. Pseudomorphs after more tabular or blocky azurite crystals also occur. Etymology and history The stone's name derives (via la, molochītis, frm, melochite, and Middle English ''melochites'') from Greek Μολοχίτης λίθος ''molochites lithos'', "mallow-green stone", from μολόχη ''molochē'', variant of μαλάχη ''malāchē'', "mallow". The mineral was given this name due to its resemblance to the leaves of the mallow plant. Malachite was mined from deposits near the Isthmus of Suez and the Sinai as early as 4000 BCE. It wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
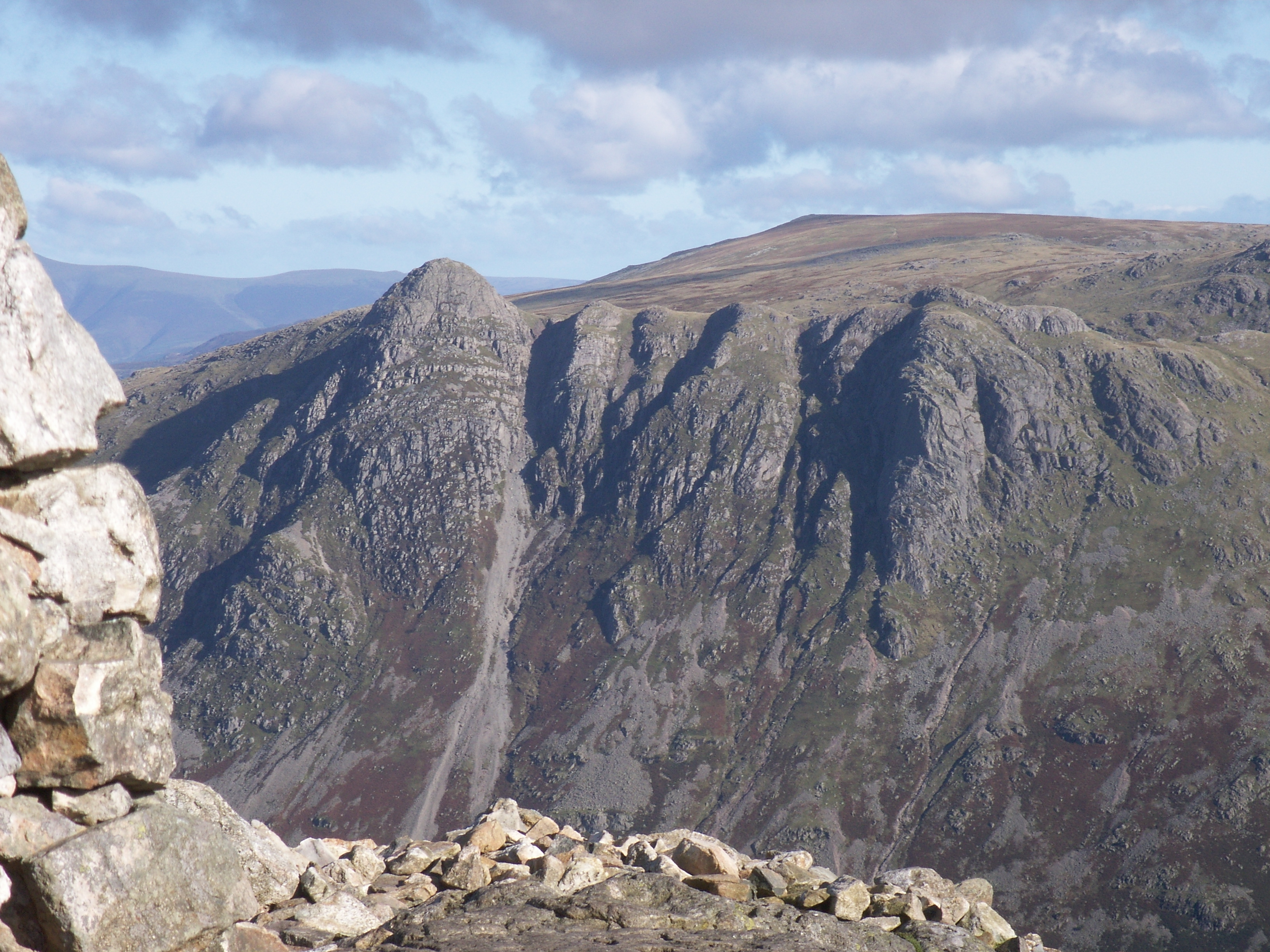
Langdale Axe Industry
The Langdale axe industry (or factory) is the name given by archaeologists to a Neolithic centre of specialised stone tool production in the Great Langdale area of the English Lake District. (For accompanying material seSupplement 1of same volume). The existence of the site, which dates from around 4,000–3,500 BC, was suggested by chance discoveries in the 1930s. More systematic investigations were undertaken by Clare Fell and others in the 1940s and 1950s, since when several field surveys of varying scope have been carried out. Typical finds include reject axes, rough-outs and blades created by knapping large lumps of the rock found in the scree or perhaps by simple quarrying or opencast mining. Hammerstones have also been found in the scree and other lithic debitage from the industry such as blades and flakes. The area has outcrops of fine-grained greenstone or hornstone suitable for making polished stone axes. Such axes have been found distributed across Great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic Period
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Lake District
The Lake District, also known as the Lakes or Lakeland, is a mountainous region in North West England. A popular holiday destination, it is famous for its lakes, forests, and mountains (or ''fells''), and its associations with William Wordsworth and other Lake Poets and also with Beatrix Potter and John Ruskin. The Lake District National Park was established in 1951 and covers an area of . It was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2017. The Lake District is today completely within Cumbria, a county and administrative unit created in 1974 by the Local Government Act 1972. However, it was historically divided between three English counties ( Cumberland, Westmorland and Lancashire), sometimes referred to as the Lakes Counties. The three counties met at the Three Shire Stone on Wrynose Pass in the southern fells west of Ambleside. All the land in England higher than above sea level lies within the National Park, including Scafell Pike, the highest mountain in England. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hornstone
Hornfels is the group name for a set of contact metamorphic rocks that have been baked and hardened by the heat of intrusive igneous masses and have been rendered massive, hard, splintery, and in some cases exceedingly tough and durable. These properties are due to fine grained non-aligned crystals with platy or prismatic habits, characteristic of metamorphism at high temperature but without accompanying deformation. The term is derived from the German word ''Hornfels'', meaning "hornstone", because of its exceptional toughness and texture both reminiscent of animal horns. These rocks were referred to by miners in northern England as whetstones. Most hornfels are fine-grained, and while the original rocks (such as sandstone, shale, slate and limestone) may have been more or less fissile owing to the presence of bedding or cleavage planes, this structure is effaced or rendered inoperative in the hornfels. Though many hornfels show vestiges of the original bedding, they break acro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
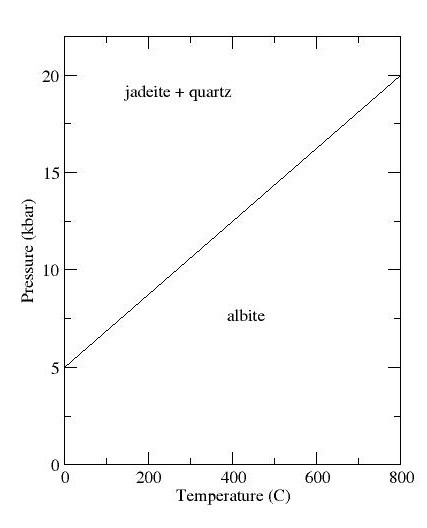
Jadeite
Jadeite is a pyroxene mineral with composition sodium, Naaluminium, Alsilicon, Si2oxygen, O6. It is hard (Mohs hardness of about 6.5 to 7.0), very tough, and dense, with a specific gravity of about 3.4. It is found in a wide range of colors, but is most often found in shades of green or white. Jadeite is formed only in subduction zones on continental margins, where rock undergoes metamorphism at high pressure but relatively low temperature. Jadeite is the principal mineral making up the most valuable form of jade, a precious stone particularly prized in China. Most gem-quality jadeite jade comes from northern Myanmar. Jade tools and implements have been found at Stone Age sites, showing that the mineral has been prized by humans since before the beginning of written history. Name The name ''jadeite'' is derived (via french: jade and la, ilia) from the Spanish language, Spanish phrase "piedra de ijada" which means "stone of the side". The Latin version of the name, ''lapis neph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jade
Jade is a mineral used as jewellery or for ornaments. It is typically green, although may be yellow or white. Jade can refer to either of two different silicate minerals: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in the amphibole group of minerals), or jadeite (a silicate of sodium and aluminium in the pyroxene group of minerals). Jade is well known for its ornamental use in East Asian, South Asian, and Southeast Asian art. It is commonly used in Latin America, such as Mexico and Guatemala. The use of jade in Mesoamerica for symbolic and ideological ritual was influenced by its rarity and value among pre-Columbian Mesoamerican cultures, such as the Olmecs, the Maya, and other ancient civilizations of the Valley of Mexico. Etymology The English word ''jade'' is derived (via French and Latin 'flanks, kidney area') from the Spanish term (first recorded in 1565) or 'loin stone', from its reputed efficacy in curing ailments of the loins and kidneys. ''Nephrite'' is der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Force
In mechanics, an impact is a high force or shock applied over a short time period when two or more bodies collide. Such a force or acceleration usually has a greater effect than a lower force applied over a proportionally longer period. The effect depends critically on the relative velocity of the bodies to one another. At normal speeds, during a perfectly inelastic collision, an object struck by a projectile will deform, and this deformation will absorb most or all of the force of the collision. Viewed from a conservation of energy perspective, the kinetic energy of the projectile is changed into heat and sound energy, as a result of the deformations and vibrations induced in the struck object. However, these deformations and vibrations cannot occur instantaneously. A high-velocity collision (an impact) does not provide sufficient time for these deformations and vibrations to occur. Thus, the struck material behaves as if it were more brittle than it would otherwise be, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chert
Chert () is a hard, fine-grained sedimentary rock composed of microcrystalline or cryptocrystalline quartz, the mineral form of silicon dioxide (SiO2). Chert is characteristically of biological origin, but may also occur inorganically as a precipitation (chemistry), chemical precipitate or a diagenesis, diagenetic replacement, as in petrified wood. Chert is typically composed of the petrified remains of siliceous ooze, the biogenic sediment that covers large areas of the deep ocean floor, and which contains the silicon skeletal remains of diatoms, Dictyochales, silicoflagellates, and radiolarians. Precambrian cherts are notable for the presence of fossil cyanobacteria. In addition to Micropaleontology, microfossils, chert occasionally contains macrofossils. However, some chert is devoid of any fossils. Chert varies greatly in color (from white to black), but most often manifests as gray, brown, grayish brown and light green to rusty redW.L. Roberts, T.J. Campbell, G.R. Rapp Jr. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)