|
Hamid Khan Lodi
Hamid Khan Lodi was the founder of the Lodi dynasty of Multan. He ruled the Emirate of Multan from 985 to 997. Biography Hamid Khan Lodi was supposedly a descendant of Sama (or Usama) Lawi who was son of Ghalib Lawi. Although Firishta wrote that he was from the Lodi tribe of Pashtuns, historians Yogendra Mishra and Henry George Raverty said he was from the Quraysh tribe of Arabs. According to Henry George Raverty and Samuel Miklos Stern, the Lodi dynasty itself might have been fabricated as its mention only starts appearing with later historians like Firishta. According to Firishta, the Hindu Shahi king Jayapala ceded the regions of Multan and Lamghan to Hamid Lodi, after joining an alliance with him and the Muslim emir of Bhera against the raids of Sabuktigin during the reign of Alp-Tegin. Sabuktigin upon becoming amir in Ghazni broke up this alliance through diplomatic means and convinced Hamid Lodi to acknowledge his overlordship. He ruled the Emirate of Multan after the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lodi Dynasty Of Multan
The Lodi dynasty was the last dynasty to rule over Emirate of Multan, from their capital city of Multan in the 10th century. History The Lodi dynasty was founded by Hamid Khan Lodi or Hamid Lawi, who was supposedly a descendant of Sama (or Usama) Lawi who was son of Ghalib Lawi. Although Firishta claimed that they were from the Lodi tribe of Pashtuns, historians Yogendra Mishra and Henry George Raverty claimed they were Quraysh Arabs. Al-Masudi who visited Multan after 912 AD states that the ruler Abu Lahab al-Munabbah bin Asad al-Qarshi was descended from the clan of Usama or Sama bin Lu'ayy bin Ghalib. '' Hudud al-'Alam'' mentions that the ruler was a Quraishite. Ibn Hawqal who visited Multan in 367 AH also mentions that the rulers were the descendant of Sama bin Loi bin Ghalib. According to Raverty and Samuel Miklos Stern, the Lodi dynasty itself might have been fabricated as its mention only starts appearing with later historians like Firishta. Banu Lawi rose to power after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamghan
Laghman (Dari: ) is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, located in the eastern part of the country. It has a population of about 502,148, which is multi-ethnic and mostly a rural society. Laghman hosts a large number of historical landmarks, minarets, monuments, and other cultural relics that are manifestation of its old history and culture. The city of Mihtarlam serves as the capital of the province. In some historical texts the name is written as "Lamghan" or as "Lamghanat". In 2021, the Taliban gained control of the province during the 2021 Taliban offensive. Etymology Laghman or Lamghan is originally named after Lamech (Mether Lam Baba), the father of Noah. History Located currently at the Kabul Museum are Aramaic inscriptions that were found in Laghman which indicated an ancient trade route from India to Palmyra. Aramaic was the bureaucratic script language of the Achaemenids whose influence had extended toward Laghman. During the invasions of Alexander the Great, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th-century Arabs
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fateh Daud
Abul Fateh Daud was a ruler from the Lodi dynasty of Multan who ruled the Emirate of Multan. He was deposed by Mahmud of Ghazni, who also massacred the Ismailis in the course of his conquest of Multan. Fateh Daud fled to a fort where he immured himself and was finally pardoned by Mahmud of Ghazni on the promise of payment of ransom. Abul Fatah Daud offered a yearly tribute of 200,000 golden dirhams and conversion from Shia Ismaili fiqh to Sunni Hanafi fiqh. The terms were accepted, and Sultan Mahmud Ghaznavi Yamīn-ud-Dawla Abul-Qāṣim Maḥmūd ibn Sebüktegīn ( fa, ; 2 November 971 – 30 April 1030), usually known as Mahmud of Ghazni or Mahmud Ghaznavi ( fa, ), was the founder of the Turkic Ghaznavid dynasty, ruling from 998 to 1030. At th ... also exacted two million dirhams from the population of Multan by force.Mahar Abdul Haq Sumra. ''Historical study of Sumra dynasty of Sindh and Punjab from 11th through mid 14th century''.Beacon Books See also * Khafif Refere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Da'i
A da'i ( ar, داعي, dāʿī, inviter, caller, ) is generally someone who engages in Dawah, the act of inviting people to Islam. See also * Dawah * Da'i al-Mutlaq, "the absolute (unrestricted) missionary" (Arabic: الداعي المطلق) * Hujja * List of da'is The following is a list of notable Da'is, that is, Muslim preachers who invite people to Islam. * Abdur Raheem Green *Abu Ammaar Yasir Qadhi, Abu Ammar Yasir Qadhi * Abul Hasan Ali Hasani Nadwi * Abu-Abdullah Adelabu * Ahmad Dahlan * Ahmed Dee ... References {{Reflist Arabic words and phrases Islamic terminology Religious titles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatimid Caliphate
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Isma'ilism, Ismaili Shia Islam, Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimid dynasty, Fatimids, a dynasty of Arab origin, trace their ancestry to Muhammad's daughter Fatimah, Fatima and her husband Ali, ‘Ali b. Abi Talib, the first Imamate in Shia doctrine, Shi‘a imam. The Fatimids were acknowledged as the rightful imams by different Isma'ilism, Isma‘ili communities, but also in many other Muslim lands, including Persia and the adjacent regions. Originating during the Abbasid Caliphate, the Fatimids conquered Tunisia and established the city of "Mahdia, al-Mahdiyya" ( ar, المهدية). The Ismaili dynasty ruled territories across the Mediterranean coast of Africa and ultimately made Egypt the center of the caliphate. At its height, the caliphate included – in addition to Egypt – varying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghazni
Ghazni ( prs, غزنی, ps, غزني), historically known as Ghaznain () or Ghazna (), also transliterated as Ghuznee, and anciently known as Alexandria in Opiana ( gr, Αλεξάνδρεια Ωπιανή), is a city in southeastern Afghanistan with a population of around 190,000 people. The city is strategically located along Highway 1, which has served as the main road between Kabul and Kandahar for thousands of years. Situated on a plateau at 2,219 metres (7,280 ft) above sea level, the city is south of Kabul and is the capital of Ghazni Province. Ghazni Citadel, the Minarets of Ghazni, the Palace of Sultan Mas'ud III, and several other cultural heritage sites have brought travelers and archeologists to the city for centuries. During the pre-Islamic period, the area was inhabited by various tribes who practiced different religions including Zoroastrianism, Buddhism and Hinduism. Arab Muslims introduced Islam to Ghazni in the 7th century and were followed in the 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alp-Tegin
, image = Pınarbaşı 5.JPG , caption = Bust of Alp Tegin as one of the founders of the " 16 Great Turkic Empires", part of the "Turkishness Monument" (''Türklük Anıtı'') in Pınarbaşı, Kayseri (opened 2000, 2012 photograph). , office = Governor of Ghazna , term_start = 962 , term_end = 963 , monarch = Mansur I , predecessor = , successor = Abu Ishaq Ibrahim , death_date = September 963 , death_place = Ghazna Alp-Tegin, ( fa, الپتگین ''Alptegīn'' or ''Alptigīn'') was a Turkic slave commander of the Samanid Empire, who would later become the semi-independent governor of Ghazna from 962 until his death in 963. Before becoming governor of Ghazni, Alp-Tegin was the commander-in-chief (''sipahsalar'') of the Samanid army in Khorasan. In a political fallout over succession of the Samanids he crossed the Hindu Kush mountains southward and captured Ghazna, located strategi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabuktigin
Abu Mansur Nasir al-Din Sabuktigin ( fa, ابو منصور سبکتگین) ( 942 – August 997), also spelled as Sabuktagin, Sabuktakin, Sebüktegin and Sebük Tigin, was the founder of the Ghaznavid dynasty, ruling from 367 A.H/977 A.D to 387 A.H/997 A.D. C.E. Bosworth"Ghaznavids"in ''Encyclopaedia Iranica''. Date: December 15, 2001. Accessdate: July 4, 2012. In Turkic the name means ''beloved prince''. Sabuktigin lived as a slave during his youth and later married the daughter of his master Alptigin, the man who seized the region of Ghazna (modern Ghazni Province in Afghanistan). Alptigin and Sabuktigin still recognized Samanid authority, and it was not until the reign of Sabuktigin's son Mahmud that the rulers of Ghazni became independent. When his father-in-law Alptigin died, Sabuktigin became the new ruler and expanded the kingdom after defeating Jayapala of Udabhandapura to cover the territory as far as the Neelum River in Kashmir and the Indus River in what is now Pak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhera
Bhera ( pa, ; ur, ) is a city and tehsil of Sargodha District, Punjab province of Pakistan. The city is known for wood-carved items, textiles (such as quilts and khussas), and certain desserts (such as pheonian and pateesa). The city is made up of the Old Town and the surrounding newer development. The Old Town is surrounded by tall walls with eight gates, and is divided up into mohallas, or neighborhoods; historically, different castes lived in different mohallas. The novel ''Mayyadas Ki Mari'' (Mayyadas's Castle), written by Indian playwright Bhisham Singh Sahni, takes place in Bhera. History According to ''Ancient Geography of India'' by Alexander Cunningham, Bhera was once known as Jobnathnagar. The ''Imperial Gazetteer of India'' records the history of Bhera: In the recent past centuries, Bhera was an important trading outpost on the road to Kabul, and boasted of a taksal (mint) during the rule of Ranjit Singh. The city was known for its knife and cutlery cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jayapala
Jayapala or Jaipal was a ruler of the Hindu Shahi dynasty from 964 to 1001 CE. His kingdom stretched from Laghman to Kashmir and Sirhind to Multan, with Peshawar being in the center. He was the son of Hutpal and the father of Anandapala. Epithets from the Bari Kot inscriptions record his full title as "Parama Bhattaraka Maharajadhiraja Sri Jayapaladeva". History Jayapala fought against the Ghaznavids in the Gandhara region of Ancient India, which is now in modern-day north-eastern Afghanistan and north-western Pakistan, until finally being defeated in Peshawar by superior forces of the latter. Jayapala attacked the Ghaznavids and invaded their capital city of Ghazni both in the reign of Sebuktigin and that of his son Mahmud, which initiated the Muslim Ghaznavid and Hindu Shahi struggles. Jayapala, however, was defeated, and he was forced to pay an indemnity to Sebuktigin. Maharaja Jayapala stopped paying tribute and took to the battlefield once more. Maharaja Jayapala, howe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
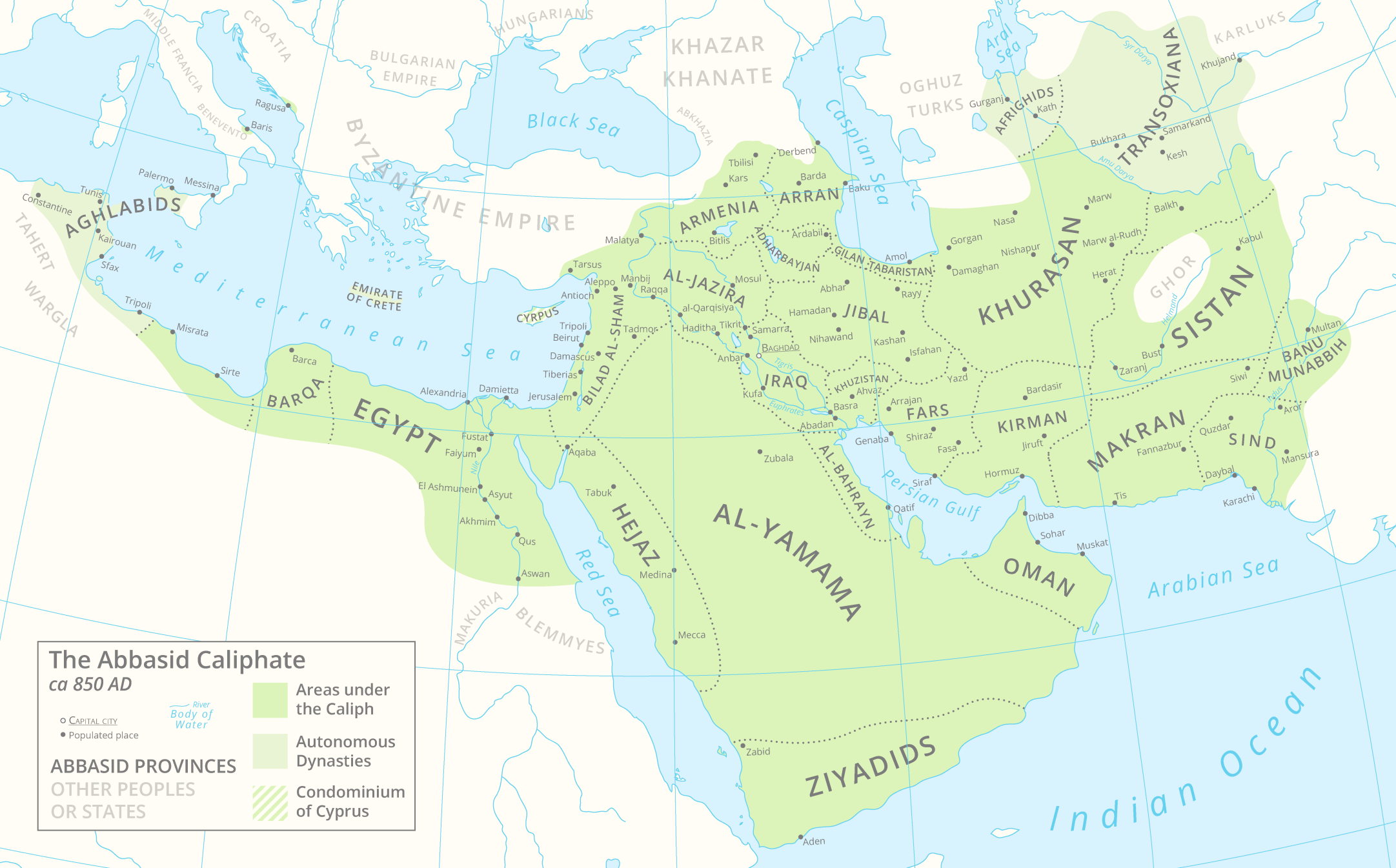
Emirate Of Multan
Emirate of Multan (855 – 1010) was a medieval kingdom in Punjab that was centred around city of Multan, present-day Punjab, Pakistan. It was initially ruled by the tribe of ''Banu Munabbih''. In 959 CE, Ismaili Qarmatians under '' Banu Lawi'' gained control of the Emirate and in 1010, it was conquered by Ghaznavid Empire. Location The Emirate of Multan became independent after Disintegration of Abbasid Caliphate. Principally located in South Punjab, it bordered Hindu Shahi Kingdom at north in Punjab and Habbarid Emirate at south in Sindh. History Multan along with Sindh came under rule of Muslims by conquest of Umayyad Caliphate under General Muhammad Bin Qasim. Over the course of the mid-ninth century, Abbasid authority in Sind gradually waned. As the central government's authority over Sind declined, the region underwent a period of decentralization. Multan also became capital of an independent emirate under an Arab tribe Banu Munabbih. Rule of Banu Munabbih (855–9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |