|
Hamelin Bay, Western Australia
Hamelin Bay is a bay and a locality on the southwest coast of Western Australia between Cape Leeuwin and Cape Naturaliste. It is named after French explorer Jacques Félix Emmanuel Hamelin, who sailed through the area in about 1801. It is south of Cape Freycinet. To the north, the beach leads to the '' Boranup Sand Patch'' and further to the mouth of the Margaret River, while south leads to Cape Leeuwin. The nearest locality to the east is Karridale on the Margaret River to Augusta road. It was also a small settlement and port in Western Australia on the coast of the Leeuwin-Naturaliste Ridge. Port and jetty The jetty was established to service the timber milling operations of Davies, at the same time as utilising a jetty at Flinders Bay just south of Augusta. One of the Davies timber railways extended onto the Hamelin Bay Jetty, which was built in 1882 and extended in 1898. Only a few piles of the original jetty remain on site. Tourist attractions The Cape to Cape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamelin Island
Hamelin Island lies north of Cape Hamelin, just out to sea from the former Hamelin Bay Jetty, on Hamelin Bay, on the south west coast of Western Australia, about 7 km north of Cape Leeuwin. The location of the island, and its protection of part of the anchorage from prevailing weather and winds was observed very early in the twentieth century. Rabbits A Western Mail (Western Australia) Christmas edition of 1930 has a photograph of the island, and calls it ''Rabbit Island''. Which relates to the 22 July 1911 article cited above - ''Leeuwin Land'', which stated that: Wrecks The Hamelin Bay was the site of many wrecks ''Wrecks'' is a one-man play by Neil LaBute, that was commissioned and produced by the Everyman Palace Theatre in Cork, Ireland. The play was a part of the city's Capital of Culture programme in 2005.LaBute, Neil''Wrecks'Wrecks: And Other Plays ..., however less have occurred on the island. One was in December 1933 of the fishing boat ''Toba''. In July 2016, a st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Division Of Forrest
The Division of Forrest is an Australian Electoral Division in Western Australia. Geography Since 1984, federal electoral division boundaries in Australia have been determined at redistributions by a redistribution committee appointed by the Australian Electoral Commission. Redistributions occur for the boundaries of divisions in a particular state, and they occur every seven years, or sooner if a state's representation entitlement changes or when divisions of a state are malapportioned. History The division was created in 1922 and is named for Sir John Forrest, the first Premier of Western Australia and a federal Cabinet minister. It is located in the south-western corner of the state and, as of the 2016 election, includes the cities of Bunbury and Busselton along with the Shires of Augusta-Margaret River, Capel, Dardanup, Donnybrook-Balingup, Harvey and Nannup (though Nannup is set to be transferred to the neighbouring seat of O'Connor at the next federal election). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Australian Museum
The Western Australian Museum is a statutory authority within the Culture and the Arts Portfolio, established under the ''Museum Act 1969''. The museum has six main sites. The state museum, now known as WA Museum Boola Bardip, officially re-opened on 21 November 2020 in the Perth Cultural Centre. The other sites are: the WA Maritime Museum and WA Shipwrecks Museum in Fremantle, the Museum of the Great Southern in Albany, the Museum of Geraldton in Geraldton, and the Museum of the Goldfields in Kalgoorlie-Boulder. History Established in 1891 in the Old Perth Gaol, it was known as the Geological Museum and consisted of geological collections. In 1892, ethnological and biological exhibits were added, and in 1897, the museum officially became the Western Australian Museum and Art Gallery. The museum employed collectors to obtain series of specimens; Tunney ventured across the state from 1895 to 1909 obtaining animals and, later, the tools and artefacts of the indigenous inhabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shark Attack
A shark attack is an attack on a human by a shark. Every year, around 80 unprovoked attacks are reported worldwide. Despite their rarity, many people fear shark attacks after occasional serial attacks, such as the Jersey Shore shark attacks of 1916, and horror fiction and films such as the ''Jaws'' series. Out of more than 489 shark species, only three of them are responsible for a double-digit number of fatal, unprovoked attacks on humans: the great white, tiger, and bull.ISAStatistics on Attacking Species of Shark/ref> The oceanic whitetip has probably killed many more castaways, but these are not recorded in the statistics. Terminology While the term "shark attack" is in common use for instances of humans being wounded by sharks, it has been suggested that this is based largely on the assumption that large predatory sharks (such as great white, bull, and tiger sharks) only seek out humans as prey. A 2013 review recommends instances where a shark clearly predates on a huma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
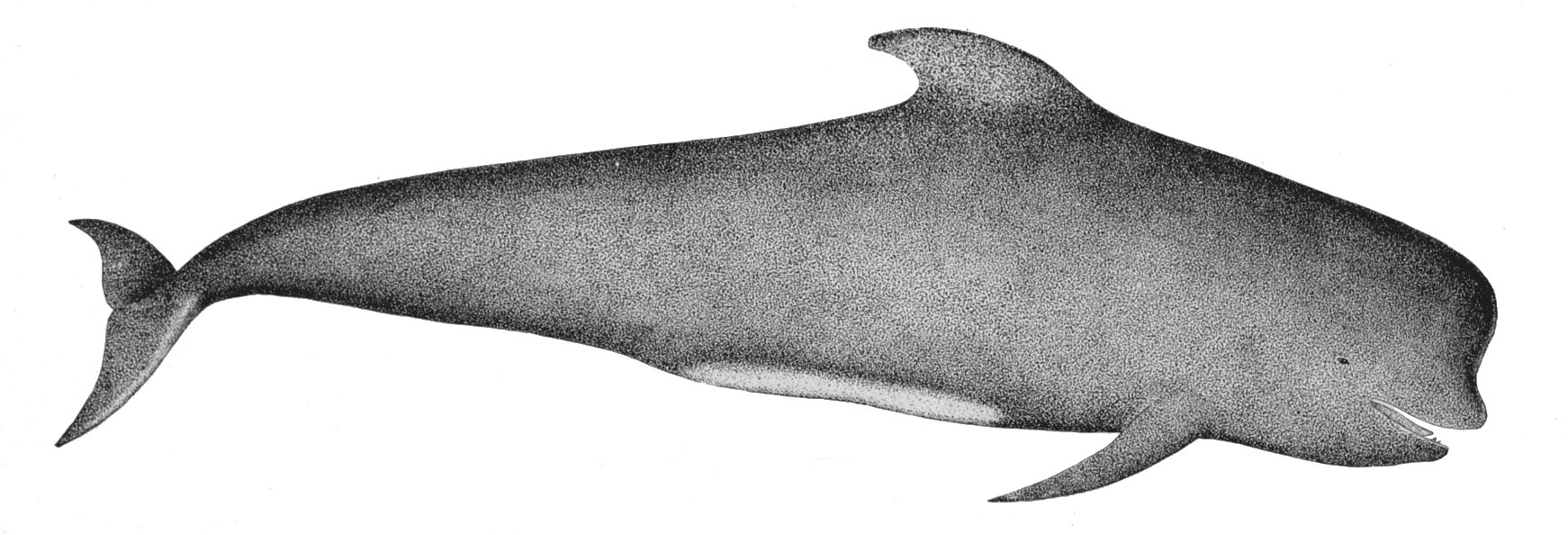
Short-finned Pilot Whales
The short-finned pilot whale (''Globicephala macrorhynchus'') is one of the two species of cetaceans in the genus '' Globicephala'', which it shares with the long-finned pilot whale (''G. melas''). It is part of the oceanic dolphin family (Delphinidae). It has a worldwide distribution with a global population of about 700,000, and there may be 3 or 4 distinct populations—two in the Pacific and one in the Atlantic and Indian Oceans. Its range is moving northward due to global warming. In the Pacific, males average and females . It generally has a stocky build with black to dark gray or brown skin, and can be distinguished from its counterpart by shorter flippers, fewer teeth, and a shorter beak. It is thought to pursue fast-moving squid typically at a depth of , but the maximum recorded depth is . The short-finned pilot whale has been reported as being highly playful and social. It typically travels in pods of 10–30 members, usually family, but has been observed moving in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long-finned Pilot Whales
The long-finned pilot whale (''Globicephala melas'') is a large species of oceanic dolphin. It shares the genus '' Globicephala'' with the short-finned pilot whale (''Globicephala macrorhynchus''). Long-finned pilot whales are known as such because of their unusually long pectoral fins. Taxonomy and naming Etymology Pilot whales get their name from the original belief that there was a "pilot" or lead individual in their groups.Olson, P.A. (2008). "Pilot whale ''Globicephala melas'' and ''G. muerorhynchus''". pp. 847–52 in ''Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals''. Perrin, W. F., Wursig, B., and Thewissen, J. G. M. (eds.). Academic Press; 2nd edition. Ridgway, S. H. (1998). ''Handbook of Marine Mammals: The second book of dolphins and the porpoises''. Volume 6, Elsevier. pp. 245–69. The name for the genus, "''Globicephala''" is derived from a combination of Latin ''globus'' ("globe") and Greek ''kephale'' ("head"). The specific name "''melas''" is Greek for "black". This species h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whale Strandings
Cetacean stranding, commonly known as beaching, is a phenomenon in which whales and dolphins strand themselves on land, usually on a beach. Beached whales often die due to dehydration, collapsing under their own weight, or drowning when high tide covers the blowhole (anatomy), blowhole. Cetacean stranding has occurred since before recorded history. Several explanations for why cetaceans strand themselves have been proposed, including changes in water temperatures, peculiarities of whales' Animal echolocation, echolocation in certain surroundings, and geomagnetic disturbances, but none have so far been universally accepted as a definitive reason for the behavior. However, a link between the mass beaching of beaked whales and use of mid-frequency active sonar has been found. Subsequently, whales that die due to stranding can decay and bloat to the point where they can exploding whale, easily explode, causing gas and their internal organs to fly out. Species Every year, up to 2,00 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Screw Steamer
A screw steamer or screw steamship is an old term for a steamship or steamboat powered by a steam engine, using one or more propellers (also known as ''screws'') to propel it through the water. Such a ship was also known as an "iron screw steam ship". In the 19th century, this designation was normally used in contradistinction to the paddle steamer, a still earlier form of steamship that was largely, but not entirely, superseded by the screw steamer. Many famous ships were screw steamers, including the RMS ''Titanic'' and RMS ''Lusitania''. These massive leviathans had three or four propellers. Ships under two hundred meters in length usually only had two or one propellers. Canney, 1998 pp.26-27 Development The screw or propeller was first developed by Swedish inventor John Ericsson for the U.S. Navy. Ericsson was the principal designer of the Monitor class of vessels. In 1844, Thomas Clyde partnered with Ericsson to apply his screw-propeller to steam vessels. After several e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinker Built
Clinker built (also known as lapstrake) is a method of boat building where the edges of hull planks overlap each other. Where necessary in larger craft, shorter planks can be joined end to end, creating a longer strake or hull plank. The technique originated in Scandinavia, and was successfully used by the Anglo-Saxons, Frisians, Scandinavians, typically in the vessels known as cogs employed by the Hanseatic League. Carvel construction, where plank edges are butted smoothly, seam to seam, supplanted clinker construction in large vessels as the demand for capacity surpassed the limits of clinker construction. (See Comparison between clinker and carvel below.). Examples of clinker-built boats that are directly descended from those of the early medieval period are seen in the traditional round-bottomed Thames skiffs, and the larger (originally) cargo-carrying Norfolk wherries of England. Etymology From ''clinch'', or ''clench'', a common Germanic word, meaning “to fasten t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lugger
A lugger is a sailing vessel defined by its rig, using the lug sail on all of its one or several masts. They were widely used as working craft, particularly off the coasts of France, England, Ireland and Scotland. Luggers varied extensively in size and design. Many were undecked, open boats, some of which operated from beach landings (such as Hastings or Deal). Others were fully decked craft (typified by the Zulu and many other sailing drifters). Some larger examples might carry lug topsails. Luggers were used extensively for smuggling from the middle of the 18th century onwards; their fast hulls and powerful rigs regularly allowed them to outpace any Revenue vessel in service. The French three-masted luggers also served as privateers and in general trade. As smuggling declined about 1840, the mainmast of British three-masted luggers tended to be discarded, with larger sails being set on the fore and mizzen. This gave more clear space in which to work fishing nets. Local ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barquentine
A barquentine or schooner barque (alternatively "barkentine" or "schooner bark") is a sailing vessel with three or more masts; with a square rigged foremast and fore-and-aft rigged main, mizzen and any other masts. Modern barquentine sailing rig While a full-rigged ship is square-rigged on all three masts, and the barque is square-rigged except for the mizzen-mast, the barquentine extends the principle by making only the foremast square-rigged. The advantages of a smaller crew, good performance before the wind and the ability to sail relatively close to the wind while carrying plenty of cargo made it a popular rig at the end of the nineteenth century. Today, barquentines are popular with modern tall ship and sail training operators as their suite of mainly fore-and-aft sails improve non-downwind performance, while their foremast of square sails offers long distance downwind speed and dramatic appearance in port. Etymology The term "barquentine" is seventeenth century in ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barge
Barge nowadays generally refers to a flat-bottomed inland waterway vessel which does not have its own means of mechanical propulsion. The first modern barges were pulled by tugs, but nowadays most are pushed by pusher boats, or other vessels. The term barge has a rich history, and therefore there are many other types of barges. History of the barge Etymology "Barge" is attested from 1300, from Old French ''barge'', from Vulgar Latin ''barga''. The word originally could refer to any small boat; the modern meaning arose around 1480. ''Bark'' "small ship" is attested from 1420, from Old French ''barque'', from Vulgar Latin ''barca'' (400 AD). The more precise meaning of Barque as "three-masted sailing vessel" arose in the 17th century, and often takes the French spelling for disambiguation. Both are probably derived from the Latin ''barica'', from Greek ''baris'' "Egyptian boat", from Coptic ''bari'' "small boat", hieroglyphic Egyptian D58-G29-M17-M17-D21-P1 and similar ''b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |