|
Halmahera Sea Languages
The Halmahera Sea languages, also known as the Raja Ampat-South Halmahera languages, are a branch of Malayo-Polynesian languages of eastern Indonesia. They are spoken on islands in the Halmahera Sea, and on its margins from the south-eastern coast of Halmahera to the Raja Ampat Islands off the western tip of New Guinea. The languages of the Raja Ampat Islands show a strong Papuan substratum influence; it is not clear that they are actually Austronesian as opposed to relexified Papuan languages. Remijsen (2001) and Blust (1978) linked the languages of Raja Ampat to the South Halmahera languages. David Kamholz (2014) breaks up Raja Ampat, so that the structure of the Halmahera Sea languages is as follows:Kamholz, David (2014). Austronesians in Papua: Diversification and change in South Halmahera–West New Guinea''. Ph.D. dissertation, University of California, Berkeley. https://escholarship.org/uc/item/8zg8b1vd * South Halmahera *Ambel–Biga: Waigeo (Ambel), Biga Biga may ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
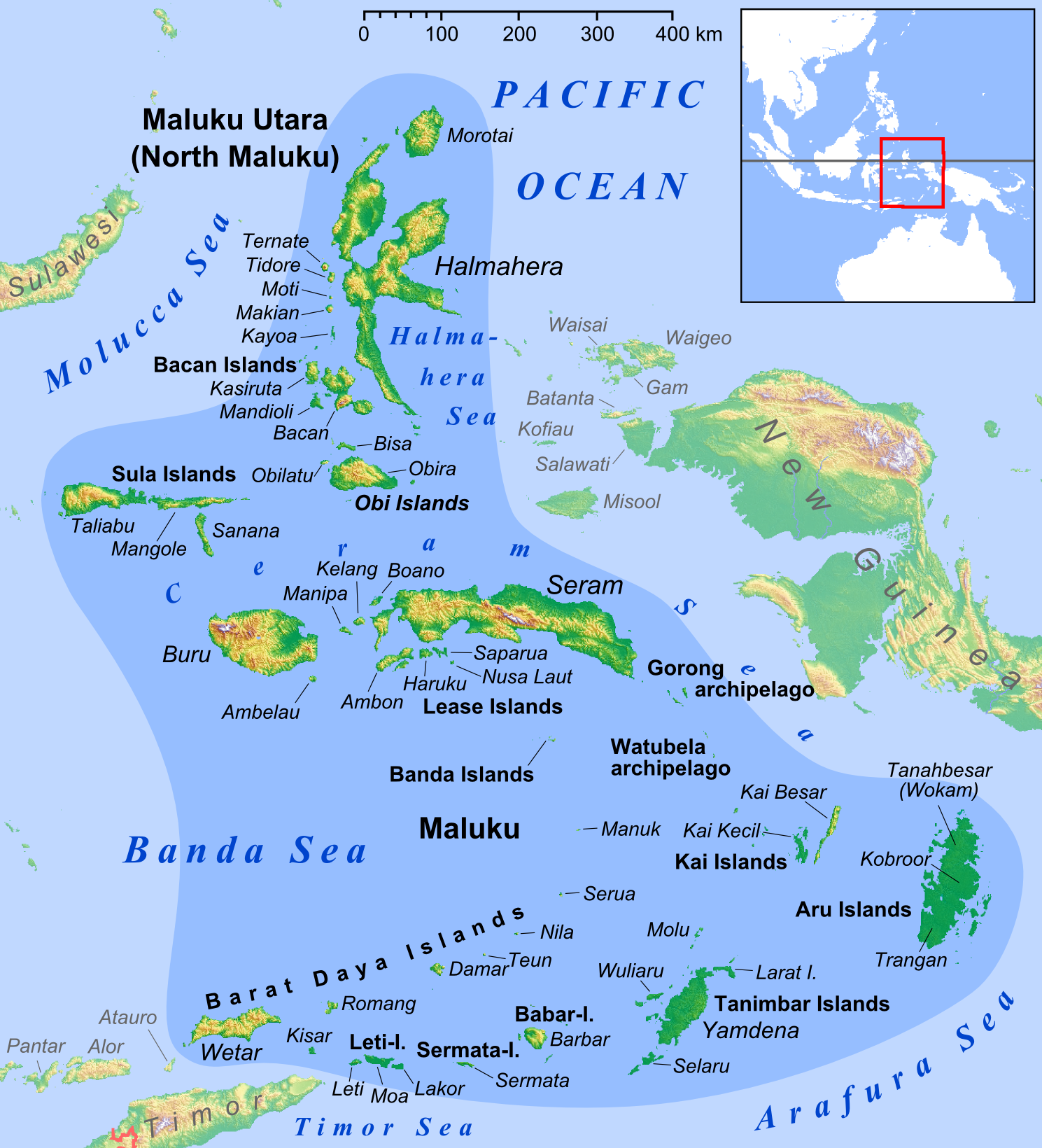
Halmahera Sea
The Halmahera Sea is a regional sea located in the central eastern part of the Australasian Mediterranean Sea. It is centered at about 1°S and 129°E and is bordered by the Pacific Ocean to the north, Halmahera to the west, Waigeo and West Papua to the east, and the Seram Sea to the south. It covers about and its topography comprises a number of separate basins and ridges, the chief of which is the Halmahera Basin reaching a depth of 2039 m. Extent The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) defines the Halmahera Sea as being one of the waters of the East Indian Archipelago. The IHO defines its limits as follows: ''On the North'' A line from Wajaboela (Morotai) to Tg. Djodjefa, the Northern point of Halmahera. ''On the East.'' A line from Tg. Gorango, the Northeastern point of Morotai Island, through Sajang and Kawé Islands to the Western extremes of Waigeo and Batanta Islands across to the Northwest point of Samawati Island, down the coast to Tg. Menonket its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Halmahera Languages
The South Halmahera languages are the branch of Austronesian languages found along the southeast coast of the island of Halmahera in the Indonesian province of North Maluku. Irarutu is spoken in the east of the Bomberai Peninsula in West Papua province. Most of the languages are only known from short word lists, but Taba and Buli are fairly well attested. They are not related to the North Halmahera languages, which are notable for being non-Austronesian. However, Ternatan influence is considerable, a legacy of the historical dominance of the Ternate Sultanate. Classification The South Halmahera languages are listed below according to ''Glottolog'' 4.0's classification, with alternate names and dialects listed from Kamholz (2014: 17):Kamholz, David (2014). Austronesians in Papua: Diversification and change in South Halmahera–West New Guinea'. Ph.D. dissertation, University of California, Berkeley. https://escholarship.org/uc/item/8zg8b1vd *East Makian – Gane **Gane (G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ma'ya Language
Ma'ya is an Austronesian language of the Raja Ampat islands in West Papua, Indonesia. It is spoken by about 6,000 people in coastal villages on the islands Misool, Salawati, and Waigeo. It is spoken on the boundary between Austronesian and Papuan languages. Dialects Ma'ya has five dialects: three on the island of Waigeo ( Laganyan, Wauyai, and Kawe), one on Salawati, and one (extinct or nearly extinct) on Batanta. The prestige dialect is the one on Salawati. The Waigeo dialects have /s/ and /ʃ/, where the varieties spoken on Salawati and Misool have /t/ and /c/ respectively. Batanta, now extinct, was evidently unintelligible with its neighbours. On Waigeo Island, the three dialects are *The ''Kawe'' dialect in Selpele and Salyo villages in the northwest part of the island. *The ''Laganyan'' dialect is spoken in Araway, Beo, and Luptintol villages on the Mayalibit Bay coast. *The ''Wauyai'' dialect is spoken in Wauyai village on the Kabui Bay coast. Phonology Consonants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matbat Language
Matbat is a heavily Papuan-influenced Austronesian language spoken in West Papua, Indonesia, on the island of Misool, Raja Ampat islands. Its dialects are ''Magey'' and ''Tomolol''. Similar to the neighboring Ma'ya language, Matbat is one of a handful of Austronesian languages with true lexical tone rather than a pitch-accent system or complete lack of phonemic tonal contrasts as with most other Austronesian languages. Distribution Matbat is spoken in the following locations within Raja Ampat Regency: *Misool Timur District: Tumolol, Lenmalas, Lenmalas Timur Barat, Audam, Foley, and Eduai villages *Misool Utara District: Atkari and Salafen villages *Misool Barat District: Magei village Phonology The phonology of the Matbat language is summarized below: /j/ can be heard freely as �or �in word-initial position. Tones Matbat has five lexical tones: high falling 41, high 3, low rising 12, low level 1, and low falling 21, which in open syllables has a peaking alloph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maden Language
Salawati is an Austronesian language spoken on the west of Salawati Island, in the Raja Ampat Islands in Indonesian New Guinea. Dialects The dialects of Salawati are as follows:Kamholz, David (2014). Austronesians in Papua: Diversification and change in South Halmahera–West New Guinea'. Ph.D. dissertation, University of California, Berkeley. https://escholarship.org/uc/item/8zg8b1vd *''Butleh'', also called ''Banlol'' (exonym) or ''Fiawat'' (village name) *''Kawit'' *''Tepin/Tipin'' References South Halmahera–West New Guinea languages Languages of western New Guinea {{indonesia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
As Language
As is an Austronesian language spoken on the north coast of the Doberai Peninsula, Indonesian New Guinea, but originally from Gag Island Gag Island is one of the Raja Ampat Islands in the Indonesian province of Southwest Papua. It is situated some 150 kilometres west of Sorong, the provincial capital. The island's population is approximately 450 living at Gambier Bay. This com .... References South Halmahera–West New Guinea languages Languages of western New Guinea {{indonesia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biga Language
Biga is a heavily Papuan-influenced Austronesian language spoken in Southwest Papua, Indonesia in the south of the island of Misool. It is spoken in the single village of Biga in Misol Timur Selatan District. References External links * Paradisec The Pacific and Regional Archive for Digital Sources in Endangered Cultures (PARADISEC) is a cross-institutional project that supports work on endangered languages and cultures of the Pacific and the region around Australia. They digitise reel-to ... open access collection of George Grace'manuscriptsfrom the University of Hawai'i. South Halmahera–West New Guinea languages Languages of western New Guinea {{indonesia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waigeo Language
Ambel (Amber), also known as Waigeo after the island where it is primarily spoken, is a heavily Papuan-influenced Austronesian language spoken on the island of Waigeo in the Raja Ampat archipelago near the northwestern tip of West Papua, Indonesia. It is spoken by approximately 1,600 people. It is endangered, as the population is shifting to Papuan Malay and few people born after the year 2000 have any knowledge of the language. Dialects Ambel is spoken by approximately 1,600 people on Waigeo, an island in the Raja Ampat archipelago near the northwestern tip of West Papua, Indonesia. There are two dialects of Ambel: *''Metsam'' Ambel, spoken in the two villages of Warsamdin and Kalitoko on Waigeo Island *''Metnyo'' Ambel, spoken in the nine villages of Warimak, Waifoi, Kabilo, Go, Kapadiri, Kabare, Bonsayor, Darumbab, and Andey on Waigeo Island Ambel speakers live alongside Biak speakers in the three villages of Warsamdin, Kabare, and Andey. Distribution Ambel is spoken in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substratum
In linguistics, a stratum (Latin for "layer") or strate is a language that influences or is influenced by another through contact. A substratum or substrate is a language that has lower power or prestige than another, while a superstratum or superstrate is the language that has higher power or prestige. Both substratum and superstratum languages influence each other, but in different ways. An adstratum or adstrate is a language that is in contact with another language in a neighbor population without having identifiably higher or lower prestige. The notion of "strata" was first developed by the Italian linguist Graziadio Isaia Ascoli (1829–1907), and became known in the English-speaking world through the work of two different authors in 1932. Thus, both concepts apply to a situation where an intrusive language establishes itself in the territory of another, typically as the result of migration. Whether the superstratum case (the local language persists and the intrusive languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raja Ampat Islands
Raja Ampat, or the ''Four Kings'', is an archipelago located off the northwest tip of Bird's Head Peninsula on the island of New Guinea, in Indonesia's Southwest Papua province. It comprises over 1,500 small islands, cays, and shoals surrounding the four main islands of Misool, Salawati, Batanta, and Waigeo, and the smaller island of Kofiau. The Raja Ampat archipelago straddles the Equator and forms part of Coral Triangle which contains the richest marine biodiversity on earth. Administratively, the archipelago is part of the province of Southwest Papua. Most of the islands constitute the Raja Ampat Regency, which was separated out from Sorong Regency in 2004. The regency encompasses around of land and sea, of which 8,034.44 km2 constitutes the land area and has a population of 64,141 at the 2020 Census. This excludes the southern half of Salawati Island, which is not part of this regency but instead constitutes the Salawati Selatan and Salawati Tengah Districts of Sorong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papuan Languages
The Papuan languages are the non- Austronesian and non-Australian languages spoken on the western Pacific island of New Guinea in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, as well as neighbouring islands, by around 4 million people. It is a strictly geographical grouping, and does not imply a genetic relationship. The concept of Papuan (non-Austronesian) speaking Melanesians as distinct from Austronesian-speaking Melanesians was first suggested and named by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1892. New Guinea is the most linguistically diverse region in the world. Besides the Austronesian languages, there are some (arguably) 800 languages divided into perhaps sixty small language families, with unclear relationships to each other or to any other languages, plus many language isolates. The majority of the Papuan languages are spoken on the island of New Guinea, with a number spoken in the Bismarck Archipelago, Bougainville Island and the Solomon Islands to the east, and in Halmahera, Timor and the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu Hiri Motu, also known as Police Motu, Pidgin Motu, or just Hiri, is a language of Papua New Guinea, which is spoken in surrounding areas of Port Moresby (Capital of Papua New Guinea). It is a simplified version of Motu, from the Austronesian l ...: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Mainland Australia, Australia by the wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The eastern half of the island is the major land mass of the independent state of Papua New Guinea. The western half, known as Western New Guinea, forms a part of Indonesia and is organized as the provinces of Papua (province), Papua, Central Papua, Highland Papua, South Papua, Southwest Papua, and West Papua (province), West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |