|
Hakui, Ishikawa
is a city located in Ishikawa Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 22,052 in 8566 households, and a population density of 270 persons per km². The total area of the city was . Geography Hakui occupies the southwestern neck of Noto Peninsula and is bordered by the Sea of Japan on west, and Toyama Prefecture to the east. Parts of the city are within the borders of the Noto Hantō Quasi-National Park. Neighbouring municipalities *Ishikawa Prefecture ** Nakanoto ** Shika ** Hōdatsushimizu *Toyama Prefecture ** Himi Climate Hakui has a humid continental climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') characterized by mild summers and cold winters with heavy snowfall. The average annual temperature in Hakui is 13.9 °C. The average annual rainfall is 2452 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 26.4 °C, and lowest in January, at around 4.0 °C. Demographics Per Japanese census data, the populatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cities Of Japan
A is a local administrative unit in Japan. Cities are ranked on the same level as and , with the difference that they are not a component of . Like other contemporary administrative units, they are defined by the Local Autonomy Law of 1947. City status Article 8 of the Local Autonomy Law sets the following conditions for a municipality to be designated as a city: *Population must generally be 50,000 or greater (原則として人口5万人以上) *At least 60% of households must be established in a central urban area (中心市街地の戸数が全戸数の6割以上) *At least 60% of households must be employed in commerce, industry or other urban occupations (商工業等の都市的業態に従事する世帯人口が全人口の6割以上) *Any other conditions set by prefectural ordinance must be satisfied (他に当該都道府県の条例で定める要件を満たしていること) The designation is approved by the prefectural governor and the Minister for Internal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
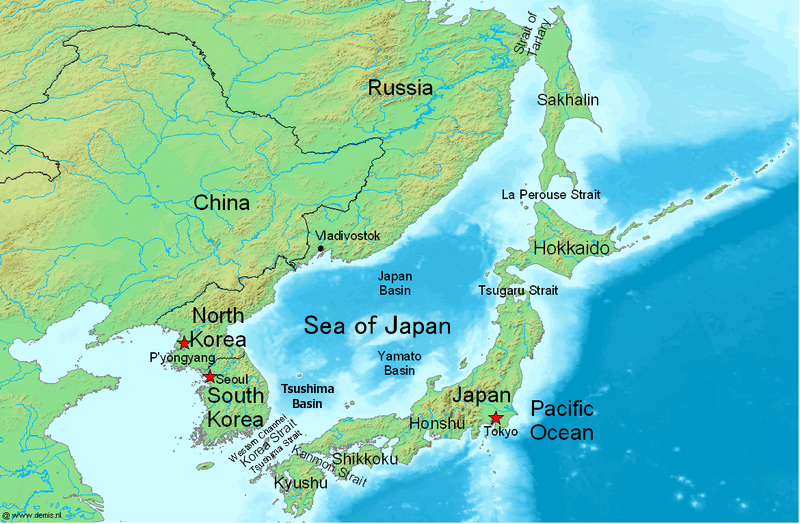
Sea Of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific Ocean. This isolation also affects faunal diversity and salinity, both of which are lower than in the open ocean. The sea has no large islands, bays or capes. Its water balance is mostly determined by the inflow and outflow through the straits connecting it to the neighboring seas and the Pacific Ocean. Few rivers discharge into the sea and their total contribution to the water exchange is within 1%. The seawater has an elevated concentration of dissolved oxygen that results in high biological productivity. Therefore, fishing is the dominant economic activity in the region. The intensity of shipments across the sea has been moderate owing to political issues, but it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Izumo Province
was an old province of Japan which today consists of the eastern part of Shimane Prefecture. It was sometimes called . The province is in the Chūgoku region. History During the early Kofun period (3rd century) this region was independent and constructed rectangular tumuli. But in the fourth century this region saw the construction of rectangular and key shaped tumuli. During the 6th or 7th century it was absorbed due to the expansion of the state of Yamato, within which it assumed the role of a sacerdotal domain. Today, the Izumo Shrine constitutes (as does the Grand Shrine of Ise) one of the most important sacred places of Shinto: it is dedicated to ''kami'', especially to Ōkuninushi (''Ō-kuni-nushi-no-mikoto''), mythical progeny of Susanoo and all the clans of Izumo. The mythological mother of Japan, the goddess Izanami, is said to be buried on Mt. Hiba, at the border of the old provinces of Izumo and Hōki, near modern-day Yasugi of Shimane Prefecture. By the Sengoku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ōkuninushi
Ōkuninushi ( historical orthography: ''Ohokuninushi''), also known as Ō(a)namuchi (''Oho(a)namuchi'') or Ō(a)namochi (''Oho(a)namochi'') among other variants, is a ''kami'' in Japanese mythology. He is one of the central deities in the cycle of myths recorded in the '' Kojiki'' (ca. 712 CE) and the '' Nihon Shoki'' (720 CE) alongside the sun goddess Amaterasu and her brother, the wild god Susanoo, who is reckoned to be either Ōkuninushi's distant ancestor or father. In these texts, Ōkuninushi (Ōnamuchi) is portrayed as the head of the ''kunitsukami'', the gods of the earth, and the original ruler of the terrestrial world, named Ashihara-no-Nakatsukuni (葦原中国, the "Central Land of Reed Plains"). When the heavenly deities (''amatsukami'') headed by Amaterasu demanded that he relinquish his rule over the land, Ōkuninushi agreed to their terms and withdrew into the unseen world (幽世, ''kakuriyo''), which was given to him to rule over in exchange. Amaterasu's grand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keta Shrine
is a Shinto shrine located in the city of Hakui, Ishikawa Prefecture, Japan. It was the former ''ichinomiya'' of Noto Province. The main ''kami'' enshrined is Ōkuninushi. The shrine's main festival is held annually on April 3. History The original construction of this shrine is unknown, but it is said to have been constructed on the location where Ōkuninushi landed with 300 of his folders from Izumo to subdue the inhabitants of Noto Peninsula during the reign of the demi-legendary 8th Emperor Kōgen or 10th Emperor Sujin. The shrine is first mentioned in history in a poem in the ''Man'yōshū'' by Otomo no Yakamochi dated 748 AD. It is also mentioned in the 768 AD ''Shoku Nihongi'', and by the 859 AD ''Nihon Sandai Jitsuroku'', it had been accorded 1st Court Rank. The shrine was patronised by the Maeda clan during the Edo period and a number of its structures date from this time. Under the pre-World War II Modern system of ranked Shinto Shrines, the shrine was classified as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichinomiya
is a Japanese historical term referring to the Shinto shrines with the highest rank in a province. Shrines of lower rank were designated , , , and so forth. ''Encyclopedia of Shinto'' ''Ichi no miya'' retrieved 2013-5-14. The term gave rise to modern place names, such as the city of Ichinomiya, Aichi. Overview The term "Ichinomiya" literally means "first shrine" and is popularly regarded as the highest ranking shrine in each province, with the second ranking shrine referred to as the "Ninomiya" and third ranking shrine as "Sannomiya", and so on. However, there is no documentary material stipulating on how the shrines in each province are to be ranked, or even when this ranking system was created. As a general rule, all shrines designated "Ichinomiya" are of ancient origin and are listed in the ''Engishiki'' records completed in 927AD. However, the shrine selected is not necessarily the largest, or oldest, in that province, and is not necessarily one of the "Meishin Taisha", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noto Province
was a province of Japan in the area that is today the northern part of Ishikawa Prefecture in Japan, including the Noto Peninsula (''Noto-hantō'') which is surrounded by the Sea of Japan. Noto bordered on Etchū and Kaga provinces to the south, and was surrounded by the Sea of Japan to the east, north and west. Its abbreviated form name was . History In 718 A.D., four districts of Echizen Province, Hakui District, Noto District (also called Kashima District), Fugeshi District and Suzu District, were separated into Noto Province. However, in the year 741, the province was abolished, and merged into Etchū Province. Noto Province was subsequently re-established in 757. The province disappears from history until the ''Wamyō Ruijushō'' of 930 AD, in which Minamoto no Shitagō is named as ''Kokushi'' of the province. The Nara period provincial capital and provincial temple were located in what is now the city of Nanao, Ishikawa; however, the Ichinomiya (Keta Shrine) wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jōmon Period
The is the time in Japanese history, traditionally dated between 6,000–300 BCE, during which Japan was inhabited by a diverse hunter-gatherer and early agriculturalist population united through a common Jōmon culture, which reached a considerable degree of sedentism and cultural complexity. The name "cord-marked" was first applied by the American zoologist and orientalist Edward S. Morse, who discovered sherds of pottery in 1877 and subsequently translated it into Japanese as ''Jōmon''.Mason, 14 The pottery style characteristic of the first phases of Jōmon culture was decorated by impressing cords into the surface of wet clay and is generally accepted to be among the oldest in the world. The Jōmon period was rich in tools and jewelry made from bone, stone, shell and antler; pottery figurines and vessels; and lacquerware.Imamura, K. (1996) ''Prehistoric Japan: New Perspectives on Insular East Asia''. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press It is often compared to pre-C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Meteorological Agency
The , abbreviated JMA, is an agency of the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism. It is charged with gathering and providing results for the public in Japan that are obtained from data based on daily scientific observation and research into natural phenomena in the fields of meteorology, hydrology, seismology and volcanology, among other related scientific fields. Its headquarters is located in Minato, Tokyo. JMA is responsible for gathering and reporting weather data and forecasts for the general public, as well as providing aviation and marine weather. JMA other responsibilities include issuing warnings for volcanic eruptions, and the nationwide issuance of earthquake warnings of the Earthquake Early Warning (EEW) system. JMA is also designated one of the Regional Specialized Meteorological Centers of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO). It is responsible for forecasting, naming, and distributing warnings for tropical cyclones in the Northwestern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himi, Toyama
is a city in western Toyama Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 48,275 in 17632 households, and a population density of 210 persons per km². Its total area is . Himi is known primarily for its commercial fishing industry. The city was founded on August 1, 1952. Geography Himi is in the far northwestern Toyama Prefecture, and is bordered by Ishikawa Prefecture (the Noto Peninsula to the west and north, and the Sea of Japan (Toyama Bay) to the east. Much of the area is a dispersed settlement typical of this region of Japan. Surrounding municipalities *Toyama Prefecture ** Takaoka *Ishikawa Prefecture ** Nanao ** Hakui ** Hōdatsushimizu ** Nakanoto Climate Himi has a humid continental climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') characterized by mild summers and cold winters with heavy snowfall. The average annual temperature in Himi is 13.9 °C. The average annual rainfall is 2409 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on aver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hōdatsushimizu, Ishikawa
is a town located in Hakui District, Ishikawa Prefecture, Japan. , the town had an estimated population of 13,418 in 4962 households, and a population density of 84 persons per km2. The total area of the town was . In 2013, the Food and Agriculture Organization recognised Hōdatsushimizu under its Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS) programme as a sustainable agricultural model. Geography Hōdatsushimizu occupies the southern neck of Noto Peninsula, facing the Sea of Japan to the west and Toyama Prefecture to the east. It is one hour from Kanazawa by train. Mount Hōdatsu, the highest mountain in the Noto Peninsula, is in Hōdatsushimizu. The town has a humid continental climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') characterized by mild summers and cold winters with heavy snowfall. The average annual temperature in Hōdatsushimizu is 13.3 °C. The average annual rainfall is 2435 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shika, Ishikawa
is a town located in Hakui District, Ishikawa Prefecture, Japan. , the town had an estimated population of 20,845 in 8090 households, and a population density of 84 persons per km2. The total area of the town is . Geography Shika occupies the southwestern coastline of Noto Peninsula, facing the Sea of Japan on the west. It is one and a half hours from Kanazawa by car. Shika has a humid continental climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') characterized by mild summers and cold winters with heavy snowfall. The average annual temperature in Shika is 13.3 °C. The average annual rainfall is 2405 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 25.7 °C, and lowest in January, at around 2.5 °C. Part of the town is within the limits of the Noto Hantō Quasi-National Park. Neighbouring municipalities *Ishikawa Prefecture ** Nanao ** Wajima ** Hakui ** Anamizu ** Nakanoto Climate Demographics Per Japanese census data, the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |