|
Hajji Mohammad Ali Khan
Hajji Mohammad Ali Khan ( fa, حاجی محمدعلی خان) was the first khan (governor) of the Shirvan Khanate, ruling from 1761 to 1763. With the permission of the Zand ruler Karim Khan Zand (), he was put in power by the inhabitants of Old Shamakhi. He governed Shirvan until 1763, when Fath-Ali Khan of Quba Quba () is a city and the administrative centre of the Quba District of Azerbaijan. The city lies on the north-eastern slopes of Shahdag mountain, at an altitude of 600 metres above sea level, on the right bank of the Kudyal river. It has a po ... gained influence there, and appointed his own governors, such as Aghasi Beg and Askar Beg, both members of the same family. References Sources * Khans Shirvan Khanate Year of death unknown Year of birth unknown {{Iran-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khan (title)
Khan ''khan/qan''; tr, han; Azerbaijani: ''xan''; Ottoman: ''han''; Old Turkic: ''kan''; Chinese: 汗 ''hán''; Goguryeo: 皆 ''key''; Buyeo: 加 ''ka''; Silla: 干 ''kan''; Gaya: 旱 ''kan''; Baekje: 瑕 ''ke''; Manchu: ; Persian: خان; Punjabi: ਖ਼ਾਨ; Hindustani: ख़ान or ख़ां (Devanagari), or (Nastaleeq); Balochi: خان; Bulgarian: хан, ''khan''; Chuvash: хун, ''hun''; Arabic: خان; bn, খান or ) () is a historic Turko-Mongol title originating among nomadic tribes in the Central and Eastern Eurasian Steppe to refer to a chief or ruler. It first appears among the Rouran and then the Göktürks as a variant of khagan (sovereign, emperor) and implied a subordinate ruler. In the Seljuk Empire, it was the highest noble title, ranking above malik (king) and emir (prince). In the Mongol Empire it signified the ruler of a horde (''ulus''), while the ruler of all the Mongols was the khagan or great khan. The title subsequently de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
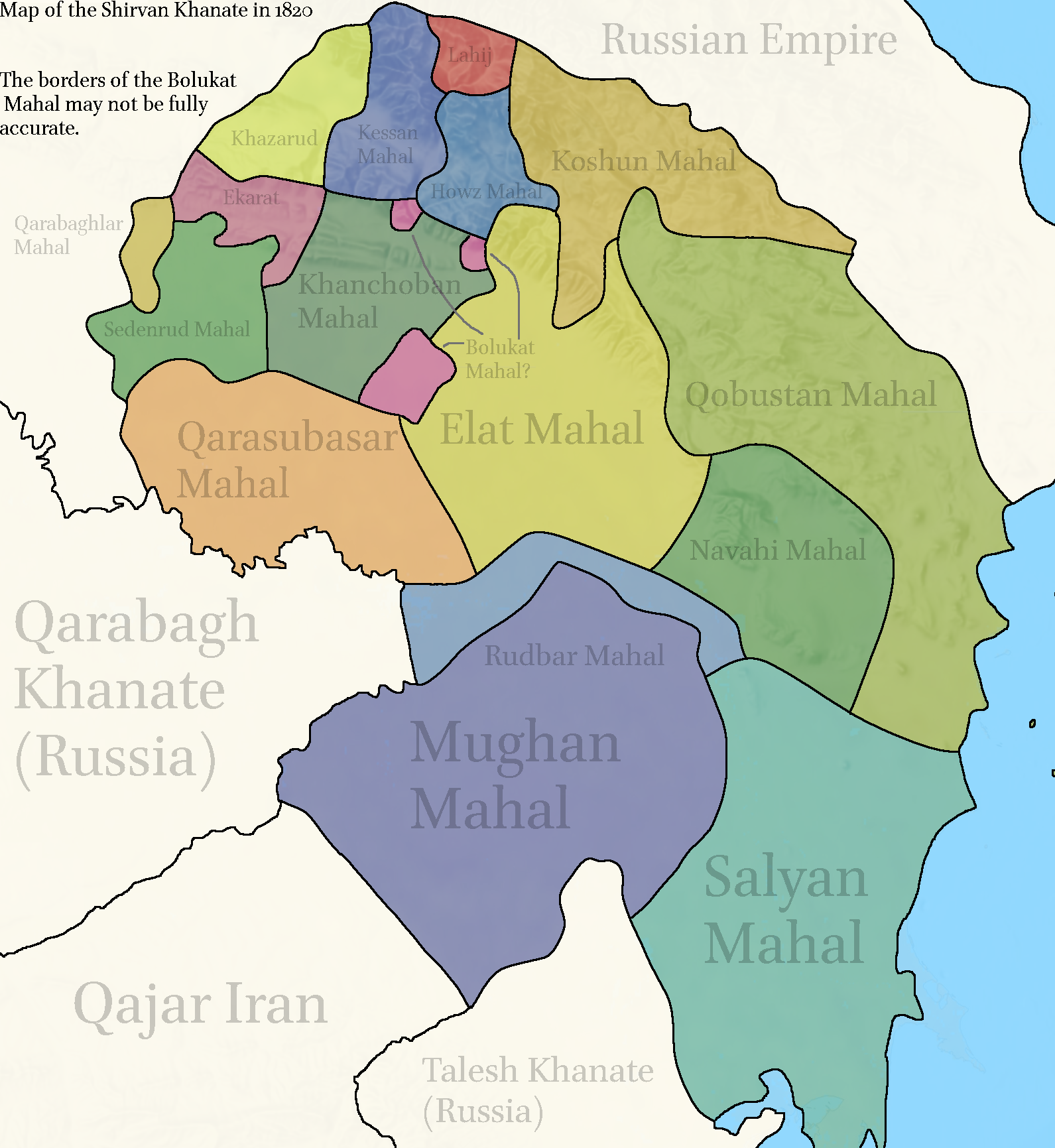
Shirvan Khanate
Shirvan Khanate ( fa, خانات شیروان, Khānāt-e Shirvan) was a Caucasian khanate under Iranian suzerainty, which controlled the Shirvan region from 1761 to 1820. Background Under the Safavid dynasty of Iran, Shirvan was a leading silk manufacturer and its principal city, Shamakhi, became an important place for trade. In 1724, most of Shirvan was annexed to the Ottoman Empire by the Treaty of Constantinople. In 1734, the Iranian military leader Nader recovered Shirvan and installed Mohammad Mehdi Khan as its ''beglarbeg'' (governor-general). The following year, Mohammad Mehdi Khan was killed by rebellious dignitaries of the province. They had been incited by the governor of Darband, Morad-Ali Soltan Ostajlu. Mohammad Qasem Beg, who was a prominent dignitary of Shirvan and Nader's ''ishikaghasi-bashi'' (chamberlain), successfully appealed to Nader to pardon Shirvan. In 1735, Nader had the inhabitants of Shamakhi resettled in New Shamakhi ( Aqsu), situated 18 miles north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zand Dynasty
The Zand dynasty ( fa, سلسله زندیه, ') was an Iranian dynasty, founded by Karim Khan Zand (1751–1779) that initially ruled southern and central Iran in the 18th century. It later quickly came to expand to include much of the rest of contemporary Iran (except for the provinces of Balochistan and Khorasan) as well as parts of Iraq. The lands of present-day Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia were controlled by khanates which were de jure part of the Zand realm, but the region was de facto autonomous. The island of Bahrain was also held for the Zands by the autonomous Al-Mazkur sheikhdom of Bushire. The reign of its most important ruler, Karim Khan, was marked by prosperity and peace. With its capital at Shiraz, arts and architecture flourished under Karim Khan's reign, with some themes in architecture being revived from the nearby sites of the Achaemenid (550–330 BC) and Sasanian (224–651 AD) era's of pre-Islamic Iran. The tombs of the medieval Persian poets Hafez a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karim Khan Zand
Mohammad Karim Khan Zand ( fa, محمدکریم خان زند, Mohammad Karīm Khân-e Zand; ) was the founder of the Zand Dynasty, ruling from 1751 to 1779. He ruled all of Iran (Persia) except for Khorasan. He also ruled over some of the Caucasian lands and occupied Basra for some years. While Karim was ruler, Iran recovered from the devastation of 40 years of war, providing the war-ravaged country with a renewed sense of tranquillity, security, peace, and prosperity. The years from 1765 to Karim Khan's death in 1779, marked the zenith of Zand rule. During his reign, relations with Britain were restored, and he allowed the East India Company to have a trading post in southern Iran. He made Shiraz his capital and ordered the construction of several architectural projects there. As noted by ''The Oxford Dictionary of Islam'', "Karim Khan Zand holds an enduring reputation as the most humane Iranian ruler of the Islamic era". When following the Islamic Revolution of 1979, the nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shamakhi
Shamakhi ( az, Şamaxı, ) is a city in Azerbaijan and the administrative centre of the Shamakhi District. The city's estimated population was 31,704. It is famous for its traditional dancers, the Shamakhi Dancers, and also for perhaps giving its name to the Soumak rugs. Eleven major earthquakes have rocked Shamakhi but through multiple reconstructions, it maintained its role as the economic and administrative capital of Shirvan and one of the key towns on the Silk Road. The only building to have survived eight of the eleven earthquakes is the landmark Juma Mosque of Shamakhi, built in the 8th century. History Shamakhi was in antiquity part of successive Persian empires and was first mentioned as ''Kamachia'' by the ancient Greco-Roman Egyptian geographer Claudius Ptolemaeus in the 1st to 2nd century AD. Shamakhi was an important town during the Middle Ages and served as a capital of the Shirvanshah realm from the 8th to 15th centuries. Shamakhi maintained economic and cult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quba Khanate
The Quba Khanate (also spelled Qobbeh; fa, خانات قبه, Khānāt-e Qobbeh) was one of the most significant semi-independent khanates that existed from 1747 to 1806, under Iranian suzerainty. It bordered Caspian sea to the east, Derbent Khanate to the north, Shaki Khanate to the west, and Baku and Shirvan Khanates to the south. In 1755 the khanate conquered Salyan from the Karabakh Khanate. History The khans of Quba were from the Qeytaq tribe, which was divided into two branches, the Majales and the Yengikend. The origin of the tribe is obscure. First attested in the 9th-century, only their chieftain and his family were Muslims, according to the historian al-Masudi (died 956). The chieftain bore the Turkic title of ''Salifan'', as well as the title of ''Kheydaqan-shah''. According to the 17th-century Ottoman historian, Evliya Çelebi (died 1682), the Qeytaq spoke Mongolian, but this was dismissed as a "hoax" by the Iranologist Vladimir Minorsky (died 1966), who demonstra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |