|
Hadar HaCarmel
Hadar HaCarmel ( he, הדר הכרמל lit. "''Splendor of the Carmel''"; or simply known as the neighbourhood of Hadar he, שכונת הדר, الهدار in Arabic) is a district of Haifa, Israel. Located on the northern slope of Mount Carmel between the upper and lower city overlooking the Port of Haifa and Haifa Bay, it was once the commercial center of Haifa. Etymology The name of the neighborhood is derived from a verse in Isaiah . History Hadar HaCarmel was founded before World War I. Shmuel Pevzner was one of the founders of the neighborhood and head of its development committee in 1922-1927. By 1944, most of Haifa's 66,000 Jewish residents lived in the district. Haifa's city hall, courthouse and government buildings were located in Hadar, but relocated to the lower city (Downtown) in the turn of the 21st century. Hadar has historically been characterized as a Jewish immigrant neighbourhood with many Holocaust survivors settled in the area, and in the early 1990s when m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadar And Carmel , several biblical characters, also known as Hadar
{{Disambiguation, geo, surname ...
Hadar may refer to: * Beta Centauri, a star * Hadar (narrowboat), a working narrow boat on UK canals Places * Hadar, Ethiopia * Hadar HaCarmel, Haifa, Israel * Hadar, Hod HaSharon, Israel * Tell Hadar, an archaeological site on the eastern coast of the Sea of Galilee * Hadar, Iran (other) * Hadar, Nebraska, US * Hader, Quneitra Governorate, Syria, also spelt Hadar People * Hadar (name) See also * Hadad (Bible) Multiple Bible, biblical characters with the name Hadad (Hadar) existed. *Hadad is the name of the Ancient Semitic religion, Semitic storm god. *Abraham's son Ishmael had a son named Hadar who was a chief. *Hadad ben Bedad, an early king of Edom. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carmelit
The Carmelit ( he, כַּרְמְלִית Arabic: كرمليت) is an underground funicular, funicular railway in Haifa, Israel. Construction started in 1956 and ended in 1959. It is the oldest underground transit system in the Middle East and currently the only underground transit system in Israel (until the expected 2023 opening of Tel Aviv Light Rail). The Carmelit has closed down for repair on three occasions. System The Carmelit, named after Mount Carmel, Israel, Mount Carmel through which it runs, is an underground funicular, funicular railway in Haifa. The difference in elevation between the first and last stations is . Carmelit cars have a slanted design, with steps within each car and on the station platform. Since the grade varies along the route, the floor of each car is never quite level, and slopes slightly "uphill" or "downhill" depending on the location, the only exception being Masada station. The Carmelit is the smallest subway system in the world, having only f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal House Of Justice
The Universal House of Justice ( fa, بیتالعدل اعظم) is the nine-member supreme ruling body of the Baháʼí Faith. It was envisioned by Baháʼu'lláh, the founder of the Baháʼí Faith, as an institution that could legislate on issues not already addressed in the Baháʼí writings, providing flexibility for the Baháʼí Faith to adapt to changing conditions. It was first elected in 1963, and subsequently every five years, by delegates consisting of the members of Baháʼí National Spiritual Assemblies throughout the world. The Universal House of Justice, as the head of the religion, has provided direction to the worldwide Baháʼí community primarily through a series of multi-year plans, as well as through annual messages delivered during the Ridván festival. The messages have focused on increasing the number of Local Spiritual Assemblies, translating Baháʼí literature, establishing Baháʼí Centres, completing Baháʼí Houses of Worship, holding in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrine Of The Báb
The Shrine of the Báb is a structure on the slopes of Mount Carmel in Haifa, Israel, where the remains of the Báb, founder of the Bábí Faith and forerunner of Baháʼu'lláh in the Baháʼí Faith, are buried; it is considered to be the second holiest place on Earth for Baháʼís, after the Shrine of Baháʼu'lláh in Acre. Its precise location on Mount Carmel was designated by Baháʼu'lláh himself to his eldest son, ʻAbdu'l-Bahá, in 1891. ʻAbdu'l-Bahá planned the structure, which was designed and completed several years later by his grandson, Shoghi Effendi. Crowning the design, as anticipated by ʻAbdu'l-Bahá, is a dome, which is set on an 18-windowed drum. That, in turn, is mounted on an octagon, a feature suggested by Shoghi Effendi. An arcade surrounds the stone edifice. A restoration project of the exterior and interior of the shrine started in 2008 and was completed in April 2011. History First mausoleum Bahá'u'lláh arrived in the Haifa-Akka region as a pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baháʼí Faith
The Baháʼí Faith is a religion founded in the 19th century that teaches the Baháʼí Faith and the unity of religion, essential worth of all religions and Baháʼí Faith and the unity of humanity, the unity of all people. Established by Baháʼu'lláh in the 19th century, it initially developed in Iran and parts of the Middle East, where it has faced ongoing Persecution of Baháʼís, persecution since its inception. The religion is estimated to have 5–8 million adherents, known as Baháʼís, spread throughout most of the world's countries and territories. The Baháʼí Faith has three central figures: the Báb (1819–1850), considered a herald who taught his followers that God would soon send a prophet similar to Jesus or Muhammad; the Báb was executed by Iranian authorities in 1850; Baháʼu'lláh (1817–1892), who claimed to be that prophet in 1863 and faced exile and imprisonment for most of his life; and his son, ʻAbdu'l-Bahá (1844–1921), who was released f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Arabs
Arab Christians ( ar, ﺍَﻟْﻤَﺴِﻴﺤِﻴُّﻮﻥ ﺍﻟْﻌَﺮَﺏ, translit=al-Masīḥīyyūn al-ʿArab) are ethnic Arabs, Arab nationals, or Arabic-speakers who adhere to Christianity. The number of Arab Christians who live in the Middle East is estimated to be between 10 and 15 million. Arab Christian communities can be found throughout the Arab world, but are concentrated in the Eastern Mediterranean region of the Levant and Egypt, with smaller communities present throughout the Arabian Peninsula and North Africa. The history of Arab Christians coincides with the history of Eastern Christianity and the history of the Arabic language; Arab Christian communities either result from pre-existing Christian communities adopting the Arabic language, or from pre-existing Arabic-speaking communities adopting Christianity. The jurisdictions of three of the five patriarchates of the Pentarchy primarily became Arabic-speaking after the early Muslim conquests – t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haifa Theatre 0401
Haifa ( he, חֵיפָה ' ; ar, حَيْفَا ') is the third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropolitan area in Israel. It is home to the Baháʼí Faith's Baháʼí World Centre, and is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a destination for Baháʼí pilgrimage. Built on the slopes of Mount Carmel, the settlement has a history spanning more than 3,000 years. The earliest known settlement in the vicinity was Tell Abu Hawam, a small port city established in the Late Bronze Age (14th century BCE).Encyclopedia Judaica, ''Haifa'', Keter Publishing, Jerusalem, 1972, vol. 7, pp. 1134–1139 In the 3rd century CE, Haifa was known as a dye-making center. Over the millennia, the Haifa area has changed hands: being conquered and ruled by the Canaanites, Israelites, Phoenicians, Assyrians, Babylonians, Persians, Hasmoneans, Romans, Byzantines, Arab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1990s Post-Soviet Aliyah
The 1990s post-Soviet aliyah began en masse in the late 1980s when the government of Mikhail Gorbachev opened the borders of the USSR and allowed Jews to leave the country for Israel. Between 1989 and 2006, about 1.6 million Soviet Jews and their non-Jewish spouses and their relatives, as defined by the Law of Return, emigrated from the former Soviet Union. About 979,000, or 61%, migrated to Israel. Another 325,000 migrated to the United States, and 219,000 migrated to Germany.Post-Soviet Aliyah and Jewish Demographic Transformation – Mark Tolts. According to the , 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab Citizens Of Israel
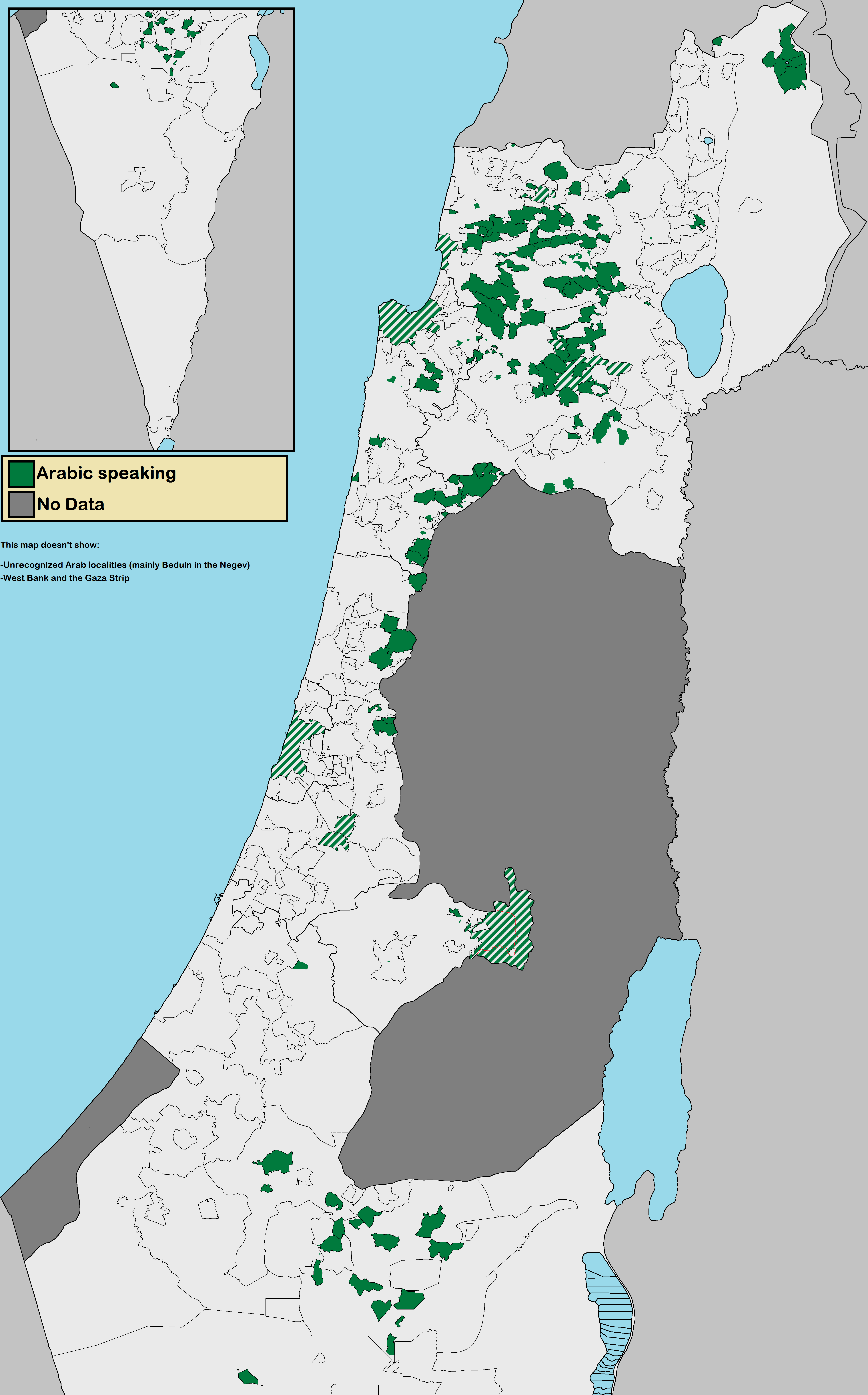
The Arab citizens of Israel are the largest ethnic minority in the country. They comprise a hybrid community of Israeli citizens with a heritage of Palestinian citizenship, mixed religions (Muslim, Christian or Druze), bilingual in Arabic and Hebrew, and with varying social identities. Self-identification as Palestinian citizens of Israel has sharpened in recent years, alongside distinct identities including Galilee and Negev Bedouin, the Druze people, and Arab Christians and Arab Muslims who do not identify as Palestinians. In Arabic, commonly used terms to refer to Israel's Arab population include 48-Arab ( ar, عرب 48, Arab Thamaniya Wa-Arba'in, label=none) and 48-Palestinian (). Since the Nakba, the Palestinians that have remained within Israel's 1948 borders have been colloquially known as "48-Arabs". In Israel itself, Arab citizens are commonly referred to as Israeli-Arabs or simply as ''Arabs''; international media often uses the term Arab-Israeli to distinguish Ara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beit HaGefen
Beit Ha'Gefen — The Arab-Jewish Cultural Center in Haifa is a multi-cultural organization that aims to bring together Arabs and Jews and promote coexistence and tolerance. Organisation Beit Ha'Gefen — The Arab-Jewish Cultural Center organizes and promotes interfaith social and cultural events. The center was established in 1963 by Haifa mayor Abba Hushi. Activities of the center include guided tours around Haifa, themed on coexistence, conferences and different cultural events. Center maintains Arab Language theatre, which is oldest such theatre in Israel Beit Ha'Gefen is an organiser of two major cultural events in Haifa: Holiday of Holidays in December, which is celebration of Ramadan, Christmas and Hanukka together and Arab Theater month in summer. Holiday of Holidays was first celebrated in December 1994, when all three Jewish, Muslim and Christian holidays happened at the same time. The main venue of this fortnight event is Wadi Nisnas neighbourhood, on outskirt of whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wadi Nisnas
Wadi Nisnas ( ar, وادي النسناس; he, ואדי ניסנאס) is a formerly mixed Jewish and Arab neighborhood in the city of Haifa in northern Israel, which is becoming mixed again. ''Nisnas'' is the Arabic word for mongoose, an indigenous animal. The ''wadi'' has a population of about 8,000 inhabitants. Wadi Nisnas was developed at the end of the nineteenth century as a Christian-Arab neighborhood outside the walls of Haifa, after 1948 the neighborhood become the center of Haifa Arab community, providing the community with education, religious, and other civic and cultural services. The current Israeli Central Bureau of Statistics census estimates that 66% of the Wadi Nisnas population are Christians, 31.5% are Muslims, and the rest are Jews. Wadi Nisnas is the setting for the 1987 novel, ''Hatsotsrah ba-Vadi'' (Hebrew: "Trumpet in the Wadi") by Sami Michael. It centers on the love story between a young Israeli Arab woman and a new Jewish immigrant from Russia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 in the region of Palestine under the terms of the League of Nations Mandate for Palestine. During the First World War (1914–1918), an Arab uprising against Ottoman rule and the British Empire's Egyptian Expeditionary Force under General Edmund Allenby drove the Ottoman Turks out of the Levant during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign. The United Kingdom had agreed in the McMahon–Hussein Correspondence that it would honour Arab independence if the Arabs revolted against the Ottoman Turks, but the two sides had different interpretations of this agreement, and in the end, the United Kingdom and France divided the area under the Sykes–Picot Agreementan act of betrayal in the eyes of the Arabs. Further complicating the issue was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |