|
Habitation Module
250px, ISS Habitation module under construction in December 1997 The Habitation Module was a particular habitation module for the International Space Station was intended to be the Station's main living quarters designed with galley, toilet, shower, sleep stations and medical facilities. About the size of a bus, the module was canceled after its pressurized hull was complete. If named and sent into space, the Habitation Module would have been berthed to ''Tranquility''. History In order to accommodate more than three people on the ISS, a lifeboat craft other than a single Soyuz TMA would be needed and such a Crew Return Vehicle The Crew Return Vehicle (CRV), sometimes referred to as the Assured Crew Return Vehicle (ACRV), was a proposed dedicated lifeboat or escape module for the International Space Station (ISS). A number of different vehicles and designs were conside ... was not there at that time. Later in the project, budget constraints and delays to the space station du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISS Habitation Module
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest Modular design, modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), European Space Agency, ESA (Europe), and Canadian Space Agency, CSA (Canada). The ownership and use of the space station is established by intergovernmental treaties and agreements. The station serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which Scientific research on the International Space Station, scientific research is conducted in astrobiology, astronomy, meteorology, physics, and other fields. The ISS is suited for testing the spacecraft systems and equipment required for possible future long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars. The International Space Station programme, ISS programme evolved from the Space Station Freedom, Space Station ''Freedom'', a 1984 American proposal to constr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitation Module
250px, ISS Habitation module under construction in December 1997 The Habitation Module was a particular habitation module for the International Space Station was intended to be the Station's main living quarters designed with galley, toilet, shower, sleep stations and medical facilities. About the size of a bus, the module was canceled after its pressurized hull was complete. If named and sent into space, the Habitation Module would have been berthed to ''Tranquility''. History In order to accommodate more than three people on the ISS, a lifeboat craft other than a single Soyuz TMA would be needed and such a Crew Return Vehicle The Crew Return Vehicle (CRV), sometimes referred to as the Assured Crew Return Vehicle (ACRV), was a proposed dedicated lifeboat or escape module for the International Space Station (ISS). A number of different vehicles and designs were conside ... was not there at that time. Later in the project, budget constraints and delays to the space station du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
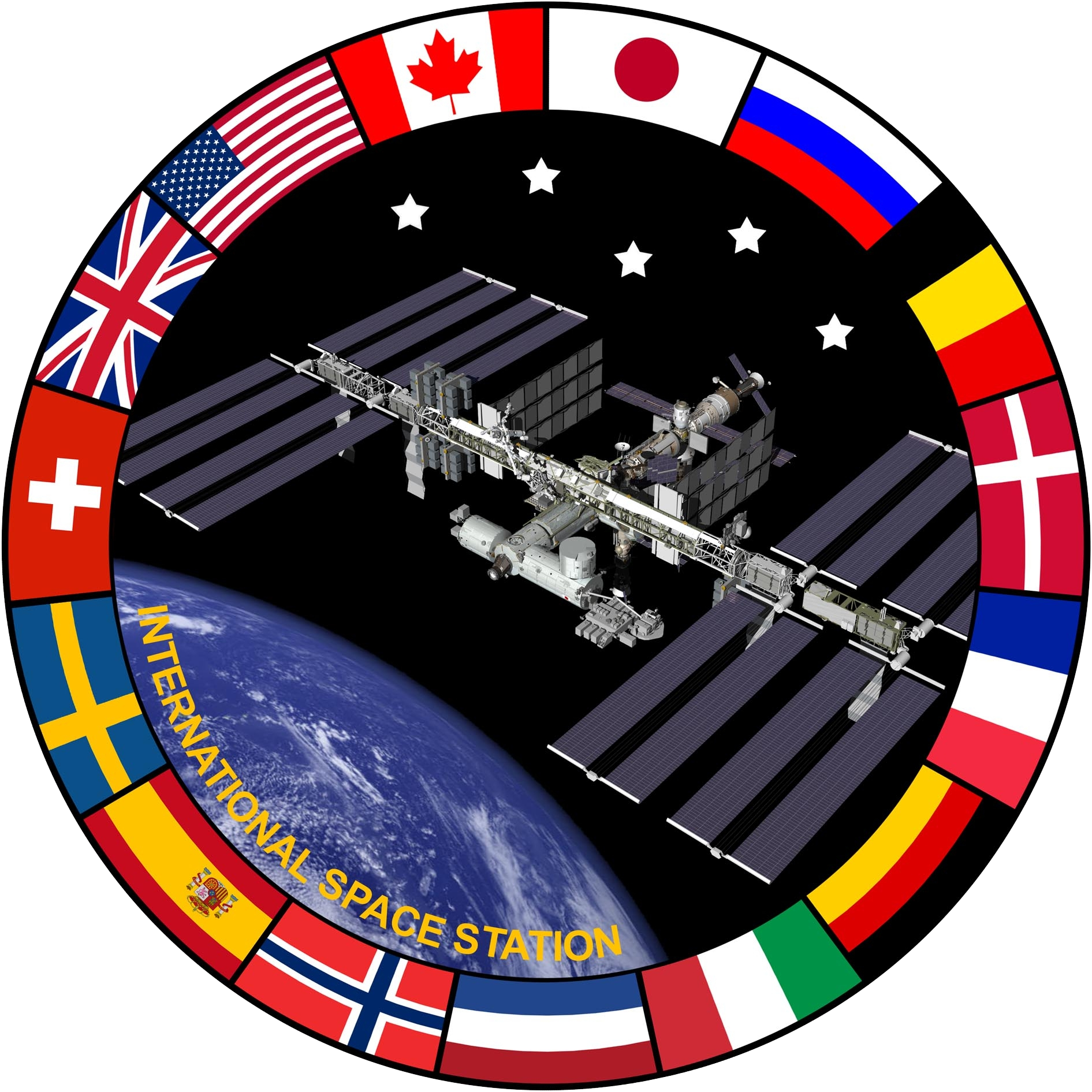
International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (Europe), and CSA (Canada). The ownership and use of the space station is established by intergovernmental treaties and agreements. The station serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which scientific research is conducted in astrobiology, astronomy, meteorology, physics, and other fields. The ISS is suited for testing the spacecraft systems and equipment required for possible future long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars. The ISS programme evolved from the Space Station ''Freedom'', a 1984 American proposal to construct a permanently crewed Earth-orbiting station, and the contemporaneous Soviet/Russian '' Mir-2'' proposal from 1976 with similar aims. The ISS is the ninth space station to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galley (kitchen)
The galley is the compartment of a ship, train, or aircraft where food is cooked and prepared. It can also refer to a land-based kitchen on a naval base, or, from a kitchen design point of view, to a straight design of the kitchen layout. Ship's cooking area A galley is the cooking area aboard a vessel, usually laid out in an efficient typical style with longitudinal units and overhead cabinets. This makes the best use of the usually limited space aboard ships. It also caters for the rolling and heaving nature of ships, making them more resistant to the effects of the movement of the ship. For this reason galley stoves are often gimballed, so that the liquid in pans does not spill out. They are also commonly equipped with bars, preventing the cook from falling against the hot stove. A small cooking area on deck was called a caboose or ''camboose'', originating from the nl, kombuis, which is still in use today. In English it is a defunct term used only for a cooking area that is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
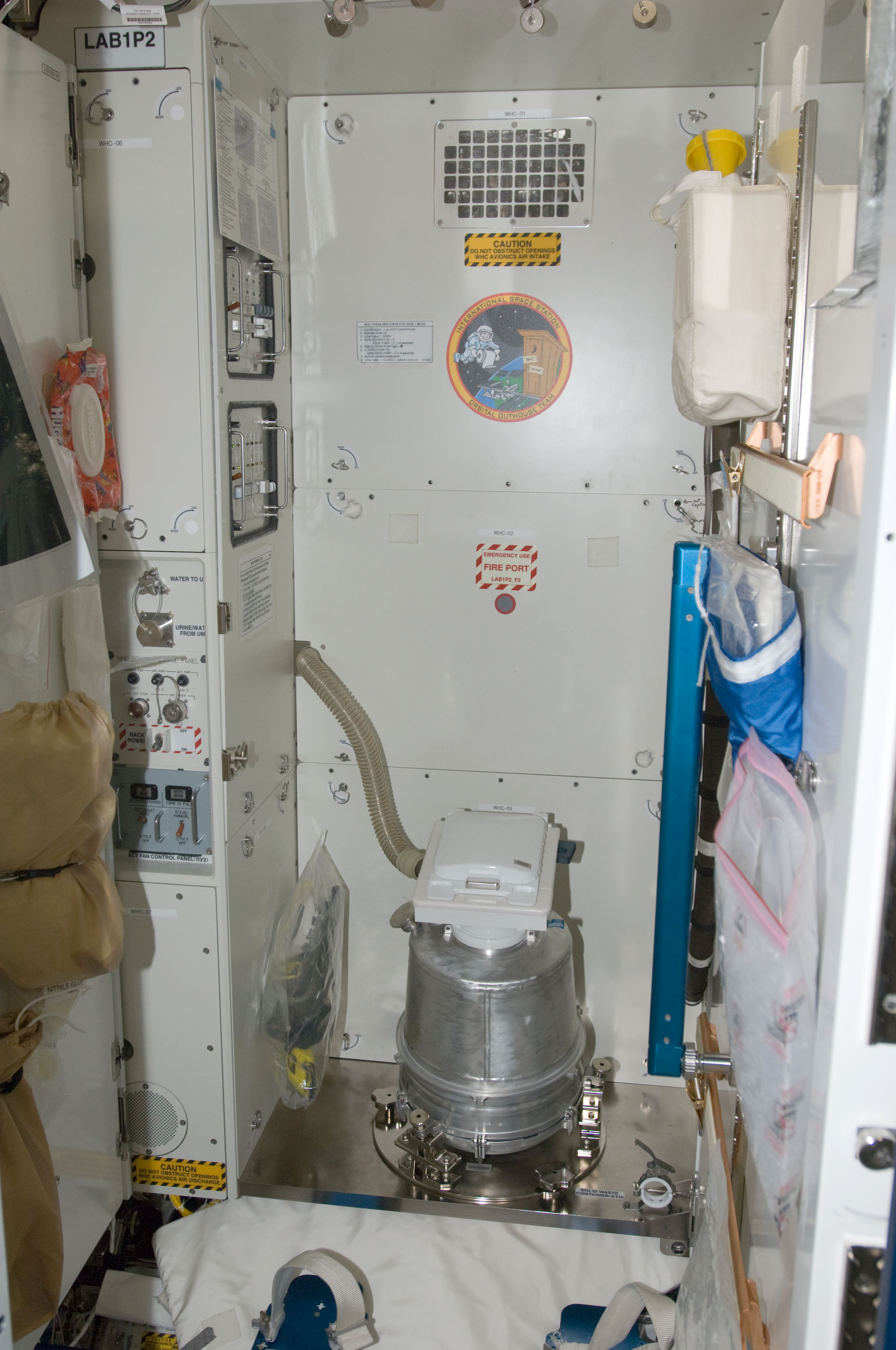
Toilet
A toilet is a piece of sanitary hardware that collects human urine and feces, and sometimes toilet paper, usually for disposal. Flush toilets use water, while dry or non-flush toilets do not. They can be designed for a sitting position popular in Europe and North America with a toilet seat, with additional considerations for those with disabilities, or for a squatting posture more popular in Asia (see squat toilet). In urban areas, flush toilets are usually connected to a sewer system that leads to septic tanks in isolated areas. The waste is known as '' blackwater'' and the combined effluent including other sources is sewage. Dry toilets are connected to a pit, removable container, composting chamber, or other storage and treatment device, including urine diversion with a urine-diverting toilet. The technology used for modern toilets varies. Toilets are commonly made of ceramic (porcelain), concrete, plastic, or wood. Newer toilet technologies include dual flushing, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tranquility (ISS Module)
''Tranquility'', also known as Node 3, is a module of the International Space Station (ISS). It contains environmental control systems, life support systems, a toilet, exercise equipment, and an observation cupola. The European Space Agency (ESA) and the Italian Space Agency (ASI) had ''Tranquility'' manufactured by Thales Alenia Space. A ceremony on 20 November 2009 transferred ownership of the module to NASA. On 8 February 2010, NASA launched the module on the Space Shuttle's STS-130 mission. Design and manufacturing ''Tranquility'' was built within the ESA-NASA ISS bartering system. ESA committed to build and fund both ''Harmony'' and ''Tranquility'' as well as the ATV in order to use NASA ISS facilities, fly astronauts on the Shuttle and for other ISS services. ESA teamed up with the Italian Space Agency (ASI) to manufacture both ''Harmony'' and ''Tranquility'' at Thales Alenia Space in Turin, Italy. The module pressure shell is constructed of 2219 aluminum and it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
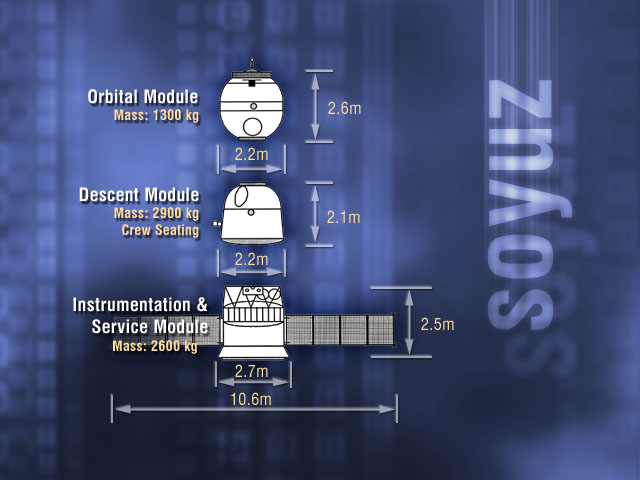
Soyuz Spacecraft
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraft and was originally built as part of the Soviet crewed lunar programs. It is launched on a Soyuz rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. Between the 2011 retirement of the Space Shuttle and the 2020 demo flight of SpaceX Crew Dragon, the Soyuz served as the only means to ferry crew to or from the International Space Station, for which it remains heavily used. Although China did launch crewed Shenzhou flights during this time, none of them docked with the ISS. History The first Soyuz flight was uncrewed and started on 28 November 1966. The first Soyuz mission with a crew, Soyuz 1, launched on 23 April 1967 but ended with a crash due to a parachute failure, killing cosmonaut Vladimir Komarov. The following flight was uncrew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crew Return Vehicle
The Crew Return Vehicle (CRV), sometimes referred to as the Assured Crew Return Vehicle (ACRV), was a proposed dedicated lifeboat or escape module for the International Space Station (ISS). A number of different vehicles and designs were considered over two decades – with several flying as developmental test prototypes – but none became operational. Since the arrival of the first permanent crew to the ISS in 2000, the emergency return capability has been fulfilled by Soyuz spacecraft and, more recently, SpaceX's Crew Dragon – each rotated every 6 months. In the original space station design, emergencies were intended to be dealt with by having a "safe area" on the station that the crew could evacuate to, pending a rescue from a U.S. Space Shuttle. However, the 1986 Space Shuttle ''Challenger'' disaster and the subsequent grounding of the shuttle fleet caused station planners to rethink this concept. Planners foresaw the need for a CRV to address three specific scenarios: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Shuttle Columbia Disaster
The Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disaster was a fatal accident in the United States space program that occurred on February 1, 2003. During the STS-107 mission, Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disintegrated as it reentered the atmosphere over Texas, killing all seven astronauts on board. The mission was the second that ended in disaster in the Space Shuttle program after the loss of ''Challenger'' and all seven crew members during ascent in 1986. During the STS-107 launch, a piece of the insulative foam broke off from the Space Shuttle external tank and struck the thermal protection system tiles on the orbiter's left wing. Similar foam shedding had occurred during previous Space Shuttle launches, causing damage that ranged from minor to near-catastrophic, but some engineers suspected that the damage to ''Columbia'' was more serious. Before reentry, NASA managers had limited the investigation, reasoning that the crew could not have fixed the problem if it had been confirmed. When ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TransHab
TransHab was a concept pursued by NASA in the 1990s to develop the technology for expandable habitats inflated by air in space. Specifically, TransHab was intended as a replacement for the already existing rigid International Space Station crew Habitation Module. When deflated, inflatable modules provide an 'easier to launch' compact form. When fully inflated, TransHab would expand to in diameter (compare to the diameter of the Columbus ISS Module). History The name of the project is a contraction of ''Transit Habitat'' reflecting the original intention to design an interplanetary vehicle to transfer humans to Mars. Considerable controversy arose during the TransHab development effort due to delays and increased costs of the ISS program. In 1999, the National Space Society issued a policy statement recommending that NASA continue R&D of inflatable technologies while ceasing development of a TransHab ISS module. Finally in 2000, despite objections from the White House, House ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bigelow Expandable Activity Module
The Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM) is an experimental expandable space station module developed by Bigelow Aerospace, under contract to NASA, for testing as a temporary module on the International Space Station (ISS) from 2016 to at most 2028, when the contract can not be extended any further. It arrived at the ISS on 10 April 2016, was berthed to the station on 16 April 2016, and was expanded and pressurized on 28 May 2016. Although originally planned to be a two year test, it has exceeded expectations and is used as additional cargo storage. The module is under ownership of NASA after Bigelow Aerospace suspended operations in 2021. History NASA originally considered the idea of inflatable habitats in the 1960s, and developed the TransHab inflatable module concept in the late 1990s. The TransHab project was canceled by Congress in 2000, and Bigelow Aerospace purchased the rights to the patents developed by NASA to pursue private space station designs. In 2006 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SpaceX CRS-8
SpaceX CRS-8, also known as SpX-8, was a Commercial Resupply Service mission to the International Space Station (ISS) which was launched on April 8, 2016, at 20:43 UTC. It was the 23rd flight of a Falcon 9 rocket, the tenth flight of a Dragon cargo spacecraft and the eighth operational mission contracted to SpaceX by NASA under the Commercial Resupply Services program. The capsule carried over of cargo to the ISS including the Bigelow Expandable Activity Module (BEAM), a prototype inflatable space habitat delivered in the vehicle's trunk, which was attached to the station and, as of May 2022, is expected to remain so for five more full years of in-orbit viability tests. After boosting the payload on its orbital trajectory, the rocket's first stage re-entered the denser layers of the atmosphere and landed vertically on the ocean landing platform ''Of Course I Still Love You'' nine minutes after liftoff, achieving a long-sought-after milestone in SpaceX reusable launch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




_(2).jpg)