|
Habitable Exoplanet Imaging Mission
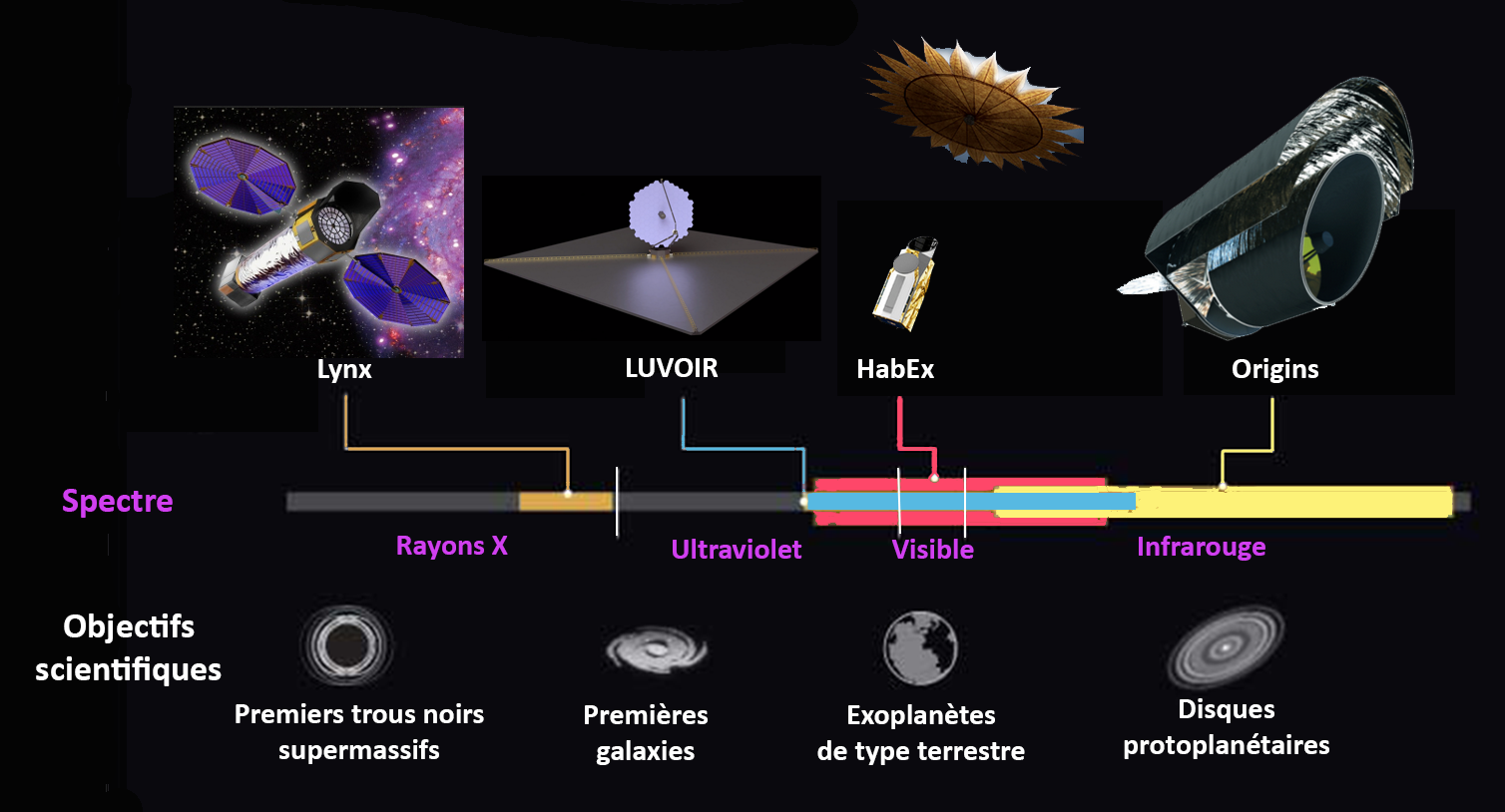
The Habitable Exoplanet Observatory (HabEx) is a space telescope concept that would be optimized to search for and image Earth-size habitable exoplanets in the habitable zones of their stars, where liquid water can exist. HabEx would aim to understand how common terrestrial worlds beyond the Solar System may be and determine the range of their characteristics. It would be an optical, UV and infrared telescope that would also use spectrographs to study planetary atmospheres and eclipse starlight with either an internal coronagraph or an external starshade. The proposal, first made in 2016, is for a large strategic science missions NASA mission. It would operate at the Lagrange point L2. Overview In 2016, NASA began considering four different space telescopes as the next Flagship (Large strategic science missions). They are the Habitable Exoplanet Observatory (HabEx), Large Ultraviolet Optical Infrared Surveyor (LUVOIR), Origins Space Telescope, and Lynx X-ray Surveyor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Observatory
A space telescope or space observatory is a telescope in outer space used to observe astronomical objects. Suggested by Lyman Spitzer in 1946, the first operational telescopes were the American Orbiting Astronomical Observatory, OAO-2 launched in 1968, and the Soviet Orion 1 ultraviolet telescope aboard space station Salyut 1 in 1971. Space telescopes avoid the filtering and distortion ( scintillation) of electromagnetic radiation which they observe, and avoid light pollution which ground-based observatories encounter. They are divided into two types: Satellites which map the entire sky (astronomical survey), and satellites which focus on selected astronomical objects or parts of the sky and beyond. Space telescopes are distinct from Earth imaging satellites, which point toward Earth for satellite imaging, applied for weather analysis, espionage, and other types of information gathering. History Wilhelm Beer and Johann Heinrich Mädler in 1837 discussed the advantages of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starlight
Starlight is the light emitted by stars. It typically refers to visible electromagnetic radiation from stars other than the Sun, observable from Earth at night, although a component of starlight is observable from Earth during daytime. Sunlight is the term used for the Sun's starlight observed during daytime. During nighttime, albedo describes solar reflections from other Solar System objects, including moonlight, planetshine, and zodiacal light. Observation Observation and measurement of starlight through telescopes is the basis for many fields of astronomy, including photometry and stellar spectroscopy. Hipparchus did not have a telescope or any instrument that could measure apparent brightness accurately, so he simply made estimates with his eyes. He sorted the stars into six brightness categories, which he called magnitudes.''Astronomy''. https://d3bxy9euw4e147.cloudfront.net/oscms-prodcms/media/documents/Astronomy-Draft-20160817.pdf: Rice University. 2016. p. 761. - via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosignature
A biosignature (sometimes called chemical fossil or molecular fossil) is any substance – such as an element, isotope, or molecule – or phenomenon that provides scientific evidence of past or present life. Measurable attributes of life include its complex physical or chemical structures and its use of free energy and the production of biomass and wastes. A biosignature can provide evidence for living organisms outside the Earth and can be directly or indirectly detected by searching for their unique byproducts. Types In general, biosignatures can be grouped into ten broad categories:NASA Astrobiology Strategy 2015 .(PDF), NASA # |
National Academies Of Sciences, Engineering, And Medicine
The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (also known as NASEM or the National Academies) are the collective scientific national academy of the United States. The name is used interchangeably in two senses: (1) as an umbrella term for its three quasi-independent honorific member organizations the National Academy of Sciences (NAS), the National Academy of Engineering (NAE), and the National Academy of Medicine (NAM); and (2) as the brand for studies and reports issued by the operating arm of the three academies, the National Research Council (NRC). The NRC was first formed in 1916 as an activity of the NAS. Now jointly governed by all three academies, the NRC produces some 200 publications annually which are published by the National Academies Press. The reports produced by the National Academies have been characterized as reflective of scientific consensus. History The US National Academy of Sciences was created by an Act of Incorporation dated March 3, 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as '' The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national " newspaper of record". For print it is ranked 18th in the world by circulation and 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 1896, through a dual-class share structure after its shares became publicly traded. A. G. Sulzberger, the paper's publisher and the company's chairman, is the fifth generation of the family to head the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extraterrestrial Atmosphere
The study of extraterrestrial atmospheres is an active field of research, both as an aspect of astronomy and to gain insight into Earth's atmosphere. In addition to Earth, many of the other astronomical objects in the Solar System have atmospheres. These include all the gas giants, as well as Atmosphere of Mars, Mars, Atmosphere of Venus, Venus and Titan (moon), Titan. Several Natural satellite, moons and other bodies also have atmospheres, as do comets and the Sun. There is evidence that extrasolar planets can have an atmosphere. Comparisons of these atmospheres to one another and to Earth's atmosphere broaden our basic understanding of atmospheric processes such as the greenhouse effect, aerosol and cloud physics, and atmospheric chemistry and dynamics. In September 2022, astronomers were reported to have formed a new group, called "Categorizing Atmospheric Technosignatures" (CATS), to list the results of exoplanet atmosphere studies for biosignatures, technosignatures and rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetary Science Decadal Survey
The Planetary Science Decadal Survey is a publication of the United States National Research Council produced for NASA and other United States Government Agencies such as the National Science Foundation.National Academy of Sciences, National Academies Press, http://www.nap.edu/download.php?record_id=13117 , ''Vision and Voyages for Planetary Science in the Decade 2013–2022'', 2011; . Retrieved February 23, 2015 The document identifies key questions facing planetary science and outlines recommendations for space and ground-based exploration ten years into the future. Missions to gather data to answer these big questions are described and prioritized, where appropriate. Similar decadal surveys cover astronomy and astrophysics, earth science, and heliophysics. As of 2022 there have been three "Decadals", one published in 2002 for the decade from 2003 to 2013, one in 2011 for 2013 to 2022, and one in 2022 for 2023 to 2032. The survey for 2023 to 2032 was released on April 19th, 2022. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Academy Of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the National Academy of Medicine (NAM). As a national academy, new members of the organization are elected annually by current members, based on their distinguished and continuing achievements in original research. Election to the National Academy is one of the highest honors in the scientific field. Members of the National Academy of Sciences serve '' pro bono'' as "advisers to the nation" on science, engineering, and medicine. The group holds a congressional charter under Title 36 of the United States Code. Founded in 1863 as a result of an Act of Congress that was approved by Abraham Lincoln, the NAS is charged with "providing independent, objective advice to the nation on matters related to science and technology. ... to provide scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lynx X-ray Observatory
The Lynx X-ray Observatory (''Lynx'') is a NASA-funded Large Mission Concept Study commissioned as part of the National Academy of Sciences 2020 Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey. The concept study phase is complete as of August 2019, and the ''Lynx'' final report has been submitted to the Decadal Survey for prioritization. If launched, ''Lynx'' would be the most powerful X-ray astronomy observatory constructed to date, enabling order-of-magnitude advances in capability over the current Chandra X-ray Observatory and XMM-Newton space telescopes. Background In 2016, following recommendations laid out in the so-called Astrophysics Roadmap of 2013, NASA established four space telescope concept studies for future Large strategic science missions. In addition to ''Lynx'' (originally called X-ray Surveyor in thRoadmap document'','' they are the Habitable Exoplanet Imaging Mission (HabEx), the Large Ultraviolet Optical Infrared Surveyor (LUVOIR), and the Origins Space Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Origins Space Telescope
Origins Space Telescope (Origins) is a concept study for a far-infrared survey space telescope mission.Preparing for the 2020 Decadal Survey Large Mission Concepts (PDF) , NASA A preliminary concept in pre-formulation, it was presented to the in 2019 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Ultraviolet Optical Infrared Surveyor
The Large Ultraviolet Optical Infrared Surveyor, commonly known as LUVOIR (), is a multi-wavelength space telescope concept being developed by NASA under the leadership of a Science and Technology Definition Team. It is one of four large astrophysics space mission concepts studied in preparation for the National Academy of Sciences 2020 Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey. While LUVOIR is a concept for a general-purpose observatory, it has the key science goal of characterizing a wide range of exoplanets, including those that might be habitable. An additional goal is to enable a broad range of astrophysics, from the reionization epoch, through galaxy formation and evolution, to star and planet formation. Powerful imaging and spectroscopy observations of Solar System bodies would also be possible. LUVOIR would be a Large Strategic Science Mission and was considered for a development start sometime in the 2020s. The LUVOIR Study Team, under Study Scientist Aki Roberge, ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Strategic Science Missions
NASA's large strategic science missions or large strategic missions, formerly known as Flagship missions or Flagship-class missions, are the costliest and most capable NASA science spacecraft. Flagship missions exist within all four divisions of NASA's Science Mission Directorate (SMD): the astrophysics, Earth science, heliophysics and planetary science divisions. "Large" refers to the budget of each mission, typically the most expensive mission in the scientific discipline. Within the Astrophysics Division and the Planetary Science Division, the large strategic missions are usually in excess of US$1 billion. Within Earth Science Division and Heliophysics Division, the large strategic missions are usually in excess of US$500 million.Powering Science: NASA's Large Strategic Science Missions (201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)

.png)