|
HNoMS Otto Sverdrup (F312)
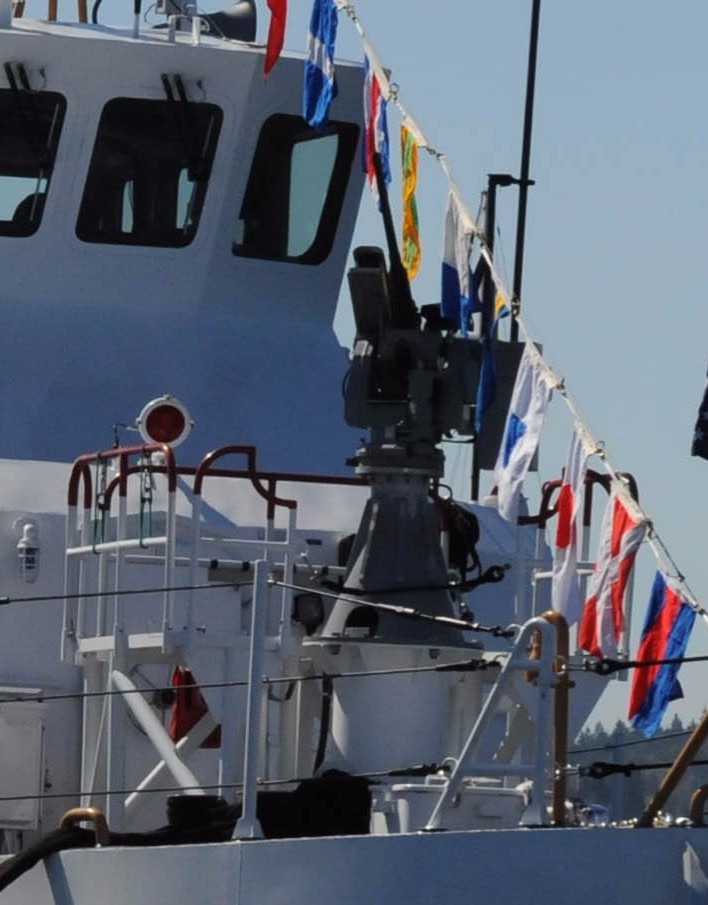
HNoMS ''Otto Sverdrup'' is a ''Fridtjof Nansen''-class frigate of the Royal Norwegian Navy. Construction and commissioning Built by the Spanish shipbuilders Navantia, in Ferrol, ''Otto Sverdrup'' was the third of the ''Fridtjof Nansen'' class to be launched and then commissioned into the Royal Norwegian Navy. Service In November 2017 ''Otto Sverdrup'' visited London's West India Dock The West India Docks are a series of three docks, quaysides and warehouses built to import goods from and export goods and occasionally passengers to the British West Indies on the Isle of Dogs in London the first of which opened in 1802. Follow ... with the Portuguese frigate ''Francisco de Almeida''. Both ships were part of Standing NATO Maritime Group 1 at the time. The current Captain of the Otto Sverdrup is Captain Iris Fivelstad. References External links * - Royal Norwegian Navy's page on the ''Fridtjof Nansen'' class {{DEFAULTSORT:Otto Sverdrup (F312) Frigates of Norway Frid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Sverdrup
Otto Neumann Knoph Sverdrup (31 October 1854, in Bindal, Helgeland – 26 November 1930) was a Norwegian sailor and Arctic explorer. Early and personal life He was born in Bindal as a son of farmer Ulrik Frederik Suhm Sverdrup (1833–1914) and his wife Petra Neumann Knoph (1831–1885). He was a great-grandnephew of Georg Sverdrup and Jacob Liv Borch Sverdrup, first cousin twice removed of Harald Ulrik Sverdrup (politician), Harald Ulrik and Johan Sverdrup, second cousin once removed of Jakob Sverdrup (politician), Jakob, Georg Sverdrup (theologian), Georg and Edvard Sverdrup, third cousin of Georg Johan Sverdrup, Georg Johan, Jakob Sverdrup (philologist), Jakob, Mimi Sverdrup Lunden, Mimi, Leif J. Sverdrup, Leif and Harald Sverdrup (oceanographer), Harald Ulrik Sverdrup. He was a brother-in-law of Johan Vaaler, and Otto himself married his own first cousin, Gretha Andrea Engelschiøn (1866–1937), in October 1891 in Oslo, Kristiania. Their daughter Audhild Sverdrup (1893– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigation, navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect objects on or under the surface of the water, such as other vessels. "Sonar" can refer to one of two types of technology: ''passive'' sonar means listening for the sound made by vessels; ''active'' sonar means emitting pulses of sounds and listening for echoes. Sonar may be used as a means of acoustic location and of measurement of the echo characteristics of "targets" in the water. Acoustic location in air was used before the introduction of radar. Sonar may also be used for robot navigation, and SODAR (an upward-looking in-air sonar) is used for atmospheric investigations. The term ''sonar'' is also used for the equipment used to generate and receive the sound. The acoustic frequencies used in sonar systems vary from very low (infrasonic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otobreda 127/54 Compact
The Otobreda 127mm/54 Compact (''127/54C'') gun is a dual purpose naval artillery piece built by the Italian company Oto Melara. It uses the 127mm round which is also used in the 5 inch/ 54 gun, albeit that this gun calibre is measured in United States customary units rather than metric. The gun uses an automatic loading system where 66 127mm rounds of various kinds can be stored ready-to-fire in three loader drums (each holding 22 rounds). The barrel is water-cooled. Currently the gun is still in use by navies around the world but it is slowly being replaced by the Otobreda 127/64 for new vessels, such as the German Navy's F125-class frigate and Italian Navy's FREMM. OTO Melara 127/64 A replacement of the 127/54 compact, Oto Melara started the design in 1992, and completed it in 2003. The new lightweight gun, weighing 17 tons without magazine or ammunition handling, has a rate of fire of 35 rpm, and can fire the long range guided Vulcano ammunition. Operators The Otobr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Range Acoustic Device
A long-range acoustic device (LRAD) is an acoustic hailing device (AHD), sound cannon and sonic weapon developed by Genasys. It has been used as a method of crowd control, which has caused permanent hearing damage, having an extremely high decibel capacity (up to 160 dB measured at one meter from the device). Other uses have included for negotiations in siege situations to deal with piracy at sea; for mass notification during natural disasters or other emergencies; and by defense forces, including several navies. History In October 2000 the , an American guided missile destroyer, was bombed in a terrorist attack by al-Qaeda operatives, using a small boat packed with explosives. The naval personnel on Cole were unable to be sure that their messages could be heard by the approaching boat at a sufficient distance to possibly avert the attack. The ship was badly damaged, 17 U.S. Navy sailors killed and 37 injured. Following this attack, navies around the world made severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protector (RWS)
The Protector RWS is a remotely controlled weapons station (RWS) that can be mounted to vehicles and stationary platforms. It has been in full scale production since December 2001. It is manufactured by Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace of Norway. Design The system consists of a stabilized firing platform, a fire-control system and control grips. Several weapons can be mounted to the platform, such as: * M2 Browning 12.7x99 .50 BMG heavy machine gun * NSV 12.7x108 heavy machine gun * M240/FN MAG 7.62×51mm NATO general-purpose machine gun * M249/FN Minimi 5.56×45mm NATO light machine gun * MK19 40×53 mm automatic grenade launcher * H&K GMG 40×53 mm automatic grenade launcher * XM307 Advanced Crew Served Weapon * Javelin anti-tank guided missile * Hellfire anti-tank guided missile (from a modified Protector) Versions Several versions of Protector have been developed with more than 20,000 units sold around the world in service with 23 countries. Between the M151 and M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Machine Gun
A heavy machine gun (HMG) is significantly larger than light machine gun, light, medium machine gun, medium or general-purpose machine guns. HMGs are typically too heavy to be man-portable (carried by one person) and require weapon mount, mounting onto a weapons platform to be operably stable or tactically mobility (military), mobile, have more formidable firepower, and generally Crew-served weapon, require a team of personnel for operation and maintenance. There are two generally recognized classes of weapons identified as HMGs. The first are weapons from World War I identified as "heavy" due to the weight and cumbersomeness of the weapons themselves, which prevents infantrymen from transporting on foot, such as the M1917 Browning machine gun. The second are large-caliber (12.7×99mm, 12.7×108mm, 14.5×114mm, or larger) machine guns, pioneered by John Browning with the M2 machine gun, designed to provide increased effective range, penetration (weapons), penetration and stopping ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M2 Browning Machine Gun
The M2 machine gun or Browning .50 caliber machine gun (informally, "Ma Deuce") is a heavy machine gun that was designed towards the end of World War I by John Browning. Its design is similar to Browning's earlier M1919 Browning machine gun, which was chambered for the .30-06 cartridge. The M2 uses Browning's larger and more powerful .50 BMG (12.7 mm) cartridge. The design has had many designations; the official U.S. military designation for the current infantry type is Browning Machine Gun, Cal. .50, M2, HB, Flexible. It is effective against infantry, unarmored or lightly armored vehicles and boats, light fortifications, and low-flying aircraft. The gun has been used extensively as a vehicle weapon and for aircraft armament by the United States since the 1930s. It was heavily used during World War II, the Korean War, the Vietnam War, the Falklands War, the Soviet–Afghan War, the Gulf War, the Iraq War, and the War in Afghanistan. It is the primary heavy machine gun of NATO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otobreda 76 Mm
The OTO Melara 76 mm gun is a naval gun built and designed by the Italian defence company OTO Melara. It is based on the OTO Melara 76/62C and evolved toward 76/62 SR and 76/62 Strales. The system is compact enough to be installed on relatively small warships. Its high rate of fire and the availability of several types of ammunition make it capable of short-range anti-missile point defence, anti-aircraft, anti-surface, and ground support. Ammunition includes armour-piercing, incendiary, directed fragmentation effects, and a guided round marketed as capable of destroying manoeuvring anti-ship missiles. It can be installed in a stealth cupola. The OTO Melara 76 mm has been widely exported, and is in use by sixty navies. It was favoured over the French 100mm naval gun for the joint French/Italian project and FREMM frigate. On 27 September 2006 Iran announced it had started mass production of a naval gun named the Fajr-27, which is a reverse-engineered OTO Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depth Charge
A depth charge is an anti-submarine warfare (ASW) weapon. It is intended to destroy a submarine by being dropped into the water nearby and detonating, subjecting the target to a powerful and destructive Shock factor, hydraulic shock. Most depth charges use explosive, high explosive charges and a fuze set to detonate the charge, typically at a specific depth. Depth charges can be dropped by ships, patrol aircraft, and helicopters. Depth charges were developed during World War I, and were one of the first viable methods of attacking a submarine underwater. They were widely used in World War I and World War II, and remained part of the anti-submarine arsenals of many navies during the Cold War, during which they were supplemented, and later largely replaced, by anti-submarine homing torpedoes. A depth charge fitted with a nuclear warhead is also known as a "nuclear depth bomb". These were designed to be dropped from a patrol plane or deployed by an anti-submarine missile from a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sting Ray Torpedo
The Sting Ray is a British acoustic homing lightweight torpedo (LWT) manufactured by GEC-Marconi, who were later bought out by BAE Systems. It entered service in 1983. Design and development In the 1950s the Royal Navy was equipped with British designed and built Mk 30 air-dropped torpedoes. These were passive homing weapons which relied on detecting the noise from submarine targets. However, as submarine noise levels decreased these weapons became ineffective. A design for a British Mk 31 torpedo which would have used active echo-location sonar failed to receive Government approval for production. US Mk 44 torpedoes were purchased for the Royal Navy in the 1960s to fill this role, and later replaced by US Mk 46 torpedoes. A desire not to be dependent on US torpedo purchases led to a research programme starting in 1964 to develop a British torpedo. Initially designated Naval and Air Staff Requirement (NASR) 7511, it was (much later in the late 1970s) designated the Sting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torpedo Tube
A torpedo tube is a cylindrical device for launching torpedoes. There are two main types of torpedo tube: underwater tubes fitted to submarines and some surface ships, and deck-mounted units (also referred to as torpedo launchers) installed aboard surface vessels. Deck-mounted torpedo launchers are usually designed for a specific type of torpedo, while submarine torpedo tubes are general-purpose launchers, and are often also capable of deploying naval mine, mines and cruise missiles. Most modern launchers are standardized on a diameter for light torpedoes (deck mounted aboard ship) or a diameter for heavy torpedoes (underwater tubes), although other sizes of torpedo tube have been used: see Torpedo#Classes and diameters, Torpedo classes and diameters. Submarine torpedo tube A submarine torpedo tube is a more complex mechanism than a torpedo tube on a surface ship, because the tube has to accomplish the function of moving the torpedo from the normal atmospheric pressure within t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface-to-surface Missile
A surface-to-surface missile (SSM) or ground-to-ground missile (GGM) is a missile designed to be launched from the ground or the sea and strike targets on land or at sea. They may be fired from hand-held or vehicle mounted devices, from fixed installations, or from a ship. They are often powered by a rocket engine or sometimes fired by an explosive charge, since the launching platform is typically stationary or moving slowly. They usually have fins and/or wings for lift and stability, although hyper-velocity or short-ranged missiles may use body lift or fly a ballistic trajectory. The V-1 flying bomb The V-1 flying bomb (german: Vergeltungswaffe 1 "Vengeance Weapon 1") was an early cruise missile. Its official Ministry of Aviation (Nazi Germany), Reich Aviation Ministry () designation was Fi 103. It was also known to the Allies as the buz ... was the first operational surface-to-surface missile. Contemporary surface-to-surface missiles are usually guided missile, guided. An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |