|
HMS Saltash
Seven ships of the Royal Navy have been named ''Saltash'': * , a 14-gun sloop launched at Plymouth in 1732 and sold out of service in 1741. * , a 14-gun sloop built at Rotherhithe in 1741 but wrecked off Portugal a year later. * , a 14-gun sloop, built at Rotherhithe in 1742 and sunk off Beachy Head in 1746. * , a 14-gun sloop built at Rotherhithe in 1746 and sold at the end of the Seven Years' War in 1763. * , a storeship built in 1748 and wrecked in 1752. * , a lighter built in 1809 and sold in 1831. * , a Hunt-class minesweeper of the ''Aberdare'' sub-class built for the Royal Navy during World War I and sold for scrap in 1947. Fiction * HMS ''Saltash'', a in the 1951 novel '' The Cruel Sea'' by Nicholas Monsarrat Lieutenant Commander Nicholas John Turney Monsarrat FRSL RNVR (22 March 19108 August 1979) was a British novelist known for his sea stories, particularly '' The Cruel Sea'' (1951) and ''Three Corvettes'' (1942–45), but perhaps known best i .... Referenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, to ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
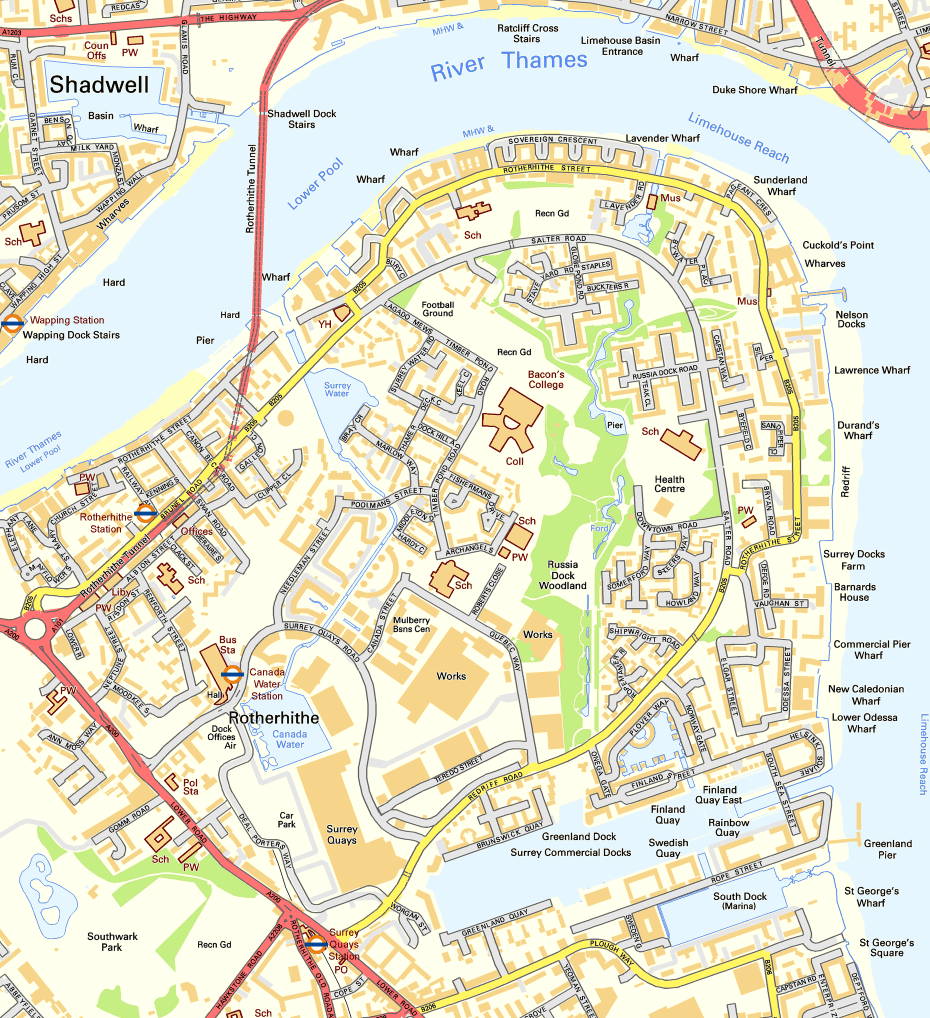
Rotherhithe
Rotherhithe () is a district of south-east London, England, and part of the London Borough of Southwark. It is on a peninsula on the south bank of the Thames, facing Wapping, Shadwell and Limehouse on the north bank, as well as the Isle of Dogs to the east of the Thames and is a part of the London Docklands, Docklands area. It borders Bermondsey to the west and Deptford to the south east. Rotherhithe has a long history as a port, with Elizabethan era, Elizabethan shipyards and working docks until the 1970s. In the 1980s, the area along the river was redeveloped as housing through a mix of warehouse conversions and new-build developments. Following the arrival of the Jubilee line in 1999 (giving quick connections to the West End of London, West End and to Canary Wharf) and the London Overground in 2010 (providing a quick route to the City of London), the rest of Rotherhithe is now a gentrification, gentrifying residential and commuter area, with urban regeneration progressing arou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beachy Head
Beachy Head is a chalk headland in East Sussex, England. It is situated close to Eastbourne, immediately east of the Seven Sisters. Beachy Head is located within the administrative area of Eastbourne Borough Council which owns the land, forming part of the Eastbourne Downland Estate. The cliff is the highest chalk sea cliff in Britain, rising to above sea level. The peak allows views of the south east coast towards Dungeness in the east, and to the Isle of Wight in the west. Geology The chalk was formed in the Late Cretaceous epoch, between 66 and 100 million years ago, when the area was under the sea. During the Cenozoic Era, the chalk was uplifted (see Cenozoic Era). When the last ice age ended, sea levels rose and the English Channel formed, cutting into the chalk to form the dramatic cliffs along the Sussex coast. Wave action contributes towards the erosion of cliffs around Beachy Head, which experience frequent small rock falls. Since chalk forms in layers separated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754–1763), the Carnatic Wars and the Anglo-Spanish War (1762–1763). The opposing alliances were led by Great Britain and France respectively, both seeking to establish global pre-eminence at the expense of the other. Along with Spain, France fought Britain both in Europe and overseas with land-based armies and naval forces, while Britain's ally Prussia sought territorial expansion in Europe and consolidation of its power. Long-standing colonial rivalries pitting Britain against France and Spain in North America and the West Indies were fought on a grand scale with consequential results. Prussia sought greater influence in the German states, while Austria wanted to regain Silesia, captured by Prussia in the previous war, and to contain Pruss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Storeship
Combat stores ships, or storeships, were originally a designation given to ships in the Age of Sail and immediately afterward that navies used to stow supplies and other goods for naval purposes. Today, the United States Navy and the Royal Navy operate modern combat store ships. The and es (for the US) and the and es (for the UK) provide supplies, including frozen, chilled and dry provisions, and propulsion and aviation fuel to combatant ships that are at sea for extended periods of time. Storeships should not be confused with fast combat support ships or tenders. Storeship Both the United States and the United Kingdom used stores ships in the War of 1812. In both the Mexican–American War and in the American Civil War, captured enemy prizes that were not considered "warlike" enough to be sold for prize money often became stores ships for a naval force operating where no friendly ports are nearby. took part in the Baja California Campaign in the Mexican–American War. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lighter (barge)
A lighter is a type of flat-bottomed barge used to transfer goods and passengers to and from moored ships. Lighters were traditionally unpowered and were moved and steered using long oars called "sweeps" and the motive power of water currents. They were operated by skilled workers called lightermen and were a characteristic sight in London's docks until about the 1960s, when technological changes made this form of lightering largely redundant. Unpowered lighters continue to be moved by powered tugs, however, and lighters may also now themselves be powered. The term is also used in the Lighter Aboard Ship (LASH) system. The name itself is of uncertain origin, but is believed to possibly derive from an old Dutch or German word, ''lichten'' (to lighten or unload). In Dutch, the word ''lichter'' is still used for smaller ships that take over goods from larger ships. Lighters, albeit powered ones, were proposed to be used in 2007 at Port Lincoln and Whyalla in South Australia to load ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minesweeper
A minesweeper is a small warship designed to remove or detonate naval mines. Using various mechanisms intended to counter the threat posed by naval mines, minesweepers keep waterways clear for safe shipping. History The earliest known usage of the naval mine dates to the Ming dynasty.Needham, Volume 5, Part 7, 203–205. Dedicated minesweepers, however, only appeared many centuries later during the Crimean War, where they were deployed by the British. The Crimean War minesweepers were rowboats trailing Grappling hook, grapnels to snag mines. Minesweeping technology picked up in the Russo-Japanese War, using aging torpedo boats as minesweepers. In Britain, naval leaders recognized before the outbreak of World War I that the development of sea mines was a threat to the nation's shipping and began efforts to counter the threat. Sir Arthur Wilson noted the real threat of the time was blockade aided by mines and not invasion. The function of the fishing fleet's trawlers with their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Class
A ship class is a group of ships of a similar design. This is distinct from a ship type, which might reflect a similarity of tonnage or intended use. For example, is a nuclear aircraft carrier (ship type) of the (ship class). In the course of building a class of ships, design changes might be implemented. In such a case, the ships of different design might not be considered of the same class; each variation would either be its own class, or a subclass of the original class (see for an example). If ships are built of a class whose production had been discontinued, a similar distinction might be made. Ships in a class often have names linked by a common factor: e.g. s' names all begin with T (, , ); and s are named after American battles (, , , ). Ships of the same class may be referred to as sister ships. Naval ship class naming conventions Overview The name of a naval ship class is most commonly the name of the lead ship, the first ship commissioned or built of its design. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Cruel Sea (novel)
''The Cruel Sea'' is a 1951 novel by Nicholas Monsarrat. It follows the lives of a group of Royal Navy sailors fighting the Battle of the Atlantic during the Second World War. It contains seven chapters, each describing a year during the war. The novel, based on the author's experience of serving in corvettes and frigates in the North Atlantic in the Second World War, gives a matter-of-fact but moving portrayal of ordinary men learning to fight and survive in a violent, exhausting battle against the elements and a ruthless enemy. Plot summary The action commences in 1939. Lieutenant-Commander George Ericson, a Merchant Navy and Royal Naval Reserve officer, is recalled to the Royal Navy and given command of the fictitious HMS ''Compass Rose'', newly built to escort convoys. His officers are mostly new to the Navy, especially the two new sub-lieutenants, Lockhart and Ferraby. Only Ericson and the petty officers are in any way experienced. Despite these initial disadvantages, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas Monsarrat
Lieutenant Commander Nicholas John Turney Monsarrat FRSL RNVR (22 March 19108 August 1979) was a British novelist known for his sea stories, particularly '' The Cruel Sea'' (1951) and ''Three Corvettes'' (1942–45), but perhaps known best internationally for his novels, ''The Tribe That Lost Its Head'' and its sequel, ''Richer Than All His Tribe''. Early life Monsarrat was born on Rodney Street in Liverpool, Lancashire, to parents Keith Waldegrave Monsarrat FRCS (among the most eminent surgeons of his time) and Marguerite Turney. Monsarrat was educated at Winchester College and Trinity College, Cambridge. In his autobiography, he wrote that the 1931 Invergordon Naval Mutiny influenced his interest in politics and social and economic issues after college. He had intended to practise law, but decided to pursue working as an author instead. He moved to London and wrote as a freelancer for newspapers. He wrote four novels and a play in the space of five years (1934–1939) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



