|
HMS Kingston (1697)
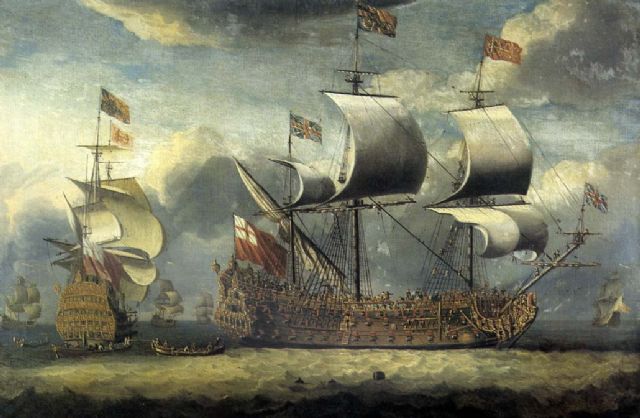
HMS ''Kingston'' was a 60-gun fourth-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built by Frame in Hull and launched on 13 March 1697. She had an eventful career, taking part in numerous engagements. Career During the War of Spanish Succession, ''Kingston'' took part in the engagements of Gibraltar (1704) under the command of Edward Acton, Vélez Málaga (1709) and Gaspé (1711). She was present at ''Wager's Action'' a naval confrontation on 8 June 1708 N.S (28 May O.S.), between a British squadron under Charles Wager and the Spanish treasure fleet, as part of the War of Spanish Succession. She was rebuilt for the first time according to the 1706 Establishment at Portsmouth Dockyard, and relaunched on 9 May 1719. She was rebuilt for a second time at Plymouth according to the 1733 proposals of the 1719 Establishment, and relaunched on 8 October 1740. ''Kingston'' was present at the Battle of Toulon in 1744. During the Seven Years' War, the ship was part of Admiral John B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a Sovereign state, sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England (which included Wales) and Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland to form a single kingdom encompassing the whole island of Great Britain and its outlying islands, with the exception of the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. The unitary state was governed by a single Parliament of Great Britain, parliament at the Palace of Westminster, but distinct legal systems – English law and Scots law – remained in use. The formerly separate kingdoms had been in personal union since the 1603 "Union of the Crowns" when James VI of Scotland became King of England and King of Ireland. Since James's reign, who had been the first to refer to himself as "king of Great Britain", a political un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
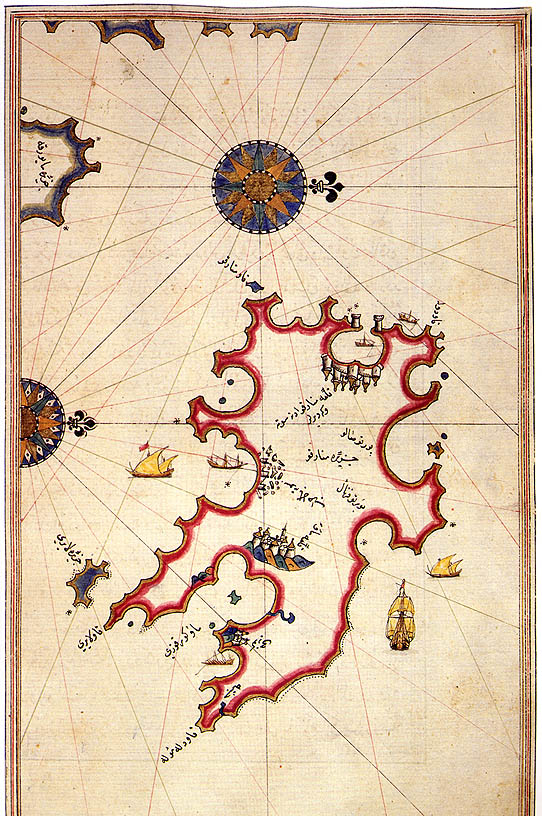
Menorca
Menorca or Minorca (from la, Insula Minor, , smaller island, later ''Minorica'') is one of the Balearic Islands located in the Mediterranean Sea belonging to Spain. Its name derives from its size, contrasting it with nearby Majorca. Its capital is Mahón ( ca, Maó), situated on the island's eastern end, although Menorca is not a province and forms a political union with the other islands in the archipelago. Ciutadella and Mahon are the main ports and largest towns. The port of Mahon is the second biggest natural port in the world. Menorca has a population of approximately 93,397 (at 1 January 2019). It is located 39°47' to 40°00'N, 3°52' to 4°24'E. Its highest point, called El Toro (from Catalan "''turó''" meaning ''hill''), is above sea level. History The island is known for its collection of megalithic stone monuments: ''navetes'', ''taules'' and ''talaiots'', which indicate very early prehistoric human activity. Some of the earliest culture on Menorca was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahón
Mahón (), officially Maó (), and also written as Mahon or Port Mahon in English, is the capital and second largest city of Menorca. The city is located on the eastern coast of the island, which is part of the archipelago and autonomous community of the Balearic Islands. Mahón has one of the longest natural harbours in the world: long and up to wide. The water is deep but remains mostly clear due to the port's enclosed nature. Mayonnaise is considered to have originated in Mahón. Its population in 2021 was estimated to be 29,125. History The name's origin is attributed to the Carthaginian general Mago Barca, brother to Hannibal, who is thought to have taken refuge there in 205 BC. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, it became part of the Eastern Roman Empire; it suffered raids from Vikings and Arabs until the Islamic Caliphate of Córdoba conquered it in 903. Mahón was captured in 1287 from the Moors by Alfonso III of Aragon and incorporated into the Kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Byng
Admiral John Byng (baptised 29 October 1704 – 14 March 1757) was a British Royal Navy officer who was court-martialled and executed by firing squad. After joining the navy at the age of thirteen, he participated at the Battle of Cape Passaro in 1718. Over the next thirty years he built up a reputation as a solid naval officer and received promotion to vice-admiral in 1747. He also served as Commodore-Governor of Newfoundland Colony in 1742, Commander-in-Chief, Leith, 1745 to 1746 and was a member of Parliament from 1751 until his death. Byng failed to relieve a besieged British garrison during the Battle of Minorca at the beginning of the Seven Years' War. He had sailed for Minorca at the head of a hastily assembled fleet of vessels, some of which were in poor condition. In the ensuing battle with a French fleet off the Minorcan coast, he was defeated and the fleet under his command considerably damaged. He then elected to return to Gibraltar to repair his ships. Upon ret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754–1763), the Carnatic Wars and the Anglo-Spanish War (1762–1763). The opposing alliances were led by Great Britain and France respectively, both seeking to establish global pre-eminence at the expense of the other. Along with Spain, France fought Britain both in Europe and overseas with land-based armies and naval forces, while Britain's ally Prussia sought territorial expansion in Europe and consolidation of its power. Long-standing colonial rivalries pitting Britain against France and Spain in North America and the West Indies were fought on a grand scale with consequential results. Prussia sought greater influence in the German states, while Austria wanted to regain Silesia, captured by Prussia in the previous war, and to contain Pruss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west. Plymouth's early history extends to the Bronze Age when a first settlement emerged at Mount Batten. This settlement continued as a trading post for the Roman Empire, until it was surpassed by the more prosperous village of Sutton founded in the ninth century, now called Plymouth. In 1588, an English fleet based in Plymouth intercepted and defeated the Spanish Armada. In 1620, the Pilgrim Fathers departed Plymouth for the New World and established Plymouth Colony, the second English settlement in what is now the United States of America. During the English Civil War, the town was held by the Roundhead, Parliamentarians and was besieged between 1642 and 1646. Throughout the Industrial Revolution, Plymouth grew as a commercial shipping port, handling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portsmouth Dockyard
His Majesty's Naval Base, Portsmouth (HMNB Portsmouth) is one of three operating bases in the United Kingdom for the Royal Navy (the others being HMNB Clyde and HMNB Devonport). Portsmouth Naval Base is part of the city of Portsmouth; it is located on the eastern shore of Portsmouth Harbour, north of the Solent and the Isle of Wight. Until the early 1970s, it was officially known as Portsmouth Royal Dockyard (or HM Dockyard, Portsmouth); thereafter the term 'Naval Base' gained currency, acknowledging a greater focus on personnel and support elements alongside the traditional emphasis on building, repairing and maintaining ships. In 1984 Portsmouth's Royal Dockyard function was downgraded and it was formally renamed the 'Fleet Maintenance and Repair Organisation' (FMRO). The FMRO was privatized in 1998, and for a time (from 2002 to 2014), shipbuilding, in the form of block construction, returned. Around 2000, the designation HMS ''Nelson'' (which until then had been specific to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Treasure Fleet
The Spanish treasure fleet, or West Indies Fleet ( es, Flota de Indias, also called silver fleet or plate fleet; from the es, label=Spanish, plata meaning "silver"), was a convoy system of sea routes organized by the Spanish Empire from 1566 to 1790, which linked Spain with its territories in the Americas across the Atlantic. The convoys were general purpose cargo fleets used for transporting a wide variety of items, including agricultural goods, lumber, various metal resources such as silver and gold, gems, pearls, spices, sugar, tobacco, silk, and other exotic goods from the overseas territories of the Spanish Empire to the Spanish mainland. Spanish goods such as oil, wine, textiles, books and tools were transported in the opposite direction. The West Indies fleet was the first permanent transatlantic trade route in history. Similarly, the related Manila galleon trade was the first permanent trade route across the Pacific. The Spanish West and East Indies fleets are considered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Wager
Admiral Sir Charles Wager (24 February 1666 – 24 May 1743) was a Royal Navy officer and politician who served as First Lord of the Admiralty from 1733 to 1742. Despite heroic active service and steadfast administration and diplomatic service, Wager can be criticized for his failure to deal with an acute manning problem. However, in reality, the Royal Navy's numerical preponderance over other navies was greater than at any other time in the century, and its dockyard facilities, overseas bases (Wager was much involved in the development of new bases in the Caribbean), victualling organization, and central co-ordination were by far the most elaborate and advanced. Although British warship design was inferior to French in some respects, the real problem was an insufficiency of the versatile and seaworthy 60-gun ships, a class that Wager's Admiralty had chosen to augment during the 1730s but, as wartime experience would show, not aggressively enough. Early life Born in Rocheste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wager's Action
Wager's Action was a naval confrontation on 8 June 1708 N.S (28 May O.S.), between a British squadron under Charles Wager and the Spanish treasure fleet, as part of the War of Spanish Succession. The battle ended in a British victory over the Spanish fleet. Background In the spring of 1708 Charles Wager was on an expedition in the Caribbean with a squadron of four ships: * '' Expedition'' (70 guns), Captain Henry Long * '' Kingston'' (60 guns), Captain Simon (Timothy) Bridges * ''Portland'' (50 guns), Captain Edward Windsor * ''Vulture'' (28 guns), fire ship under Commander Caesar Brooks In April the squadron took in supplies on the small island of Pequeña Barú, part of the Rosario Islands, just 30 miles away from Cartagena. Here the Spanish were aware of their presence, and the governor of Cartagena sent warnings to the Spanish fleet, which was anchored in Portobelo. Nevertheless, the commander of the treasure fleet, José Fernández de Santillán, decided to sail from Port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Walker Expedition To Quebec
The Quebec expedition, or the Walker expedition to Quebec, was a British attempt to attack Quebec in 1711 in Queen Anne's War, the North American theatre of the War of Spanish Succession. It failed when seven transports and one storeship were wrecked and some 850 soldiers drowned in one of the worst naval disasters in British history. The expedition was planned by the administration of Robert Harley, chief minister of the crown, and was based on plans originally proposed in 1708. Harley decided to mount the expedition as part of a major shift in British military policy, emphasizing strength at sea. The expedition's leaders, Admiral Hovenden Walker and Brigadier-General John Hill, were chosen for their politics and connections to the crown, and its plans were kept secret even from the Admiralty. French agents were able to discover British intentions and warn authorities in Quebec. The expedition expected to be fully provisioned in Boston, the capital of colonial Massachusett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |