|
HMS Iphigenia (1780)
HMS ''Iphigenia'' was a 32–gun fifth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She was launched in 1781, and served barely 20 years when she was accidentally lost in a fire at Alexandria in 1801. American War of Independence In 1782, ''Iphigenia'' was sent to the Jamaica station and served there for three years. In 1786, she paid off at Sheerness.http://www.ageofnelson.org/MichaelPhillips/info.php?ref=0143 Michael Phillips' ships of the old Navy French Revolutionary Wars After returning from Jamaica station, ''Iphigenia'' served on the Milford and Irish stations in the Irish Sea. In response to the French invasion of Belgium in the War of the First Coalition, at the end of 1792, she took part in the Scheldt expedition that was foiled by ice in the estuary. While operating in the English Channel, ''Iphigenia'' captured the French privateer ''Elizabeth'' on 16 February 1793. On 25 November 1793 ''Iphigenia'' and the frigate HMS ''Penelope'' engaged and captured the French 32-gun frigat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mistleythorn
Mistley is a large village and civil parish in the Tendring district of northeast Essex, England. It is around 11 miles northeast of Colchester and is east of, and almost contiguous with, Manningtree. The parish consists of Mistley and New Mistley, both lying beside the Stour Estuary, and Mistley Heath a kilometre to the south. Mistley railway station serves Mistley on the Mayflower Line. Mistley is the location of one of five Cold War control rooms in Essex. Built in 1951, it was opened as a museum called the Secret Bunker in 1996 but closed in 2002. History A Roman road leading from Mistley to the nearby provincial capital of Roman Britain at Camulodunum (modern Colchester) has led to the suggestion that there may have been a port in the vicinity of the modern village which served the town in the Roman period. Mistley is the village where Matthew Hopkins, the ''Witchfinder General'', was reputed to have lived, according to legend owning the Thorn Inn. He was buried a few ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval General Service Medal (1847)
__NOTOC__ The Naval General Service Medal (NGSM) was a campaign medal approved in 1847, and issued to officers and men of the Royal Navy in 1849. The final date for submitting claims was 1 May 1851.British Battles and Medals, page 34. Admiral Thomas Bladen Capel was one of the members of the board that authorised the medal. The NGSM was awarded retrospectively for various naval actions during the period 1793–1840, a period that included the French Revolutionary Wars, the Napoleonic Wars and the Anglo-American War of 1812. Each battle or campaign covered by the medal was represented by a clasp on the ribbon. The medal was never issued without a clasp, 231 of which were sanctioned.British Battles and Medals, page 33. The clasps covered a variety of actions, from boat service, ship to ship skirmishes, to major fleet actions such as the Battle of Trafalgar. This medal and its army counterpart, the Military General Service Medal, were amongst the first real British campaign medals, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fifth-rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a fifth rate was the second-smallest class of warships in a hierarchical system of six " ratings" based on size and firepower. Rating The rating system in the Royal Navy as originally devised had just four rates, but early in the reign of Charles I, the original fourth rate (derived from the "Small Ships" category under his father, James I) was divided into new classifications of fourth, fifth, and sixth rates. While a fourth-rate ship was defined as a ship of the line, fifth and the smaller sixth-rate ships were never included among ships-of-the-line. Nevertheless, during the Anglo-Dutch Wars of the 17th century, fifth rates often found themselves involved among the battle fleet in major actions. Structurally, these were two-deckers, with a complete battery on the lower deck, and fewer guns on the upper deck (below the forecastle and quarter decks, usually with no guns in the waist on this deck). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amazon-class Frigate (1773)
The ''Amazon''-class frigates of 1773, made up of 32-gun fifth rates with a main battery of 12-pounder guns. They were designed by the Surveyor of the Navy, John Williams during his employment by the Admiralty.https://threedecks.org/index.php?display_type=show_crewman&id=23268 The class comprised eighteen ships; ''Amazon'', ''Ambuscade'' and ''Thetis'' were launched in 1773; the second batch - ''Cleopatra'', ''Amphion'', ''Orpheus'', ''Juno'', ''Success'', ''Iphigenia'', ''Andromache'', '' Syren'', ''Iris'', ''Greyhound'', ''Meleager In Greek mythology, Meleager (, grc-gre, Μελέαγρος, Meléagros) was a hero venerated in his ''temenos'' at Calydon in Aetolia. He was already famed as the host of the Calydonian boar hunt in the epic tradition that was reworked by Ho ...'', , ''Solebay'', ''Terpsichore'' and ''Blonde'' - were launched in 1779 to 1787 References Fifth-rate frigates of the Royal Navy 1773 ships {{UK-mil-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sailing Frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied somewhat. The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuverability, intended to be used in scouting, escort and patrol roles. The term was applied loosely to ships varying greatly in design. In the second quarter of the 18th century, the 'true frigate' was developed in France. This type of vessel was characterised by possessing only one armed deck, with an unarmed deck below it used for berthing the crew. Late in the 19th century (British and French prototypes were constructed in 1858), armoured frigates were developed as powerful ironclad warships, the term frigate was used because of their single gun deck. Later developments in ironclad ships rendered the frigate designation obsolete and the term fell out of favour. During the Second World War the name 'frigate' was reintroduced to des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full-rigged Ship
A full-rigged ship or fully rigged ship is a sailing vessel's sail plan with three or more masts, all of them square-rigged. A full-rigged ship is said to have a ship rig or be ship-rigged. Such vessels also have each mast stepped in three segments: lower mast, top mast, and topgallant mast. Other large, multi-masted sailing vessels may be regarded as ships while lacking one of the elements of a full-rigged ship, e.g. having one or more masts support only a fore-and-aft sail or having a mast that only has two segments. Masts The masts of a full-rigged ship, from bow to stern, are: * Foremast, which is the second tallest mast * Mainmast, the tallest * Mizzenmast, the third tallest * Jiggermast, which may not be present but will be fourth tallest if so If the masts are of wood, each mast is in three or more pieces. They are (in order, from bottom up): * The lowest piece is called the ''mast'' or the ''lower''. * Topmast * Topgallant mast * Royal mast, if fitted On steel-m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
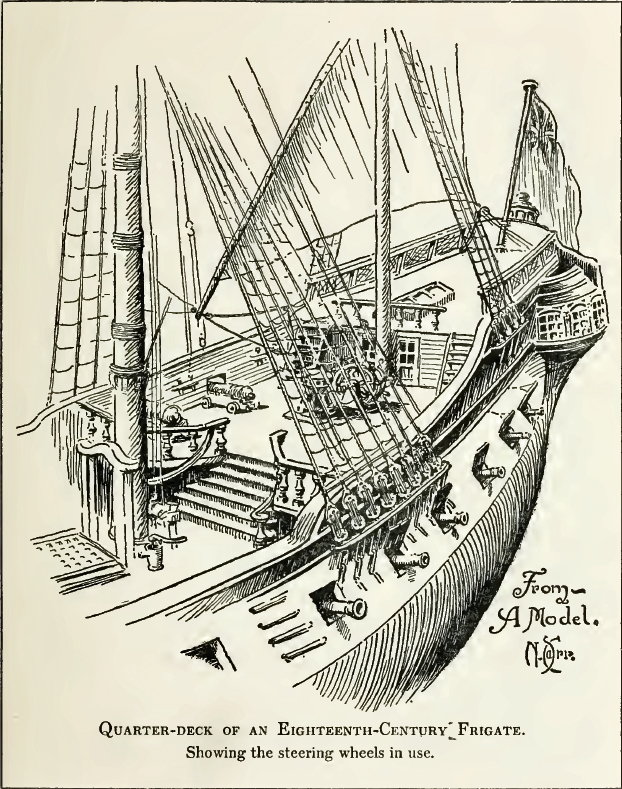
Quarterdeck
The quarterdeck is a raised deck behind the main mast of a sailing ship. Traditionally it was where the captain commanded his vessel and where the ship's colours were kept. This led to its use as the main ceremonial and reception area on board, and the word is still used to refer to such an area on a ship or even in naval establishments on land. Many such facilities have areas decorated like shipboard quarterdecks. In the 20th century the word came to be applied to the area at the stern of the ship, often (on naval vessels) used for secondary weapons and (on battleships) seaplane catapults. In modern military designs the stern has been roofed over by the helicopter deck but a large space remains underneath which is typically used for sonar equipment or small boats and which is still referred to as the quarterdeck in Commonwealth navies. Ceremonial use There are ancient traditions of offering special deference to the quarterdeck. Greek, Roman, and Carthaginian warships all c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forecastle
The forecastle ( ; contracted as fo'c'sle or fo'c's'le) is the upper deck of a sailing ship forward of the foremast, or, historically, the forward part of a ship with the sailors' living quarters. Related to the latter meaning is the phrase " before the mast" which denotes anything related to ordinary sailors, as opposed to a ship's officers. History and design In medieval shipbuilding, a ship of war was usually equipped with a tall, multi-deck castle-like structure in the bow of the ship. It served as a platform for archers to shoot down on enemy ships, or as a defensive stronghold if the ship were boarded. A similar but usually much larger structure, called the aftcastle, was at the aft end of the ship, often stretching all the way from the main mast to the stern. Having such tall upper works on the ship was detrimental to sailing performance. As cannons were introduced and gunfire replaced boarding as the primary means of naval combat during the 16th century, the medieval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carronade
A carronade is a short, smoothbore, cast-iron cannon which was used by the Royal Navy. It was first produced by the Carron Company, an ironworks in Falkirk, Scotland, and was used from the mid-18th century to the mid-19th century. Its main function was to serve as a powerful, short-range, anti-ship and anti-crew weapon. The technology behind the carronade was greater dimensional precision, with the shot fitting more closely in the barrel thus transmitting more of the propellant charge's energy to the projectile, allowing a lighter gun using less gunpowder to be effective. Carronades were initially found to be very successful, but they eventually disappeared as naval artillery advanced, with the introduction of rifling and consequent change in the shape of the projectile, exploding shells replacing solid shot, and naval engagements being fought at longer ranges. History The carronade was designed as a short-range naval weapon with a low muzzle velocity for merchant ships, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied somewhat. The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuverability, intended to be used in scouting, escort and patrol roles. The term was applied loosely to ships varying greatly in design. In the second quarter of the 18th century, the 'true frigate' was developed in France. This type of vessel was characterised by possessing only one armed deck, with an unarmed deck below it used for berthing the crew. Late in the 19th century (British and French prototypes were constructed in 1858), armoured frigates were developed as powerful ironclad warships, the term frigate was used because of their single gun deck. Later developments in ironclad ships rendered the frigate designation obsolete and the term fell out of favour. During the Second World War the name 'frigate' was reintroduced to des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, to ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Admiralty
The Admiralty was a department of the Government of the United Kingdom responsible for the command of the Royal Navy until 1964, historically under its titular head, the Lord High Admiral – one of the Great Officers of State. For much of its history, from the early 18th century until its abolition, the role of the Lord High Admiral was almost invariably put "in commission" and exercised by the Lords Commissioner of the Admiralty, who sat on the governing Board of Admiralty, rather than by a single person. The Admiralty was replaced by the Admiralty Board in 1964, as part of the reforms that created the Ministry of Defence and its Navy Department (later Navy Command). Before the Acts of Union 1707, the Office of the Admiralty and Marine Affairs administered the Royal Navy of the Kingdom of England, which merged with the Royal Scots Navy and the absorbed the responsibilities of the Lord High Admiral of the Kingdom of Scotland with the unification of the Kingdom of Great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)