|
HMS Glory
Ten ships of the Royal Navy have been named HMS ''Glory'', or the French variant HMS ''Gloire'': * was a 44-gun fifth rate, formerly the French 44-gun ship ''La Gloire'', captured from the French in 1747, and was sold to be broken up in 1763. * was a 32-gun fifth rate launched in 1763. She was renamed HMS ''Apollo'' in 1774 and was broken up in 1786. * was an 8-gun lugger, formerly the French ''Gloire''. She was captured in 1781 and broken up in 1783. * was a 98-gun second rate In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a second-rate was a ship of the line which by the start of the 18th century mounted 90 to 98 guns on three gun decks; earlier 17th-century second rates had fewer guns ... launched in 1788. She was converted to a prison ship in 1809, a powder hulk in 1814, and broken up in 1825. * HMS ''Gloire'' (1795) was the 32-gun French frigate ''Gloire'' captured from the French in 1795; she was sold in 1802. * was a 36-gun fifth r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, to ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fifth Rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a fifth rate was the second-smallest class of warships in a hierarchical system of six " ratings" based on size and firepower. Rating The rating system in the Royal Navy as originally devised had just four rates, but early in the reign of Charles I, the original fourth rate (derived from the "Small Ships" category under his father, James I) was divided into new classifications of fourth, fifth, and sixth rates. While a fourth-rate ship was defined as a ship of the line, fifth and the smaller sixth-rate ships were never included among ships-of-the-line. Nevertheless, during the Anglo-Dutch Wars of the 17th century, fifth rates often found themselves involved among the battle fleet in major actions. Structurally, these were two-deckers, with a complete battery on the lower deck, and fewer guns on the upper deck (below the forecastle and quarter decks, usually with no guns in the waist on this deck). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lugger
A lugger is a sailing vessel defined by its rig, using the lug sail on all of its one or several masts. They were widely used as working craft, particularly off the coasts of France, England, Ireland and Scotland. Luggers varied extensively in size and design. Many were undecked, open boats, some of which operated from beach landings (such as Hastings or Deal). Others were fully decked craft (typified by the Zulu and many other sailing drifters). Some larger examples might carry lug topsails. Luggers were used extensively for smuggling from the middle of the 18th century onwards; their fast hulls and powerful rigs regularly allowed them to outpace any Revenue vessel in service. The French three-masted luggers also served as privateers and in general trade. As smuggling declined about 1840, the mainmast of British three-masted luggers tended to be discarded, with larger sails being set on the fore and mizzen. This gave more clear space in which to work fishing nets. Local ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
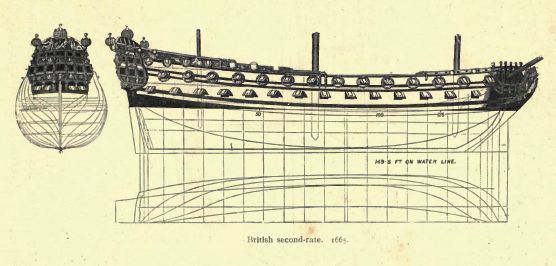
Second-rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a second-rate was a ship of the line which by the start of the 18th century mounted 90 to 98 guns on three gun decks; earlier 17th-century second rates had fewer guns and were originally two-deckers or had only partially armed third gun decks. A "second rate" was the second largest class of warships in a hierarchical system of six "ratings" based on size and firepower. They were essentially smaller and hence cheaper versions of the three-decker first rates. Like the first rates, they fought in the line of battle, but unlike the first rates, which were considered too valuable to risk in distant stations, the second rates often served also in major overseas stations as flagships. They had a reputation for poor handling and slow sailing. They were popular as flagships of admirals commanding the Windward and/or Leeward Islands station, which was usually a Rear-admiral of the red. Rating Typically measuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prison Ship
A prison ship, often more accurately described as a prison hulk, is a current or former seagoing vessel that has been modified to become a place of substantive detention for convicts, prisoners of war or civilian internees. While many nations have deployed prison ships over time, the practice was most widespread in 18th- and 19th-century Britain, as the government sought to address the issues of overcrowded civilian jails on land and an influx of enemy detainees from the War of Jenkins' Ear, the Seven Years' War and the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. History The terminology "hulk" comes from the Royal Navy meaning a ship incapable of full service either through damage or from initial non-completion. In England in 1776, during the reign of King George III, due to a shortage of prison space in London, the concept of "prison hulks" moored in the Thames, was introduced to meet the need for prison space. The first such ship came into use on 15 July 1776 under command o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Frigate Gloire (1778)
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to France ** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents ** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with France ** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices Fortnite French places Arts and media * The French (band), a British rock band * "French" (episode), a live-action episode of ''The Super Mario Bros. Super Show!'' * ''Française'' (film), 2008 * French Stewart (born 1964), American actor Other uses * French (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) * French (tunic), a particular type of military jacket or tunic used in the Russian Empire and Soviet Union * French's, an American brand of mustard condiment * French catheter scale, a unit of measurement of diameter * French Defence, a chess opening * French kiss, a type of kiss involving the tongue See also * France (other) * Franch, a surname * Frenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Frigate Iphigénie (1810)
The French frigate ''Iphigénie'' was a of a nominal 44 guns, launched in 1810. The British captured her in 1814. The British named her HMS ''Palma'', and then renamed her HMS ''Gloire''. She was sold in 1817, never having been commissioned into the Royal Navy. In 1813, along with ''Alcmène'', she served at Cherbourg, in the squadron of contre-amiral Amable Troude, to protect the harbour. Capture In early 1814, Commander Jean-Léon Émeric was put in charge of a two-frigate squadron comprising ''Iphigénie'' and ''Alcmène'', under Commander Ducrest de Villeneuve, for a cruise between the Azores and Cap-Vert, off Guinea. On 16 January 1814, the British 74-gun third-rate ship of the line , together with her prize, the ex-French letter of marque brig ''Jason'', and sixth-rate post ship were in company when they spotted ''Alcmène'' and ''Iphigénie''. After a chase that left ''Cyane'' far behind, ''Venerable'' captured ''Alcmène'' after a fight. ''Venerable'' lost tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depot Ship
A depot ship is an auxiliary ship used as a mobile or fixed base for submarines, destroyers, minesweepers, fast attack craft, landing craft, or other small ships with similarly limited space for maintenance equipment and crew dining, berthing and relaxation. Depot ships may be identified as tenders in American English. Depot ships may be specifically designed for their purpose or be converted from another purpose. Function Depot ships provide services unavailable from local naval base shore facilities. Industrialized countries may build naval bases with extensive workshops, warehouses, barracks, and medical and recreation facilities. Depot ships operating within such bases may provide little more than command staff offices,Lenton (1975) pp.391-394 while depot ships operating at remote bases may perform unusually diverse support functions. Some United States Navy submarine depot ships operating in the Pacific during World War II included sailors with Construction Battalion ratings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Cruiser Askold
''Askold'' (russian: Аскольд) was a protected cruiser built for the Imperial Russian Navy. She was named after the legendary Varangian Askold. Her thin, narrow hull and maximum speed of were considered impressive for the time. ''Askold'' had five thin funnels which gave it a unique silhouette for any vessel in the Imperial Russian Navy. This led British sailors to nickname her ''Packet of Woodbines'' after the thin cigarettes popular at the time. However, the five funnels also had a symbolic importance, as it was popularly considered that the number of funnels was indicative of performance, and some navies were known to add extra fake funnels to impress dignitaries in less advanced countries. Background After the completion of the , the Imperial Russian Navy issued requirements for three large protected cruisers to three separate companies: was ordered from William Cramp & Sons in Philadelphia, United States, ''Askold'' was ordered from Krupp- Germaniawerft in Kiel, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy Ship Names
There are two lists of Royal Navy ships: * List of active Royal Navy ships lists all currently commissioned vessels in the Royal Navy. * List of ship names of the Royal Navy lists all names that Royal Navy ships ever bore. See also * *{{Portal-inline, War *Bibliography of 18th–19th century Royal Naval history * List of Royal Navy vessels active in 1981 * List of Royal Navy vessels active in 1982 The following vessels were in commission, planned or under construction for HM Royal Navy in 1982. Many of these vessels took part in the 1982 Falklands War. Aircraft Carriers * – . * – , , & . The carriers ''Hermes'' and ''Invincible'' wer ... List of Royal Navy ships List of Royal Navy ships ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


.jpg)
.jpg)