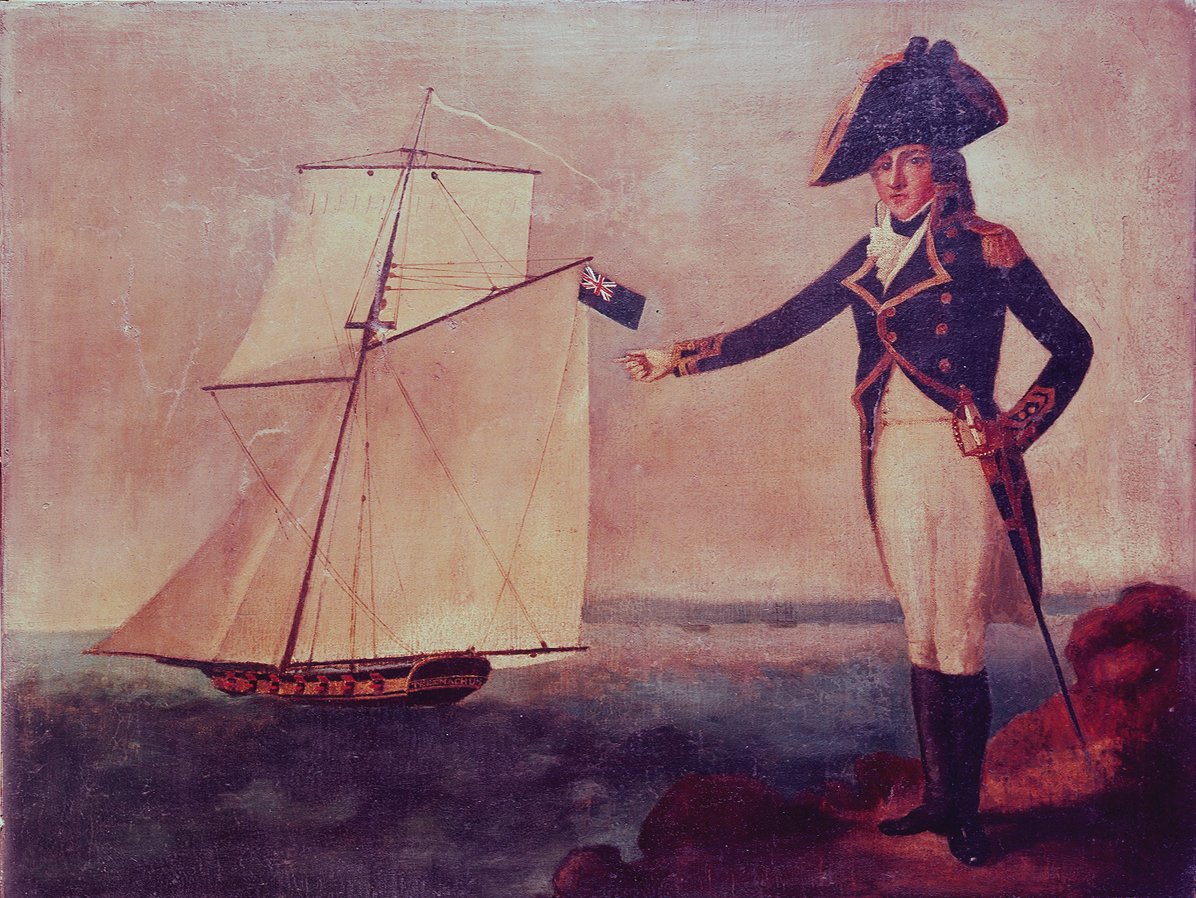|
HMS Doris (1795)
HMS ''Doris'' was a 36-gun fifth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy, launched on 31 August 1795. which saw service in the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. ''Doris'' was built by Cleveley, of Gravesend. Service She entered service in November 1795, operating as part of the Channel Fleet during the Napoleonic Wars. Her first captain was the Hon. Charles Jones, who in 1797 became Lord Ranelagh. In June 1796, ''Doris'' and captured the French corvette ''Légère'', of twenty-two 9-pounder guns and 168 men. ''Légère'' had left Brest on 4 June in company with three frigates. During her cruise she had captured six prizes. However, on 23 June she encountered the two British frigates at . After a 10-hour chase the British frigates finally caught up with her; a few shots were exchanged and then ''Légère'' struck. The Navy took into her service as HMS ''Legere''. In January 1797 ''Doris'' shared with and in the capture of the French privateer ''Eclair''. ''Unicorn'' was th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Donegal (1798)
HMS ''Donegal'' was launched in 1794 as ''Barra'', a 74-gun ship of the line of the French Navy. She was renamed ''Pégase'' in October 1795, and ''Hoche'' in December 1797. The British Royal Navy captured her at the Battle of Tory Island on 12 October 1798 and recommissioned her as HMS ''Donegal''. Capture ''Hoche'' took part in the French attempt to land in County Donegal, in the west of Ulster, to support the Irish Rebellion of 1798. She formed the flagship of an expedition under Commodore Jean-Baptiste-François Bompart, consisting of ''Hoche'' and eight frigates, and transporting 3,000 French troops. Aboard ''Hoche'' was Wolfe Tone, the leading figure in the Society of United Irishmen. The ships were chased by a number of British frigates after they had left the port of Brest on 16 September. Despite throwing them off, they were then pursued by a fleet of larger ships under the command of Commodore Sir John Borlase Warren. Both sides were hampered by the heavy wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duguay-Trouin (French Privateer)
During the late 18th and early 19th centuries, many French privateers and letters of marque bore the name ''Duguay-Trouin'', named for René Duguay-Trouin: René Trouin, Sieur du Gué (10 June 1673–1736), French privateer, admiral and Commander in the Order of Saint Louis. Between 1760 and 1810, warships of the Royal Navy captured seven different French privateers all with the name ''Duguay-Trouin''. In British records the name is sometimes given as ''Du Guay Trouin'', ''Dugai Trouin'', ''Drigai Trouin'', or ''Guay Trouin''. * ''Du Guay Trouin'', a privateer that captured on 30 December 1760. * was a 150-tonne French privateer sloop of 168 men and 18 to 20 guns, under Pierre-Denis Ducassou, that captured in on 29 January 1780 and brought to Plymouth where the British Royal Navy took her into service. The Navy sold ''Duguay-Trouin'' on 30 October 1783. She then became the mercantile West Indiaman and slaver ''Christopher'', and was lost in 1804. * Privateer ''Duguay-Trouin' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peace Of Amiens
The Treaty of Amiens (french: la paix d'Amiens, ) temporarily ended hostilities between France and the United Kingdom at the end of the War of the Second Coalition. It marked the end of the French Revolutionary Wars; after a short peace it set the stage for the Napoleonic Wars. Britain gave up most of its recent conquests; France was to evacuate Naples and Egypt. Britain retained Ceylon (Sri Lanka) and Trinidad. It was signed in the city of Amiens on 25 March 1802 (4 Germinal X in the French Revolutionary calendar) by Joseph Bonaparte and Marquess Cornwallis as a "Definitive Treaty of Peace". The consequent peace lasted only one year (18 May 1803) and was the only period of general peace in Europe between 1793 and 1814. Under the treaty, Britain recognised the French Republic. Together with the Treaty of Lunéville (1801), the Treaty of Amiens marked the end of the Second Coalition, which had waged war against Revolutionary France since 1798. National goals Great Britain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Victory
HMS ''Victory'' is a 104-gun first-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, ordered in 1758, laid down in 1759 and launched in 1765. She is best known for her role as Lord Nelson's flagship at the Battle of Trafalgar on 21 October 1805. She additionally served as Keppel's flagship at Ushant, Howe's flagship at Cape Spartel and Jervis's flagship at Cape St Vincent. After 1824, she was relegated to the role of harbour ship. In 1922, she was moved to a dry dock at Portsmouth, England, and preserved as a museum ship. She has been the flagship of the First Sea Lord since October 2012 and is the world's oldest naval ship still in commission, with years' service as of . Construction In December 1758, William Pitt the Elder, in his role as head of the British government, placed an order for the building of 12 ships, including a first-rate ship that would become ''Victory''. During the 18th century, ''Victory'' was one of ten first-rate ships to be constructed. The outline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieutenant
A lieutenant ( , ; abbreviated Lt., Lt, LT, Lieut and similar) is a commissioned officer rank in the armed forces of many nations. The meaning of lieutenant differs in different militaries (see comparative military ranks), but it is often subdivided into senior (first lieutenant) and junior (second lieutenant and even third lieutenant) ranks. In navies, it is often equivalent to the army rank of captain; it may also indicate a particular post rather than a rank. The rank is also used in fire services, emergency medical services, security services and police forces. Lieutenant may also appear as part of a title used in various other organisations with a codified command structure. It often designates someone who is " second-in-command", and as such, may precede the name of the rank directly above it. For example, a "lieutenant master" is likely to be second-in-command to the "master" in an organisation using both ranks. Political uses include lieutenant governor in various g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goulet De Brest
The Goulet de Brest is a 3-km-long strait linking the roadstead of Brest to the Atlantic Ocean. Only 1.8 km wide, the is situated between the Pointe du Petit Minou and the Pointe du Portzic to the north and the îlot des Capucins and the Pointe des Espagnols to the south. At each turn of the tide, the ocean refills the roadstead in a current that can attain 4 to 5 knots. Sailing ships would thus wait in the cove of Camaret-sur-Mer for a favourable current to carry them into the . On 2 January 1793, the ''Childers'' Incident – the first shots of the war between Great Britain and France during the French Revolutionary Wars – took place in the . Military significance It is the only opening into the roadstead of Brest, and thus the only access to the town. Consequently, successive French governments have lined the with military installations to protect the town and the naval fleet based there, and to keep a watch on shipping using it. The geography of the favours ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hired Armed Cutter Telemachus
His Majesty's hired armed cutter ''Telemachus'' served the Royal Navy from 17 June 1795 until 15 January 1801. She was of 128 tons (bm), and carried fourteen 4-pounder guns. During her five and a half years of service to the Royal Navy she captured eight French privateers as well as many merchant vessels. Naval service On 5 August 1796 she was under the command of Lieutenant John Crispo when off The Needles she sailed in pursuit of a sloop and a cutter, which fled to the east. At 11am ''Telemachus'' caught up with the sloop, recapturing ''John''. ''John'', William Ayles, master, was of Weymouth and had been sailing with a cargo of coal when the enemy cutter had captured her. Crispo quickly took charge of ''John'' and then sailed in the pursuit of the enemy cutter. ''Telemachus'' caught up with the cutter off the Owers Bank at half-past two in the afternoon, and fired a shot, at which point the cutter struck. She proved to be the French privateer ''Marguarita'', armed with four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
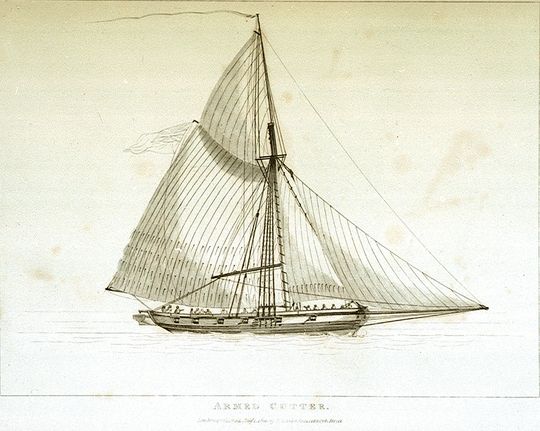
Cutter (ship)
A cutter is a type of watercraft. The term has several meanings. It can apply to the rig (or sailplan A sail plan is a description of the specific ways that a sailing craft is rigged. Also, the term "sail plan" is a graphic depiction of the arrangement of the sails for a given sailing craft.> In the English language, ships were usually describe ...) of a sailing vessel (but with regional differences in definition), to a governmental enforcement agency vessel (such as a coast guard or border force cutter), to a type of ship's boat which can be used under sail or oars, or, historically, to a type of fast-sailing vessel introduced in the 18th century, some of which were used as small warships. As a sailing rig, a cutter is a single-masted boat, with two or more headsails. On the eastern side of the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, the two headsails on a single mast is the fullest extent of the modern definition. In U.S. waters, a greater level of complexity applies, with the placemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hired Armed Vessels
During the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries the Royal Navy made use of a considerable number of hired armed vessels. These were generally smaller vessels, often cutters and luggers, that the Navy used for duties ranging from carrying and passengers to convoy escort, particularly in British coastal waters, and reconnaissance.Winfield (2008), p.387. Doctrine The Navy Board usually hired the vessel complete with master and crew rather than bareboat. Contracts were for a specified time or on an open-ended monthly hire basis. During periods of peace, such as the period between the Treaty of Amiens and the commencement of the Napoleonic Wars, the Admiralty returned the vessels to their owners, only to rehire many on the outbreak of war. The Admiralty provided a regular naval officer, usually a lieutenant for the small vessels, to be the commander. The civilian master then served as the sailing master. For purposes of prize money or salvage, hired armed vessels received the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corvette
A corvette is a small warship. It is traditionally the smallest class of vessel considered to be a proper (or " rated") warship. The warship class above the corvette is that of the frigate, while the class below was historically that of the sloop-of-war. The modern roles that a corvette fulfills include coastal patrol craft, missile boat and fast attack craft. These corvettes are typically between 500 tons and 2,000 .although recent designs may approach 3,000 tons, having size and capabilities that overlap with smaller frigates. However unlike contemporary frigates, a modern corvette does not have sufficient endurance and seaworthiness for long voyages. The word "corvette" is first found in Middle French, a diminutive of the Dutch word ''corf'', meaning a "basket", from the Latin ''corbis''. The rank "corvette captain", equivalent in many navies to "lieutenant commander", derives from the name of this type of ship. The rank is the most junior of three "captain" ranks in sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |