|
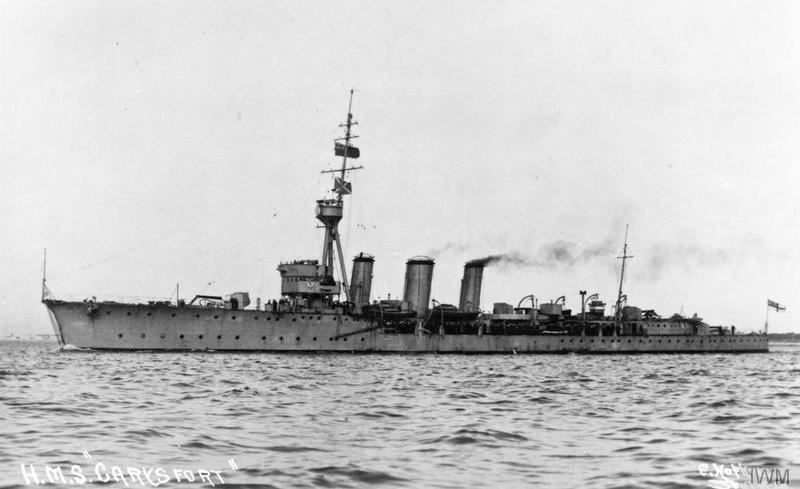
HMS Coventry (D43)
HMS ''Coventry'' was a C-class light cruiser of the Royal Navy, named after the English city of Coventry. She was part of the ''Ceres'' group of the C-class of cruisers. Early career and wartime service ''Coventry'' was initially going to be called HMS ''Corsair''. She was laid down on 4 August 1916, launched 6 July 1917 and completed for naval service in February 1918. HMS ''Coventry'' was in the 5th Light Cruiser squadron from February 1918 till May 1919, and served in the Baltic in this time. Commissioned with the pennant (D43) in May 1919 she was accepted into the Atlantic fleet, until in 1920 when HMS ''Coventry'' became the HQ ship for naval Inter allied Disarmament Commission. She went into refit in late 1920 and once the refit was completed she joined the 2nd Light cruiser squadron and she became flagship to the Rear-Admiral Mediterranean Fleet Andrew Cunningham. A torpedo explosion while in Gibraltar in March 1923 caused the death of two of her crew, Chief Stok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C Class Cruiser
The C class was a group of twenty-eight light cruisers of the Royal Navy, and were built in a sequence of seven groups known as the ''Caroline'' class (six ships), the ''Calliope'' class (two ships), the ''Cambrian'' class (four ships), the ''Centaur'' class (two ships), the ''Caledon'' class (four ships), the ''Ceres'' class (five ships) and the ''Carlisle'' class (five ships). They were built for the rough conditions of the North Sea, and proved to be rugged and capable vessels, despite being somewhat small and cramped. The ''Caroline'' class The ''Caroline'' class were all ordered in July and August 1913, as the first six of eight "light armoured cruisers" under the 1913 programme. The ships were launched in 1914 or 1915 and commissioned in 1915. They had an armament of two single 6 in aft, eight 4 in and two 6-pounder guns. Their anti-aircraft (A/A) weaponry consisted of four 3-pounder. Their aft 6 in guns were superfiring; the class had three funnels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, and with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, such a device was called an automotive, automobile, locomotive, or fish torpedo; colloquially a ''fish''. The term ''torpedo'' originally applied to a variety of devices, most of which would today be called naval mine, mines. From about 1900, ''torpedo'' has been used strictly to designate a self-propelled underwater explosive device. While the 19th-century battleship had evolved primarily with a view to engagements between armored warships with naval artillery, large-caliber guns, the invention and refinement of torpedoes from the 1860s onwards allowed small torpedo boats and other lighter surface combatant , surface vessels, submarines/submersibles, even improvised fishing boats or frogmen, and later light aircraft, to destroy large shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and Corsica. Crete rests about south of the Greek mainland, and about southwest of Anatolia. Crete has an area of and a coastline of 1,046 km (650 mi). It bounds the southern border of the Aegean Sea, with the Sea of Crete (or North Cretan Sea) to the north and the Libyan Sea (or South Cretan Sea) to the south. Crete and a number of islands and islets that surround it constitute the Region of Crete ( el, Περιφέρεια Κρήτης, links=no), which is the southernmost of the 13 top-level administrative units of Greece, and the fifth most populous of Greece's regions. Its capital and largest city is Heraklion, on the north shore of the island. , the region had a population of 636,504. The Dodecanese are located to the no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Edward Sephton
Alfred Edward Sephton Victoria Cross, VC (19 April 1911 – 19 May 1941) was an England, English recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest and most prestigious award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to United Kingdom, British and Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth forces. Details He was 30 years old, and a petty officer in the Royal Navy during the Second World War when the following deed took place for which he was awarded the VC. On 18 May 1941 in the Mediterranean, south of Crete, Petty Officer Sephton was a director layer on HMS Coventry (D43), HMS ''Coventry'' when she went to the assistance of a hospital ship which was being attacked by German dive-bombers. When the enemy engaged ''Coventry'', strafing her with machine-gun fire, Petty Officer Sephton was mortally wounded, a bullet actually passing through his body and injuring an able seaman beside him. Although in great pain and partially blinded, nevertheless he stuck to his instruments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean Theatre Of World War II
The Mediterranean and Middle East Theatre was a major theatre of operations during the Second World War. The vast size of the Mediterranean and Middle East theatre saw interconnected naval, land, and air campaigns fought for control of the Mediterranean, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, the Middle East and Southern Europe. The fighting in this theatre lasted from 10 June 1940, when Italy entered the war on the side of Germany, until 2 May 1945 when all Axis forces in Italy surrendered. However, fighting would continue in Greece – where British troops had been dispatched to aid the Greek government – during the early stages of the Greek Civil War. The British referred to this theatre as the Mediterranean and Middle East Theatre (so called due to the location of the fighting and the name of Middle East Command), the Americans called it the Mediterranean Theater of War and the German informal official history of the fighting is The Mediterranean, South-East Europe, and North A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Cross
The Victoria Cross (VC) is the highest and most prestigious award of the British honours system. It is awarded for valour "in the presence of the enemy" to members of the British Armed Forces and may be awarded posthumously. It was previously awarded by countries of the Commonwealth of Nations, most of which have established their own honours systems and no longer recommend British honours. It may be awarded to a person of any military rank in any service and to civilians under military command. No civilian has received the award since 1879. Since the first awards were presented by Queen Victoria in 1857, two-thirds of all awards have been personally presented by the British monarch. The investitures are usually held at Buckingham Palace. The VC was introduced on 29 January 1856 by Queen Victoria to honour acts of valour during the Crimean War. Since then, the medal has been awarded 1,358 times to 1,355 individual recipients. Only 15 medals, of which 11 to members of the Britis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Cape Spartivento
The Battle of Cape Spartivento, known as the Battle of Cape Teulada in Italy, was a naval battle during the Battle of the Mediterranean in the Second World War, fought between naval forces of the Royal Navy and the Italian ''Regia Marina'' on 27 November 1940. Origins On the night of 11 November 1940, the British incapacitated or destroyed half of the Italian fleet's battleships in a daring aerial assault as they lay at rest at Taranto. Until then, the Italians had left their capital ships in harbour, hoping its mere presence as a fleet in being would deter British shipping through the area, though they would not decline battle if given the opportunity.Greene & Massignani, p. 116 Six days later, on the night of 17 November, an Italian force consisting of two battleships ( and ) and a number of supporting units attempted to intercept two British aircraft carriers, and and their cruiser escorts, who were ''en route'' to Malta in an attempt to provide planes to reinforce that is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Submarine Neghelli
Italian submarine ''Neghelli'' was an built for the Royal Italian Navy (''Regia Marina'') during the 1930s. It was named after a town of Negele Borana, Negele in Ethiopia. Design and description The ''Adua''-class submarines were essentially repeats of the preceding . They Displacement (ship), displaced surfaced and submerged. The submarines were long, had a beam (nautical), beam of and a draft (hull), draft of .Chesneau, pp. 309–10 For surface running, the boats were powered by two diesel engines, each driving one propeller shaft. When submerged each propeller was driven by a electric motor. They could reach on the surface and underwater. On the surface, the ''Adua'' class had a range of at , submerged, they had a range of at .Bagnasco, p. 154 The boats were armed with six internal torpedo tubes, four in the bow and two in the stern. They were also armed with one Škoda 10 cm K10#OTO 100.2F47 History, deck gun for combat on the surface. The light anti-aircraft ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |