|
HMS Berwick (1775)
HMS ''Berwick'' was a 74-gun ''Elizabeth''-class third rate of the Royal Navy, launched at Portsmouth Dockyard on 18 April 1775, to a design by Sir Thomas Slade. She fought the French at the Battle of Ushant (1778) and the Dutch at the Battle of Dogger Bank (1781). The French captured her in the action of 8 March 1795 during the French Revolutionary Wars and she served with them with some success then and at the start of the Napoleonic Wars until the British recaptured her at the Battle of Trafalgar. ''Berwick'' sank shortly thereafter in a storm. Royal Navy service As one of the newest ships of the line, she was commissioned in December 1777. On the entry of France into the American War of Independence in 1778 ''Berwick'' joined the Channel Fleet. In July, she took part in the Battle of Ushant under the command of Captain the Hon. Keith Stewart. She served with the Channel Fleet throughout 1779. In 1780 she was sent out to the West Indies as part of a squadron under Commodo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a Sovereign state, sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England (which included Wales) and Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland to form a single kingdom encompassing the whole island of Great Britain and its outlying islands, with the exception of the Isle of Man and the Channel Islands. The unitary state was governed by a single Parliament of Great Britain, parliament at the Palace of Westminster, but distinct legal systems – English law and Scots law – remained in use. The formerly separate kingdoms had been in personal union since the 1603 "Union of the Crowns" when James VI of Scotland became King of England and King of Ireland. Since James's reign, who had been the first to refer to himself as "king of Great Britain", a political un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action Of 8 March 1795
The action of 8 March 1795 was a minor naval engagement in the Mediterranean theatre of the French Revolutionary Wars. The action was part of series of battles fought in the spring of 1795 between British and French fleets for control of the Ligurian Sea and thus the blockade of the French naval base of Toulon. The engagement was the first significant action of the year and was fought principally between the damaged British 74-gun ship of the line and the French 32-gun frigate ''Alceste'', with the later assistance of the frigate ''Vestale'' and the 74-gun ''Duquesne'', distantly supported by the rest of the French Mediterranean Fleet. The action took place against the backdrop of a wider campaign, in which much of the French fleet had been badly damaged in 1793 during the Siege of Toulon. Freshly repaired, the French had sailed on a mission to intimidate the neutral city of Genoa and possibly invade British-held Corsica. The British fleet had until recently been anchored for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
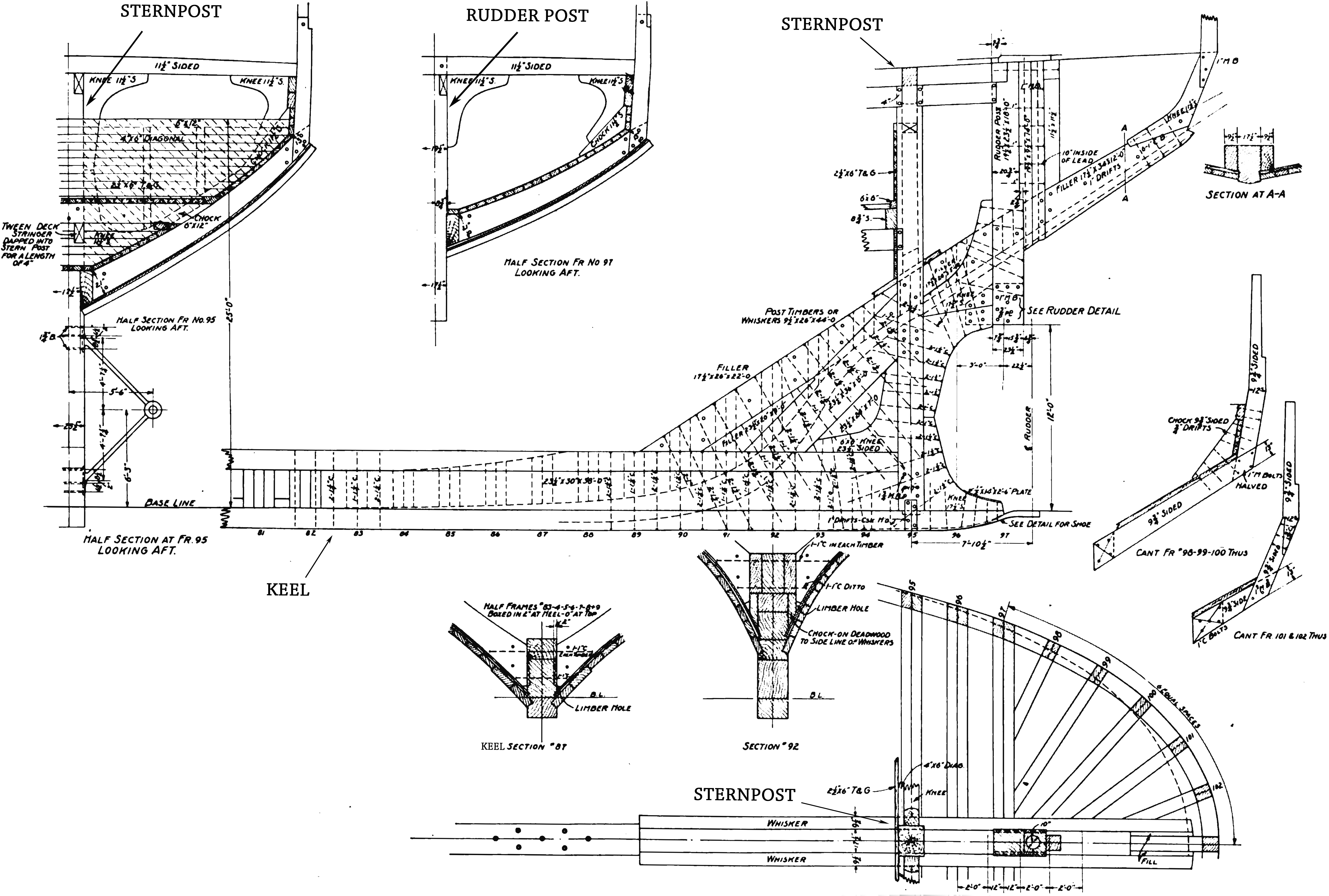
Stern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. Originally, the term only referred to the aft port section of the ship, but eventually came to refer to the entire back of a vessel. The stern end of a ship is indicated with a white navigation light at night. Sterns on European and American wooden sailing ships began with two principal forms: the ''square'' or ''transom'' stern and the ''elliptical'', ''fantail'', or ''merchant'' stern, and were developed in that order. The hull sections of a sailing ship located before the stern were composed of a series of U-shaped rib-like frames set in a sloped or "cant" arrangement, with the last frame before the stern being called the ''fashion timber(s)'' or ''fashion piece(s)'', so called for "fashioning" the after part of the ship. This frame is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Hyde Parker, 5th Baronet
Vice-Admiral Sir Hyde Parker, 5th Baronet (1 February 1714 – 1782) was a British naval commander. Parker was born at Tredington in Worcestershire. His father, a clergyman, was a son of Sir Henry Parker. His paternal grandfather had married a daughter of Alexander Hyde, Bishop of Salisbury. He began his career at sea in the merchant service. Entering the Royal Navy at the age of 24, he was made lieutenant in 1744, and in 1748 he was made post-captain. In his royal navy career, he captured a Spanish galleon that was worth £600,000. This gave his family its wealth. Currently, his descendants live in the south wing of Melford Hall. Seven Years War In October 1755 Hyde Parker commissioned the newly launched post ship . A year later, in her he captured the French privateer ''Très Vénėrable''. During the latter part of the Seven Years' War he served in the East Indies, taking part in the capture of Pondicherry in 1761 and of Manila in 1762. In the latter year Parker with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carronade
A carronade is a short, smoothbore, cast-iron cannon which was used by the Royal Navy. It was first produced by the Carron Company, an ironworks in Falkirk, Scotland, and was used from the mid-18th century to the mid-19th century. Its main function was to serve as a powerful, short-range, anti-ship and anti-crew weapon. The technology behind the carronade was greater dimensional precision, with the shot fitting more closely in the barrel thus transmitting more of the propellant charge's energy to the projectile, allowing a lighter gun using less gunpowder to be effective. Carronades were initially found to be very successful, but they eventually disappeared as naval artillery advanced, with the introduction of rifling and consequent change in the shape of the projectile, exploding shells replacing solid shot, and naval engagements being fought at longer ranges. History The carronade was designed as a short-range naval weapon with a low muzzle velocity for merchant ships, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Ship Belle Poule (1765)
''Belle Poule'' was a French frigate of the , designed by Léon-Michel Guignace. She is most famous for her duel with the British frigate on 17 June 1778, which began the French involvement in the American War of Independence. 1768 – 1777 ''Belle Poule'' was built in Bordeaux between March 1765 and early 1767. She served in two campaigns in the West Indies, where due to her good sailing performance she was selected for the first French attempt at covering her hull with copper to resist marine growths. From 1772 to 1776, she was sent on hydrographic missions, during which the young La Pérouse came to the attention of his superiors. On 12 December 1776, she left India to return to Brest. At the time, France was not yet engaged in the American War of Independence, but there had been numerous incidents involving French and British ships. Indeed, on 27 April 1777, ''Belle Poule'' was chased by a British ship of the line, which she easily evaded to reach Brest. In December ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jamaica Station (Royal Navy)
The Jamaica Station was a formation or command of the United Kingdom's Royal Navy stationed at Port Royal in Jamaica from 1655 to 1830. History The station was formed, following the capture of Jamaica, by assembling about a dozen frigates in 1655. The first "Admiral and General-at-Sea" was Sir William Penn.Cundall, p. xx Its main objectives in the early years were to defend Jamaica and to harass Spanish ports and shipping. In the late 1720s three successive commanders of the station lost their lives to tropical diseases while undertaking a Blockade of Porto Bello during the Anglo-Spanish War. The general ill-health associated with the station continued throughout the century. An assessment of Navy strength at the Jamaica station in 1742 found around 3,000 men were fit to serve out of a total Navy complement of 6,620. A Navy hospital was constructed in 1745 but its location was poor and many patients brought in for shipboard diseases developed additional tropical illnesses while i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melbourne University Press
Melbourne University Publishing (MUP) is the book publishing arm of the University of Melbourne. History MUP was founded in 1922 as Melbourne University Press to sell text books and stationery to students, and soon began publishing books itself. Over the years scholarly works published under the MUP imprint have won numerous awards and prizes. The name ''Melbourne University Publishing'' was adopted for the business in 2003 following a restructure by the university, but books continue to be published under the ''Melbourne University Press'' imprint. The Miegunyah Press is an imprint of MUP, established in 1967 under a bequest from businessman and philanthropist Russell Grimwade, with the intention of subsidising the publication of illustrated scholarly works that would otherwise be uneconomic to publish. Grimwade's great-grandnephew Andrew Grimwade is the present patron. ''Miegunyah'' is from an Aboriginal Australian language, meaning "my house". [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New South Wales
) , nickname = , image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates: , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of New South Wales , established_title2 = Establishment , established_date2 = 26 January 1788 , established_title3 = Responsible government , established_date3 = 6 June 1856 , established_title4 = Federation , established_date4 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Wales , demonym = , capital = Sydney , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center = 128 local government areas , admin_center_type = Administration , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_name2 = Margaret Beazley , leader_title3 = Premier , leader_name3 = Dominic Perrottet (Liberal) , national_representation = Parliament of Australia , national_representation_type1 = Senat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Hunter (Royal Navy Officer)
Vice Admiral John Hunter (29 August 1737 – 13 March 1821) was an officer of the Royal Navy, who succeeded Arthur Phillip as the second Governor of New South Wales, serving from 1795 to 1800.J. J. Auchmuty,Hunter, John (1737–1821), ''Australian Dictionary of Biography'', Volume 1, MUP, 1966, pp 566–572. Retrieved 12 August 2009 Both a sailor and a scholar, he explored the Parramatta River as early as 1788, and was the first to surmise that Tasmania might be an island. As governor, he tried to combat serious abuses by the military in the face of powerful local interests led by John MacArthur. Hunter's name is commemorated in historic locations such as Hunter Valley and Hunter Street, Sydney. Family and early life John Hunter was born in Leith, Scotland, the son of William Hunter, a captain in the merchant service, and Helen, ''née'' Drummond, daughter of J. Drummond and niece of George Drummond, several-time lord provost of Edinburgh. As a boy Hunter was sent to live wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keith Stewart
Vice-Admiral Keith Stewart (1739 – 3 March 1795) was a Scottish Royal Navy officer and politician who sat in the House of Commons on two occasions. Having began his naval career in around 1753, Stewart was promoted to commander in 1761 and then advanced to post-captain in 1762 because of political negotiations undergone by his father Alexander Stewart, 6th Earl of Galloway. Stewart commanded HMS ''Berwick'' at the Battle of Ushant in 1778 and in 1781 was appointed Commander-in-Chief, North Sea only to be superseded by Hyde Parker soon afterwards. As such he served at the Battle of Dogger Bank as a volunteer on ''Berwick''. Resuming his command in the North Sea after the battle, Stewart resigned his position towards the start of 1782 when he failed to stop a Dutch convoy escaping him in the Downs. Instead given command of HMS ''Cambridge'', he served at the Relief of Gibraltar and the subsequent Battle of Cape Spartel. Apart from a very brief command of HMS ''Formi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American War Of Independence
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of the United States, fighting began on April 19, 1775, followed by the Lee Resolution on July 2, 1776, and the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776. The American Patriots were supported by the Kingdom of France and, to a lesser extent, the Dutch Republic and the Spanish Empire, in a conflict taking place in North America, the Caribbean, and the Atlantic Ocean. Established by royal charter in the 17th and 18th centuries, the American colonies were largely autonomous in domestic affairs and commercially prosperous, trading with Britain and its Caribbean colonies, as well as other European powers via their Caribbean entrepôts. After British victory over the French in the Seven Years' War in 1763, tensions between the motherland and her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_-_geograph.org.uk_-_950933.jpg)

