|
HMS Bedford
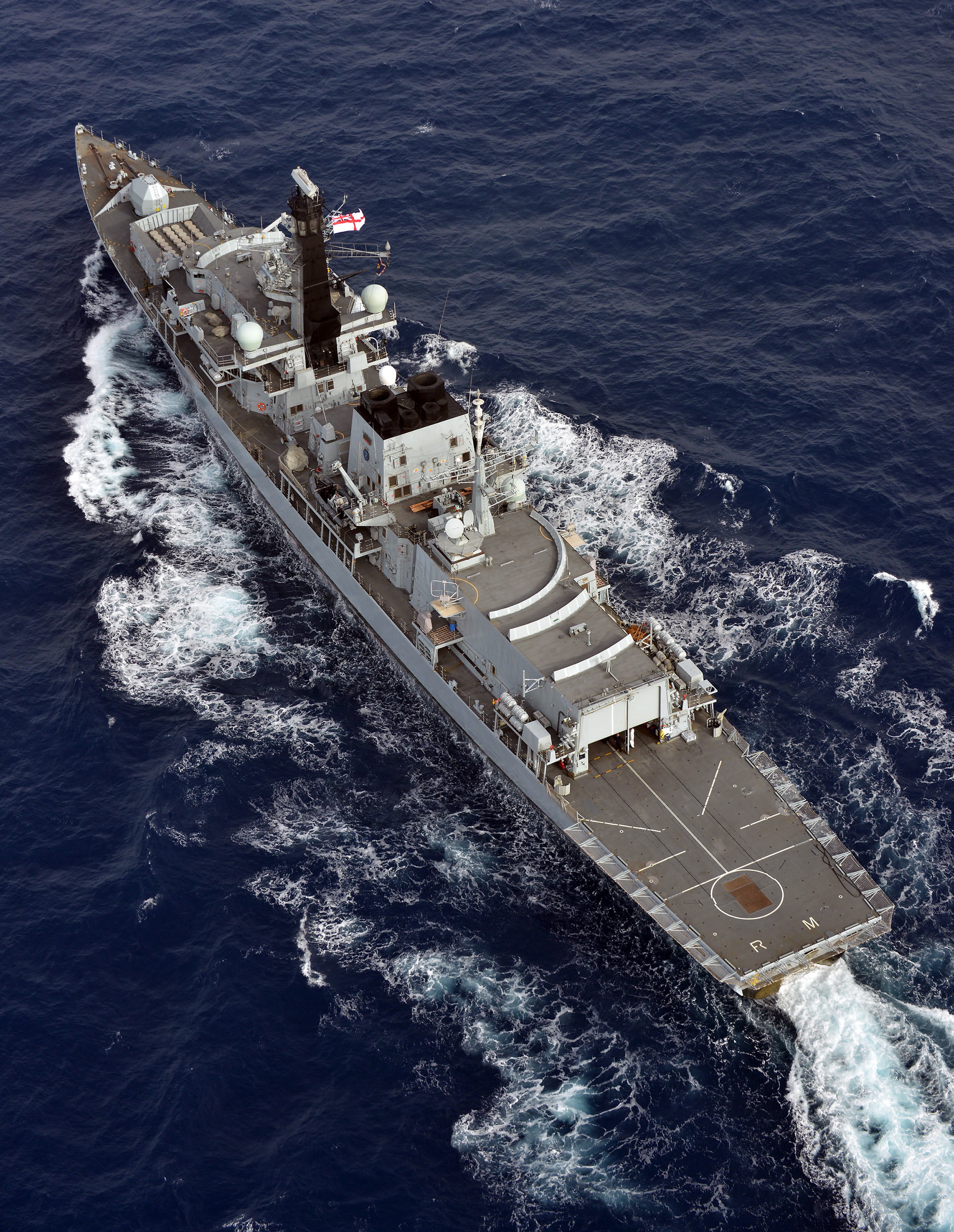
Three ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS ''Bedford'', named initially after William Russell, 1st Duke of Bedford, William Russell, created Duke of Bedford in May 1694 and ''not'' after the town of Bedford: * was a 70-gun third rate launched in 1698. She was rebuilt in 1741 to carry 64-guns, was hulked in 1767 and sold in 1787. * was a 74-gun third rate launched in 1775. She was used as a prison ship from 1801 and was broken up in 1817. * was a armoured cruiser launched in 1901. She was wrecked in 1910 and the wreck was sold later that year. In film *HMS ''Bedford'' is a fictional Type 23 frigate featured in the 18th James Bond feature film ''Tomorrow Never Dies''. She was instrumental in the destruction of Elliot Carver's stealth ship. See also * was a 34-gun fifth rate launched in 1697, and purchased that year for Navy service. She was rebuilt in 1709 and converted into a fire ship in 1716. She was sunk as a foundation at Sheerness in 1725. {{DEFAU ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, to ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Russell, 1st Duke Of Bedford
William Russell, 1st Duke of Bedford KG PC (August 1616 – 7 September 1700) was an English nobleman and politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1640 until 1641 when he inherited his Peerage as 5th Earl of Bedford and removed to the House of Lords. He fought in the Parliamentarian army and later defected to the Royalists during the English Civil War. Early life, 1616–1640 He was the son of Francis Russell, 4th Earl of Bedford and his wife Catherine, the daughter and coheir of Giles Brydges, 3rd Baron Chandos. Russell was educated at Magdalen College, Oxford, and then, in 1635 went to Madrid where he hoped to learn Spanish. He returned by July 1637, at which point he concluded a marriage (initially against his father's wishes), to Anne, the sole heir of Robert Carr, 1st Earl of Somerset. Career during the English Civil War, 1640–1644 Bedford as Parliamentarian, 1640–1642 In April 1640, Russell was elected Member of Parliament (MP) for Tavistock in the Shor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bedford
Bedford is a market town in Bedfordshire, England. At the 2011 Census, the population of the Bedford built-up area (including Biddenham and Kempston) was 106,940, making it the second-largest settlement in Bedfordshire, behind Luton, whilst the Borough of Bedford had a population of 157,479. Bedford is also the historic county town of Bedfordshire. Bedford was founded at a ford on the River Great Ouse and is thought to have been the burial place of King Offa of Mercia, who is remembered for building Offa's Dyke on the Welsh border. Bedford Castle was built by Henry I of England, Henry I, although it was destroyed in 1224. Bedford was granted borough status in 1165 and has been represented in Parliament since 1265. It is known for its large Italians in the United Kingdom, population of Italian descent. History The name of the town is believed to derive from the name of a Saxon chief called Beda, and a Ford (crossing), ford crossing the River Great Ouse. Bedford was a marke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy, a third rate was a ship of the line which from the 1720s mounted between 64 and 80 guns, typically built with two gun decks (thus the related term two-decker). Years of experience proved that the third rate ships embodied the best compromise between sailing ability (speed, handling), firepower, and cost. So, while first-rates and second-rates were both larger and more powerful, third-rate ships were the optimal configuration. Rating When the rating system was first established in the 1620s, the third rate was defined as those ships having at least 200 but not more than 300 men; previous to this, the type had been classified as "middling ships". By the 1660s, the means of classification had shifted from the number of men to the number of carriage-mounted guns, and third rates at that time mounted between 48 and 60 guns. By the turn of the century, the criterion boundaries had increased and third rate carried more than 60 guns, with seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prison Ship
A prison ship, often more accurately described as a prison hulk, is a current or former seagoing vessel that has been modified to become a place of substantive detention for convicts, prisoners of war or civilian internees. While many nations have deployed prison ships over time, the practice was most widespread in 18th- and 19th-century Britain, as the government sought to address the issues of overcrowded civilian jails on land and an influx of enemy detainees from the War of Jenkins' Ear, the Seven Years' War and the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. History The terminology "hulk" comes from the Royal Navy meaning a ship incapable of full service either through damage or from initial non-completion. In England in 1776, during the reign of King George III, due to a shortage of prison space in London, the concept of "prison hulks" moored in the Thames, was introduced to meet the need for prison space. The first such ship came into use on 15 July 1776 under command o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armoured Cruiser
The armored cruiser was a type of warship of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It was designed like other types of cruisers to operate as a long-range, independent warship, capable of defeating any ship apart from a battleship and fast enough to outrun any battleship it encountered. For many decades, naval technology had not advanced far enough for designers to produce a cruiser which combined an armored belt with the long range and high speed required to fulfill its mission. For this reason, beginning in the 1880s and 1890s, many navies preferred to build protected cruisers, which only relied on a light armored deck to protect the vital parts of the ship. However, by the late 1880s, the development of modern rapid-fire breech-loading cannon and high-explosive shells made the reintroduction of side armor a necessity. The invention of face-hardened armor in the mid-1890s offered effective protection with less weight than previously. Varying in size, the armored cruiser was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type 23 Frigate
The Type 23 frigate or Duke class is a class of frigates built for the United Kingdom's Royal Navy. The ships are named after British Dukes, thus leading to the class being commonly known as the Duke class. The first Type 23, , was commissioned in 1989, and the sixteenth, was commissioned in June 2002. They form the core of the Royal Navy's destroyer and frigate fleet and serve alongside the Type 45 destroyers. They were designed for anti-submarine warfare, but have been used for a range of uses. Twelve Type 23 frigates remain in service with the Royal Navy, with three vessels having been sold to the Chilean Navy, and one being retired in 2021. The Royal Navy's Type 23 frigates will be replaced by the Type 26 Global Combat Ship and the Type 31 frigate. it is anticipated that HMS ''St Albans'' will be the last to retire from the Royal Navy, in 2035. Development When first conceived in the late 1970s, the Type 23 was intended to be a light anti-submarine frigate with a towed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Bond
The ''James Bond'' series focuses on a fictional British Secret Service agent created in 1953 by writer Ian Fleming, who featured him in twelve novels and two short-story collections. Since Fleming's death in 1964, eight other authors have written authorised Bond novels or novelisations: Kingsley Amis, Christopher Wood, John Gardner, Raymond Benson, Sebastian Faulks, Jeffery Deaver, William Boyd, and Anthony Horowitz. The latest novel is ''With a Mind to Kill'' by Anthony Horowitz, published in May 2022. Additionally Charlie Higson wrote a series on a young James Bond, and Kate Westbrook wrote three novels based on the diaries of a recurring series character, Moneypenny. The character—also known by the code number 007 (pronounced "double-oh-seven")—has also been adapted for television, radio, comic strip, video games and film. The films are one of the longest continually running film series and have grossed over US$7.04 billion in total at the box office ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomorrow Never Dies
''Tomorrow Never Dies'' is a 1997 spy film, the eighteenth in the ''James Bond'' series produced by Eon Productions and the second to star Pierce Brosnan as fictional MI6 agent James Bond. Directed by Roger Spottiswoode from a screenplay by Bruce Feirstein, it follows Bond as he attempts to stop Elliot Carver (Jonathan Pryce), a power-mad media mogul, from engineering world events to initiate World War III. The film was produced by Michael G. Wilson and Barbara Broccoli, and was the first Bond film made after the death of producer Albert R. Broccoli (to whom it pays tribute in the end credits), and the last released under the United Artists label. Filming locations included France, Thailand, Germany, Mexico and the United Kingdom. ''Tomorrow Never Dies'' performed well at the box office, grossing over $333 million worldwide, becoming the fourth-highest-grossing film of 1997 and earning a Golden Globe nomination despite mixed reviews. While its performance at the U.S. box of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elliot Carver
''Tomorrow Never Dies'' is a 1997 spy film, the eighteenth in the ''James Bond'' series produced by Eon Productions and the second to star Pierce Brosnan as fictional MI6 agent James Bond. Directed by Roger Spottiswoode from a screenplay by Bruce Feirstein, it follows Bond as he attempts to stop Elliot Carver (Jonathan Pryce), a power-mad media mogul, from engineering world events to initiate World War III. The film was produced by Michael G. Wilson and Barbara Broccoli, and was the first Bond film made after the death of producer Albert R. Broccoli (to whom it pays tribute in the end credits), and the last released under the United Artists label. Filming locations included France, Thailand, Germany, Mexico and the United Kingdom. ''Tomorrow Never Dies'' performed well at the box office, grossing over $333 million worldwide, becoming the fourth-highest-grossing film of 1997 and earning a Golden Globe nomination despite mixed reviews. While its performance at the U.S. box ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fifth Rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a fifth rate was the second-smallest class of warships in a hierarchical system of six " ratings" based on size and firepower. Rating The rating system in the Royal Navy as originally devised had just four rates, but early in the reign of Charles I, the original fourth rate (derived from the "Small Ships" category under his father, James I) was divided into new classifications of fourth, fifth, and sixth rates. While a fourth-rate ship was defined as a ship of the line, fifth and the smaller sixth-rate ships were never included among ships-of-the-line. Nevertheless, during the Anglo-Dutch Wars of the 17th century, fifth rates often found themselves involved among the battle fleet in major actions. Structurally, these were two-deckers, with a complete battery on the lower deck, and fewer guns on the upper deck (below the forecastle and quarter decks, usually with no guns in the waist on this deck). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire Ship
A fire ship or fireship, used in the days of wooden rowed or sailing ships, was a ship filled with combustibles, or gunpowder deliberately set on fire and steered (or, when possible, allowed to drift) into an enemy fleet, in order to destroy ships, or to create panic and make the enemy break formation. Ships used as fire ships were either warships whose munitions were fully spent in battle, surplus ones which were old and worn out, or inexpensive purpose-built vessels rigged to be set afire, steered toward targets, and abandoned quickly by the crew. Explosion ships or "hellburners" were a variation on the fire ship, intended to cause damage by blowing up in proximity to enemy ships. Fireships were used to great effect by the outgunned English fleet against the Spanish Armada during the Battle of Gravelines, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
