|
HMGN
HMGN (High Mobility Group Nucleosome-binding) proteins are members of the broader class of high mobility group (HMG) chromosomal proteins that are involved in regulation of transcription, replication, recombination, and DNA repair. HMGN1 and HMGN2 (initially designated HMG-14 and HMG-17 respectively) were discovered by E.W. Johns research group in the early 1970s. HMGN3, HMGN4, and HMGN5 were discovered later and are less abundant. HMGNs are nucleosome binding proteins that help in transcription, replication, recombination, and DNA repair. They can also alter the chromatin epigenetic landscape, helping to stabilize cell identity. There is still relatively little known about their structure and function. HMGN proteins are found in all vertebrates, and play a role in chromatin structure and histone modification. HMGNs come in long chains of amino acids, containing around 100 for HMGN1-4, and roughly 200 in HMGN5. Recent research on the HMGN family is focused on their effect on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hmgn
HMGN (High Mobility Group Nucleosome-binding) proteins are members of the broader class of high mobility group (HMG) chromosomal proteins that are involved in regulation of transcription, replication, recombination, and DNA repair. HMGN1 and HMGN2 (initially designated HMG-14 and HMG-17 respectively) were discovered by E.W. Johns research group in the early 1970s. HMGN3, HMGN4, and HMGN5 were discovered later and are less abundant. HMGNs are nucleosome binding proteins that help in transcription, replication, recombination, and DNA repair. They can also alter the chromatin epigenetic landscape, helping to stabilize cell identity. There is still relatively little known about their structure and function. HMGN proteins are found in all vertebrates, and play a role in chromatin structure and histone modification. HMGNs come in long chains of amino acids, containing around 100 for HMGN1-4, and roughly 200 in HMGN5. Recent research on the HMGN family is focused on their effect on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMGN1
Non-histone chromosomal protein HMG-14 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HMGN1'' gene. Function Chromosomal protein HMG14 and its close analog HMG17 (MIM 163910) bind to the inner side of the nucleosomal DNA, potentially altering the interaction between the DNA and the histone octamer. The 2 proteins may be involved in the process that maintains transcribable genes in a unique chromatin conformation. Their ubiquitous distribution and relative abundance, as well as the high evolutionary conservation of the DNA-binding domain of the HMG14 family of proteins, suggest that they may be involved in an important cellular function. Interactions HMGN1 has been shown to interact with YWHAZ. See also * HMGN2 *High mobility group protein HMG14 and HMG17 High mobility group protein HMG14 and HMG17 also known as nucleosomal binding domain is a Protein family, family of evolutionarily related proteins. High mobility group (HMG) proteins constitute a family of relatively ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMGN3
High mobility group nucleosome-binding domain-containing protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HMGN3'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b .... Thyroid hormone receptors are hormone-dependent transcription factors that regulate expression of a variety of specific target genes. The protein encoded by this gene binds thyroid hormone receptor beta, but only in the presence of thyroid hormone. The encoded protein, a member of the HMGN protein family, is thought to reduce the compactness of the chromatin fiber in nucleosomes, thereby enhancing transcription from chromatin templates. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. References Further reading * * * * * * External links * {{gene-6-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Mobility Group
High-Mobility Group or HMG is a group of chromosomal proteins that are involved in the regulation of DNA-dependent processes such as transcription, replication, recombination, and DNA repair. Families The HMG proteins are subdivided into 3 superfamilies each containing a characteristic functional domain: * HMGA – contains an AT-hook domain ** HMGA1 ** HMGA2 * HMGB – contains a HMG-box domain ** HMGB1 ** HMGB2 ** HMGB3 ** HMGB4 * HMGN – contains a nucleosomal binding domain ** HMGN1 ** HMGN2 ** HMGN3 ** HMGN4 ** HMGN5 Proteins containing any of these embedded in their sequence are known as HMG motif proteins. HMG-box proteins are found in a variety of eukaryotic organisms. They were originally isolated from mammalian cells, and named according to their electrophoretic mobility in polyacrylamide gels. Other families with HMG-box domain * SOX gene family ** Sex-Determining Region Y Protein ** SOX1, SOX2, etc. * TCF/LEF family (T cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMGN2
Non-histone chromosomal protein HMG-17 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HMGN2'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b .... See also * High mobility group protein HMG14 and HMG17 * HMGN1 (HMG-14) References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Mobility Group
High-Mobility Group or HMG is a group of chromosomal proteins that are involved in the regulation of DNA-dependent processes such as transcription, replication, recombination, and DNA repair. Families The HMG proteins are subdivided into 3 superfamilies each containing a characteristic functional domain: * HMGA – contains an AT-hook domain ** HMGA1 ** HMGA2 * HMGB – contains a HMG-box domain ** HMGB1 ** HMGB2 ** HMGB3 ** HMGB4 * HMGN – contains a nucleosomal binding domain ** HMGN1 ** HMGN2 ** HMGN3 ** HMGN4 ** HMGN5 Proteins containing any of these embedded in their sequence are known as HMG motif proteins. HMG-box proteins are found in a variety of eukaryotic organisms. They were originally isolated from mammalian cells, and named according to their electrophoretic mobility in polyacrylamide gels. Other families with HMG-box domain * SOX gene family ** Sex-Determining Region Y Protein ** SOX1, SOX2, etc. * TCF/LEF family (T cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMGN4
High mobility group nucleosome-binding domain-containing protein 4 is a transcription factor that in humans is encoded by the ''HMGN4'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene, a member of the HMGN protein family, is thought to reduce the compactness of the chromatin fiber in nucleosome A nucleosome is the basic structural unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes. The structure of a nucleosome consists of a segment of DNA wound around eight histone proteins and resembles thread wrapped around a spool. The nucleosome is the fundame ...s, thereby enhancing transcription from chromatin templates. Transcript variants utilizing alternative polyadenylation signals exist for this gene. See also * High-mobility group References Further reading * * * * * Transcription factors {{gene-6-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Repair
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in tens of thousands of individual molecular lesions per cell per day. Many of these lesions cause structural damage to the DNA molecule and can alter or eliminate the cell's ability to transcribe the gene that the affected DNA encodes. Other lesions induce potentially harmful mutations in the cell's genome, which affect the survival of its daughter cells after it undergoes mitosis. As a consequence, the DNA repair process is constantly active as it responds to damage in the DNA structure. When normal repair processes fail, and when cellular apoptosis does not occur, irreparable DNA damage may occur, including double-strand breaks and DNA crosslinkages (interstrand crosslinks or ICLs). This can eventually lead to malignant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
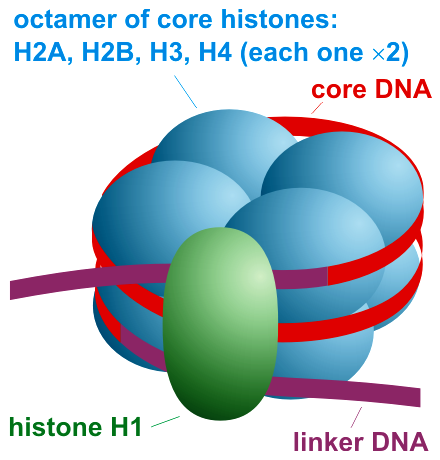
Histone H1
Histone H1 is one of the five main histone protein families which are components of chromatin in eukaryotic cells. Though highly conserved, it is nevertheless the most variable histone in sequence across species. Structure Metazoan H1 proteins feature a central globular "winged helix" domain and long C- and short N-terminal tails. H1 is involved with the packing of the "beads on a string" sub-structures into a high order structure, whose details have not yet been solved. H1 found in protists and bacteria, otherwise known as nucleoproteins HC1 and HC2 (, ), lack the central domain and the N-terminal tail. H1 is less conserved than core histones. The globular domain is the most conserved part of H1. Function Unlike the other histones, H1 does not make up the nucleosome "bead". Instead, it sits on top of the structure, keeping in place the DNA that has wrapped around the nucleosome. H1 is present in half the amount of the other four histones, which contribute two molecules ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H3K4me1
H3K4me1 is an epigenetic modification to the DNA packaging protein Histone H3. It is a mark that indicates the mono-methylation at the 4th lysine residue of the histone H3 protein and often associated with gene enhancers. Nomenclature H3K4me1 indicates monomethylation of lysine 4 on histone H3 protein subunit: Lysine methylation This diagram shows the progressive methylation of a lysine residue. The mono-methylation denotes the methylation present in H3K4me1. Understanding histone modifications The genomic DNA of eukaryotic cells is wrapped around special protein molecules known as histones. The complexes formed by the looping of the DNA are known as chromatin. The basic structural unit of chromatin is the nucleosome: this consists of the core octamer of histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4) as well as a linker histone and about 180 base pairs of DNA. These core histones are rich in lysine and arginine residues. The carboxyl (C) terminal end of these histones contribute to his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H3K27ac
H3K27ac is an epigenetic modification to the DNA packaging protein histone H3. It is a mark that indicates acetylation of the lysine residue at N-terminal position 27 of the histone H3 protein. H3K27ac is associated with the higher activation of transcription and therefore defined as an ''active enhancer'' mark. H3K27ac is found at both proximal and distal regions of transcription start site (TSS). Lysine acetylation and deacetylation Proteins are typically acetylated on lysine residues, and the acetylation reaction relies on acetyl-coenzyme A as the acetyl group donor. In histone acetylation and deacetylation, histone proteins are acetylated and deacetylated on lysine residues in the N-terminal tail as part of gene regulation. Typically, these reactions are catalyzed by enzymes with ''histone acetyltransferase'' (HAT) or ''histone deacetylase'' (HDAC) activity, although HATs and HDACs can modify the acetylation status of non-histone proteins as well. The regulation of tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |