|
HLA-DR5
HLA-DR5 (DR5) is a broad-antigen serotype that is further split into HLA-DR11 and HLA-DR12 antigen serotypes. HLA-DR5 (Human Leukocyte Antigen DR5) is a protein that is encoded by a gene in the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) complex. The HLA complex is a group of genes located on chromosome 6 that plays a critical role in the immune system. HLA-DR5 is a type of HLA class II molecule that is expressed on the surface of immune cells called dendritic cells and monocytes. HLA-DR5 is involved in the presentation of peptides, which are short chains of amino acids, to T cells, a type of immune cell that plays a key role in the immune response. When HLA-DR5 presents a peptide to a T cell, it can stimulate the T cell to become activated and mount an immune response against the peptide. HLA-DR5 has been the focus of research in the field of immunology due to its potential role in the development of autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis, and in the response to certain infection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HLA-DR12
HLA-DR12(DR12) is a HLA- DR serotype that recognizes the DRB1*1201 to *1203, *1206. DR12 serotype is a split antigen of the older HLA-DR5 serotype group which also contains the similar HLA-DR11 antigens. Serology The table above describes the efficiency of serological typing of DR12 and DR5. Serotypes are unknown the following alleles: DRB1*1204,*1205 to *1207 to *1215 Alleles There are only 2 common allels for DRB1*12, *1201 and *1202. *1202 is more common on the West Pacific Rim and particularly Indochina and the South Pacific. Disease associations DR12 is associated with vulval lichen sclerosus, and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis. DRB1*1201 is associated with iritis in juvenile arthritis, primary antiphospholipid syndrome, tiopronin intolerance in rheumatoid arthritis, adult chronic articular Still's disease DRB1*1202 is found to be increased in narcolepsy associated sudden death syndrome in the Thai population, and narcolepsy in the Japanese population. Extend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HLA-DR11
HLA-DR11 (DR11) is a HLA- DR serotype that recognizes the DRB1*1101 to *1110. DR11 serotype is a split antigen of the older HLA-DR5 serotype group which also contains the similar HLA-DR12 antigens. Serology The table above describes the efficiency of serological typing of DR11 and DR5. Serotypes are unknown the following alleles: DRB1*1110 to *1157 Disease associations By serotype DR11 is associated with grape anaphylaxis, well-differentiated thyroid cancer, low antibody production in Hepatitis C. By allele(s) DRB1*11 is associated systemic sclerosis (SSc) & anti-DNA topoisomerase I (anti-topo I) antibody DRB1*1101 is associated Anti-Ro/SSA with anti-La/SSB antibodies in neonatal lupus erythematosus, mite sensitive asthma, cervical cancer risk (HPV?) DRB1*1102: Tiopronin intolerance in rheumatoid arthritis DRB1*1104: pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis By haplotype DR11 is an identifier for the DR11-DQ7/DR7-DQ2 transhaplotype isoform of celiac disease. DR11-D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiphospholipid Syndrome
Antiphospholipid syndrome, or antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS or APLS), is an autoimmune, hypercoagulable state caused by antiphospholipid antibodies. APS provokes blood clots (thrombosis) in both arteries and veins as well as pregnancy-related complications such as miscarriage, stillbirth, preterm delivery, and severe preeclampsia. Although the exact etiology of APS is still not clear, genetics is believed to play a key role in the development of the disease. The diagnostic criteria require one clinical event (i.e. thrombosis or pregnancy complication) and two positive blood test results spaced at least three months apart that detect lupus anticoagulant, anti-apolipoprotein antibodies, or anti-cardiolipin antibodies. Antiphospholipid syndrome can be primary or secondary. Primary antiphospholipid syndrome occurs in the absence of any other related disease. Secondary antiphospholipid syndrome occurs with other autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involved, with the same joints typically involved on both sides of the body. The disease may also affect other parts of the body, including skin, eyes, lungs, heart, nerves and blood. This may result in a low red blood cell count, inflammation around the lungs, and inflammation around the heart. Fever and low energy may also be present. Often, symptoms come on gradually over weeks to months. While the cause of rheumatoid arthritis is not clear, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves the body's immune system attacking the joints. This results in inflammation and thickening of the joint capsule. It also affects the underlying bone and cartilage. The diagnosis is made mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
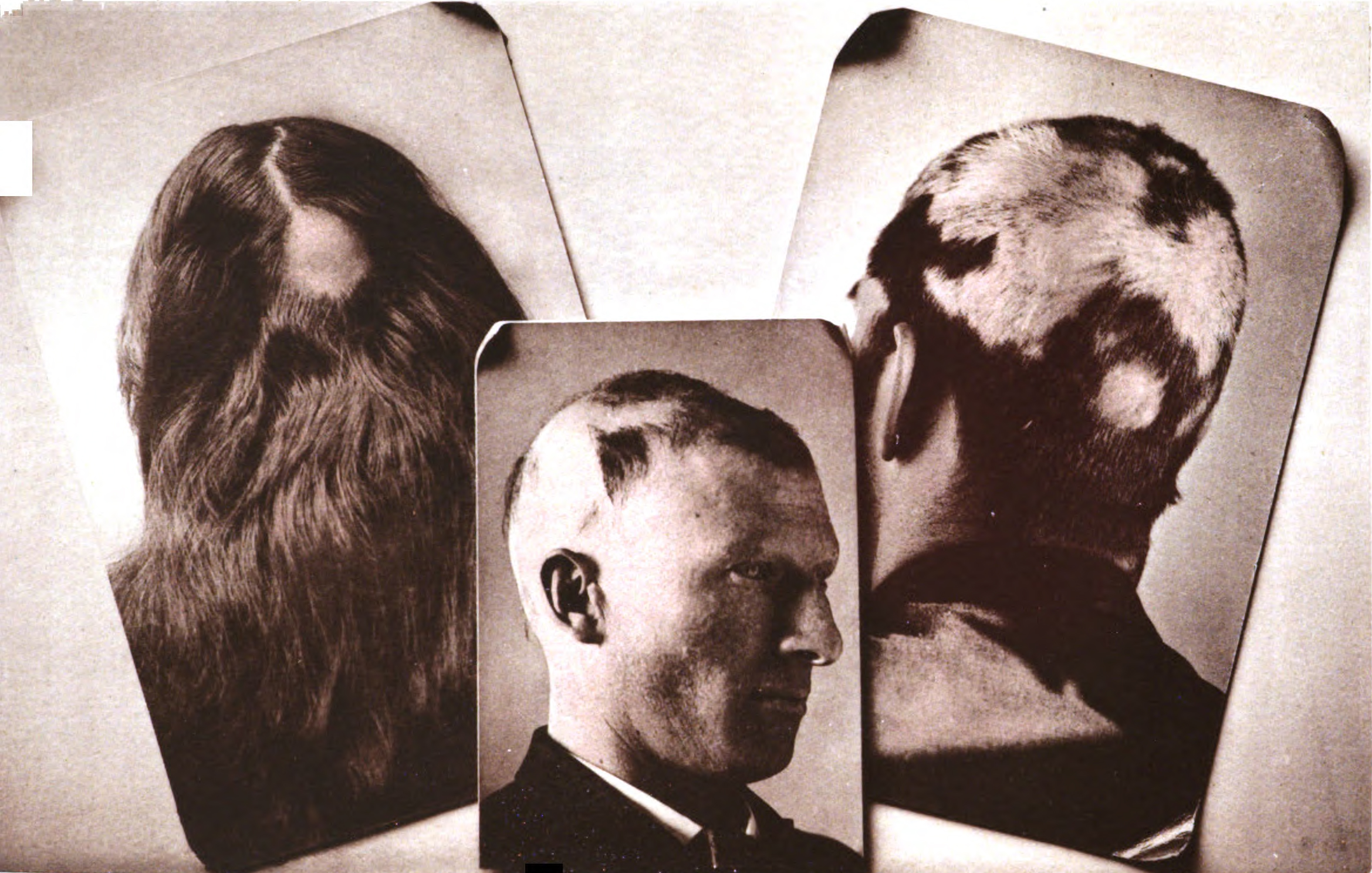
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata, also known as spot baldness, is a condition in which hair is lost from some or all areas of the body. Often, it results in a few bald spots on the scalp, each about the size of a coin. Psychological stress and illness are possible factors in bringing on alopecia areata in individuals at risk, but in most cases there is no obvious trigger. People are generally otherwise healthy. In a few cases, all the hair on the scalp is lost ('' alopecia totalis''), or all body hair is lost (''alopecia universalis''). Hair loss can be permanent, or temporary. It is distinct from pattern hair loss, which is common among males. Alopecia areata is believed to be an autoimmune disease resulting from a breach in the immune privilege of the hair follicles. Risk factors include a family history of the condition. Among identical twins, if one is affected, the other has about a 50% chance of also being affected. The underlying mechanism involves failure by the body to recognize i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain. These episodes can result in physical injuries, either directly such as broken bones or through causing accidents. In epilepsy, seizures tend to recur and may have no immediate underlying cause. Isolated seizures that are provoked by a specific cause such as poisoning are not deemed to represent epilepsy. People with epilepsy may be treated differently in various areas of the world and experience varying degrees of social stigma due to the alarming nature of their symptoms. The underlying mechanism of epileptic seizures is excessive and abnormal neuronal activity in the cortex of the brain which can be observed in the electroencephalogram (EEG) of an individual. The reason this occurs in most cases of epilepsy is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systemic Scleroderma
Systemic scleroderma, or systemic sclerosis, is an autoimmune rheumatic disease characterised by excessive production and accumulation of collagen, called fibrosis, in the skin and internal organs and by injuries to small arteries. There are two major subgroups of systemic sclerosis based on the extent of skin involvement: limited and diffuse. The limited form affects areas below, but not above, the elbows and knees with or without involvement of the face. The diffuse form also affects the skin above the elbows and knees and can also spread to the torso. Visceral organs, including the kidneys, heart, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract can also be affected by the fibrotic process. Prognosis is determined by the form of the disease and the extent of visceral involvement. Patients with limited systemic sclerosis have a better prognosis than those with the diffuse form. Death is most often caused by lung, heart, and kidney involvement. The risk of cancer is increased slightly. Survival ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycosis Fungoides
Mycosis fungoides, also known as Alibert-Bazin syndrome or granuloma fungoides, is the most common form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. It generally affects the skin, but may progress internally over time. Symptoms include rash, tumors, skin lesions, and itchy skin. While the cause remains unclear, most cases are not hereditary. Most cases are in people over 20 years of age, and it is more common in men than women. Treatment options include sunlight exposure, ultraviolet light, topical corticosteroids, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy. Signs and symptoms The symptoms of mycosis fungoides are categorized into three clinical stages: the patch stage, the plaque stage, and the tumour stage. The patch stage is defined by flat, reddish patches of varying sizes that may have a wrinkled appearance. They can also look yellowish in people with darker skin. The plaque stage follows the patch stage of mycosis fungoides. It is characterized by the presence of raised lesions that appear reddis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
Hashimoto's thyroiditis, also known as chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis and Hashimoto's disease, is an autoimmune disease in which the thyroid gland is gradually destroyed. Early on, symptoms may not be noticed. Over time, the thyroid may enlarge, forming a painless goiter. Some people eventually develop hypothyroidism with accompanying weight gain, fatigue, constipation, depression, hair loss, and general pains. After many years the thyroid typically shrinks in size. Potential complications include thyroid lymphoma. Furthermore, because it is common for untreated patients of Hashimoto's to develop hypothyroidism, further complications can include, but are not limited to, high cholesterol, heart disease, heart failure, high blood pressure, myxedema, and potential pregnancy problems. Hashimoto's thyroiditis is thought to be due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Risk factors include a family history of the condition and having another autoimmune disease. Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pernicious Anemia
Pernicious anemia is a type of vitamin B12 deficiency anemia, a disease in which not enough red blood cells are produced due to the malabsorption of vitamin B12. Malabsorption in pernicious anemia results from the lack or loss of intrinsic factor needed for the absorption of vitamin B12. Anemia is defined as a condition in which the blood has a lower than normal amount of red blood cells or hemoglobin. There may be larger red blood cells than normal but they are not always present. The most common initial symptoms are tiredness, and weakness. Other signs and symptoms of anemia include breathlessness, dizziness, a sore red tongue, lightheadedness, headaches, poor ability to exercise, cold hands and feet, low blood pressure, pale or yellow skin, chest pain, and an irregular heartbeat. The digestive tract may also be disturbed giving symptoms that can include nausea and vomiting, heartburn, upset stomach and loss of appetite. Pernicious anemia can cause osteoporosis and may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis
{{Disambiguation ...
Juvenile may refer to: *Juvenile status, or minor (law), prior to adulthood * Juvenile (organism) *Juvenile (rapper) (born 1975), American rapper * ''Juvenile'' (2000 film), Japanese film * ''Juvenile'' (2017 film) *Juvenile (greyhounds), a greyhound competition *Juvenile particles, a type of volcanic ejecta *A two-year-old horse in horse racing terminology See also *"The Juvenile", a song by Ace of Base *Juvenile novel **Any of "Heinlein juveniles" *Juvenile delinquency * Juvenilia, works by an author while a youth *Juvenal (other) Juvenal was a poet. Juvenal or Juvenals may also refer to: * Juvenal (name), and persons with the name * Juvenals, a student society * An immature bird {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual may not notice any symptoms, or may experience a brief period of influenza-like illness. Typically, this is followed by a prolonged incubation period with no symptoms. If the infection progresses, it interferes more with the immune system, increasing the risk of developing common infections such as tuberculosis, as well as other opportunistic infections, and tumors which are rare in people who have normal immune function. These late symptoms of infection are referred to as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). This stage is often also associated with unintended weight loss. HIV is spread primarily by unprotected sex (including anal and vaginal sex), contaminated blood transfusions, hypodermic needles, and from mother to ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |