|
HDAC5
Histone deacetylase 5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''HDAC5'' gene. Function Histones play a critical role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression, and developmental events. Histone acetylation/deacetylation alters chromosome structure and affects transcription factor access to DNA. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the class II histone deacetylase/acuc/apha family. It possesses histone deacetylase activity and represses transcription when tethered to a promoter. It coimmunoprecipitates only with HDAC3 family member and might form multicomplex proteins. It also interacts with myocyte enhancer factor-2 (MEF2) proteins, resulting in repression of MEF2-dependent genes. This gene is thought to be associated with colon cancer. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. AMP-activated protein kinase regulation of the glucose transporter GLUT4 occurs by phosphorylation of HDAC5. HDAC5 is involved in memory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histone Deacetylase
Histone deacetylases (, HDAC) are a class of enzymes that remove acetyl groups (O=C-CH3) from an ε-N-acetyl lysine amino acid on a histone, allowing the histones to wrap the DNA more tightly. This is important because DNA is wrapped around histones, and DNA expression is regulated by acetylation and de-acetylation. Its action is opposite to that of histone acetyltransferase. HDAC proteins are now also called lysine deacetylases (KDAC), to describe their function rather than their target, which also includes non-histone proteins. HDAC super family Together with the acetylpolyamine amidohydrolases and the acetoin utilization proteins, the histone deacetylases form an ancient protein superfamily known as the histone deacetylase superfamily. Classes of HDACs in higher eukaryotes HDACs, are classified in four classes depending on sequence homology to the yeast original enzymes and domain organization: HDAC (except class III) contain zinc and are known as Zn2+-dependent hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histone Deacetylase
Histone deacetylases (, HDAC) are a class of enzymes that remove acetyl groups (O=C-CH3) from an ε-N-acetyl lysine amino acid on a histone, allowing the histones to wrap the DNA more tightly. This is important because DNA is wrapped around histones, and DNA expression is regulated by acetylation and de-acetylation. Its action is opposite to that of histone acetyltransferase. HDAC proteins are now also called lysine deacetylases (KDAC), to describe their function rather than their target, which also includes non-histone proteins. HDAC super family Together with the acetylpolyamine amidohydrolases and the acetoin utilization proteins, the histone deacetylases form an ancient protein superfamily known as the histone deacetylase superfamily. Classes of HDACs in higher eukaryotes HDACs, are classified in four classes depending on sequence homology to the yeast original enzymes and domain organization: HDAC (except class III) contain zinc and are known as Zn2+-dependent hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocyte-specific Enhancer Factor 2A
Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MEF2A'' gene. MEF2A is a transcription factor in the Mef2 family. In humans it is located on chromosome 15q26. Certain mutations in MEF2A cause an autosomal dominant form of coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction. Function The process of differentiation from mesodermal precursor cells to myoblasts has led to the discovery of a variety of tissue-specific factors that regulate muscle gene expression. The myogenic basic helix-loop-helix proteins, including myoD (MIM 159970), myogenin (MIM 159980), MYF5 (MIM 159990), and MRF4 (MIM 159991) are 1 class of identified factors. A second family of DNA binding regulatory proteins is the myocyte-specific enhancer factor-2 (MEF2) family. Each of these proteins binds to the MEF2 target DNA sequence present in the regulatory regions of many, if not all, muscle-specific genes. The MEF2 genes are members of the MADS gene family (named for the yeast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HDAC3
Histone deacetylase 3 is an enzyme encoded by the ''HDAC3'' gene in both humans and mice. Function Histones are highly alkaline proteins that package and order DNA into structural units called nucleosomes, which comprise the major protein component of chromatin. The posttranslational and enzymatically mediated lysine acetylation and deacetylation of histone tails changes the local chromatin structure through altering the electrostatic attraction between the negatively charged DNA backbone and histones. HDAC3 is a Class I member of the histone deacetylase superfamily (comprising four classes based on function and DNA sequence homology) that is recruited to enhancers to modulate both the epigenome and nearby gene expression. HDAC3 is found exclusively in the cell nucleus where it is the sole endogenous histone deacetylase biochemically purified in the nuclear-receptor corepressor complex containing NCOR and SMRT (NCOR2). Thus, HDAC3 unlike other HDACs, has a unique role in mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HDAC Inhibitors
Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDAC inhibitors, HDACi, HDIs) are chemical compounds that inhibit histone deacetylases. HDIs have a long history of use in psychiatry and neurology as mood stabilizers and anti-epileptics. More recently they are being investigated as possible treatments for cancers, parasitic and inflammatory diseases. Cellular biochemistry/pharmacology To carry out gene expression, a cell must control the coiling and uncoiling of DNA around histones. This is accomplished with the assistance of histone acetyl transferases (HAT), which acetylate the lysine residues in core histones leading to a less compact and more transcriptionally active euchromatin, and, on the converse, the actions of histone deacetylases (HDAC), which remove the acetyl groups from the lysine residues leading to the formation of a condensed and transcriptionally silenced chromatin. Reversible modification of the terminal tails of core histones constitutes the major epigenetic mechanism for re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
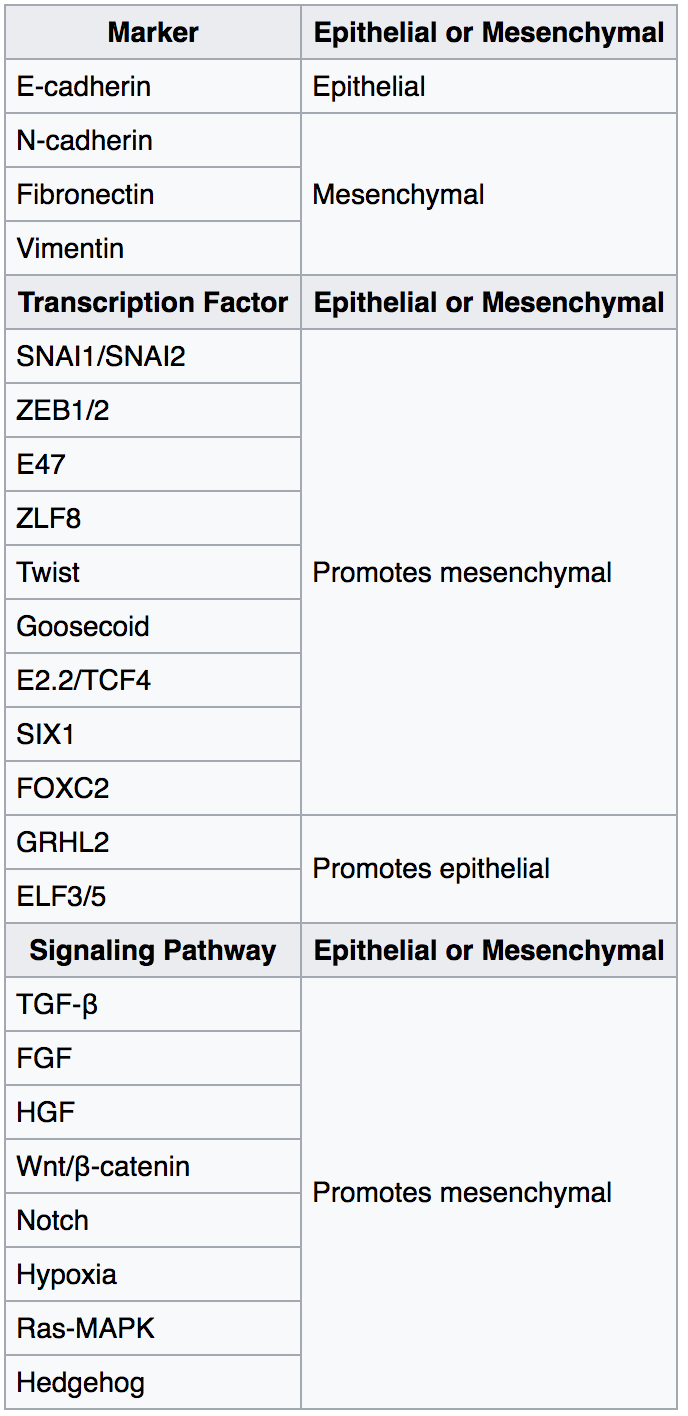
Epithelial–mesenchymal Transition
The epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a process by which epithelial cells lose their cell polarity and cell–cell adhesion, and gain migratory and invasive properties to become mesenchymal stem cells; these are multipotent stromal cells that can differentiate into a variety of cell types. EMT is essential for numerous developmental processes including mesoderm formation and neural tube formation. EMT has also been shown to occur in wound healing, in organ fibrosis and in the initiation of metastasis in cancer progression. Introduction Epithelial–mesenchymal transition was first recognized as a feature of embryogenesis by Betty Hay in the 1980s. EMT, and its reverse process, MET ( mesenchymal-epithelial transition) are critical for development of many tissues and organs in the developing embryo, and numerous embryonic events such as gastrulation, neural crest formation, heart valve formation, secondary palate development, and myogenesis. Epithelial and mesenchyma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GATA1
GATA-binding factor 1 or GATA-1 (also termed Erythroid transcription factor) is the founding member of the GATA family of transcription factors. This protein is widely expressed throughout vertebrate species. In humans and mice, it is encoded by the ''GATA1'' and ''Gata1'' genes, respectively. These genes are located on the X chromosome in both species. GATA1 regulates the expression (i.e. formation of the genes' products) of an ensemble of genes that mediate the development of red blood cells and platelets. Its critical roles in red blood cell formation include promoting the maturation of precursor cells, e.g. erythroblasts, to red blood cells and stimulating these cells to erect their cytoskeleton and biosynthesize their oxygen-carrying components viz., hemoglobin and heme. GATA1 plays a similarly critical role in the maturation of blood platelets from megakaryoblasts, promegakaryocytes, and megakaryocytes; the latter cells then shed membrane-enclosed fragments of their cytop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Finger And BTB Domain-containing Protein 16
Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 16 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ZBTB16'' gene. Function This gene is a member of the Krueppel C2H2-type zinc-finger protein family and encodes a zinc finger transcription factor that contains nine Kruppel-type zinc finger domains at the carboxyl terminus. This protein is located in the nucleus, is involved in cell cycle progression, and interacts with a histone deacetylase. Specific instances of aberrant gene rearrangement at this locus have been associated with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) and physiological roles have been identified in mouse Natural Killer T cells and gamma-delta T cells. Alternate transcriptional splice variants have been characterized in human. Interactions Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 16 has been shown to interact with: * Angiotensin II receptor type 1, * BCL6, * BMI1, * Calcitriol receptor, * FHL2, * GATA1, * GATA2, * HDAC1, * HDAC4, * HDAC5, * HDAC6, * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YWHAQ
14-3-3 protein theta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''YWHAQ'' gene. Function This gene product belongs to the 14-3-3 family of proteins that mediate signal transduction by binding to phosphoserine-containing proteins. This highly conserved protein family is found in both plants and mammals, and this protein is 99% identical to the mouse and rat orthologs. This gene is upregulated in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. It contains in its 5' UTR a 6 bp tandem repeat sequence that is polymorphic; however, there is no correlation between the repeat number and the disease. Interactions YWHAQ has been shown to interact with: * BAX, * BAD, * C-Raf, * CRTC2, * CBL * HDAC5, * MEF2D, * NRIP1, * PFKFB2, * PRKD1, * PRKCZ, * TERT Telomerase reverse transcriptase (abbreviated to TERT, or hTERT in humans) is a catalytic subunit of the enzyme telomerase, which, together with the telomerase RNA component (TERC), comprises the most important unit of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Receptor Co-repressor 2
The nuclear receptor co-repressor 2 () is a transcriptional coregulatory protein that contains several nuclear receptor-interacting domains. In addition, NCOR2 appears to recruit histone deacetylases to DNA promoter regions. Hence NCOR2 assists nuclear receptors in the down regulation of target gene expression. NCOR2 is also referred to as a silencing mediator for retinoid or thyroid-hormone receptors (SMRT) or T3 receptor-associating cofactor 1 (TRAC-1). Function NCOR2/SMRT is a transcriptional coregulatory protein that contains several modulatory functional domains including multiple autonomous repression domains as well as two or three C-terminal nuclear receptor-interacting domains. NCOR2/SMRT serves as a repressive coregulatory factor (corepressor) for multiple transcription factor pathways. In this regard, NCOR2/SMRT functions as a platform protein, facilitating the recruitment of histone deacetylases to the DNA promoters bound by its interacting transcription factors. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NRIP1
Nuclear receptor-interacting protein 1 (NRIP1) also known as receptor-interacting protein 140 (RIP140) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NRIP1'' gene. Function Nuclear receptor interacting protein 1 (NRIP1) is a nuclear protein that specifically interacts with the hormone-dependent activation domain AF2 of nuclear receptors. Also known as RIP140, this protein is a key regulator which modulates transcriptional activity of a variety of transcription factors, including the estrogen receptor. RIP140 has an important role in regulating lipid and glucose metabolism, and regulates gene expression in metabolic tissues including heart, skeletal muscle, and liver. A major role for RIP140 in adipose tissue is to block the expression of genes involved in energy dissipation and mitochondrial uncoupling, including uncoupling protein 1 and carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1b. Estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRa) can activate RIP140 during adipogenesis, by means of directl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BCL6
Bcl-6 (B-cell lymphoma 6) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BCL6'' gene. BCL6 is a master transcription factor for regulation of T follicular helper cells (TFH cells) proliferation. BCL6 has three evolutionary conserved structural domains. The interaction of these domains with corepressors allows for germinal center development and leads to B cell proliferation. The ''deletion'' of BCL6 is known to lead to failure to germinal center formation in the follicles of the lymph nodes, preventing B cells from undergoing somatic hypermutation. ''Mutations'' in BCL6 can lead to B cell lymphomas because it promotes unchecked B cell growth. Clinically, BCL6 can be used to diagnose B cell lymphomas and is shown to be upregulated in a number of cancers. Other BCL genes, including BCL2, BCL3, BCL5, BCL7A, BCL9, and BCL10, also have clinical significance in lymphoma. Normal Physiological Function Structure The protein encoded by the BCL6 gene is a zinc finger transcription f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |