|
Hydrogenation Of Carbon–nitrogen Double Bonds
In chemistry, the hydrogenation of carbon–nitrogen double bonds is the addition of the elements of dihydrogen (H2) across a carbon–nitrogen double bond, forming amines or amine derivatives. Although a variety of general methods have been developed for the enantioselective hydrogenation of ketones, methods for the hydrogenation of carbon–nitrogen double bonds are less general. Hydrogenation of imines is complicated by both ''syn''/''anti'' isomerization and tautomerization to enamines, which may be hydrogenated with low enantioselectivity in the presence of a chiral catalyst. Additionally, the substituent attached to nitrogen affects both the reactivity and spatial properties of the imine, complicating the development of a general catalyst system for imine hydrogenation. Despite these challenges, methods have been developed that address particular substrate classes, such as ''N''-aryl, ''N''-alkyl, and endocyclic imines. If the complex is chiral and non-racemic and the substrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-Picolylamine
2-Picolylamine is an organic compound with the formula H2NCH2C5H4N. A colorless liquid, it is a common bidentate ligand and a precursor to more complex multidentate ligands such as tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine. It is usually prepared by hydrogenation of 2-cyanopyridine. One such complex is Baratta's catalyst RuCl2(PPh3)2(ampy) (ampy = 2-picolylamine) for transfer hydrogenation. Salts of the complex e(pyCH2NH2)3sup>2+ exhibit spin crossover behavior, whereby the complex switches from high to low spin configurations, depending on the temperature. Safety The oral in quail Quail is a collective name for several genera of mid-sized birds generally placed in the order Galliformes. The collective noun for a group of quail is a flock, covey, or bevy. Old World quail are placed in the family Phasianidae, and New Wor ... is low, being 750 mg/kg. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Picolylamine, 2- 2-Pyridyl compounds Amines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
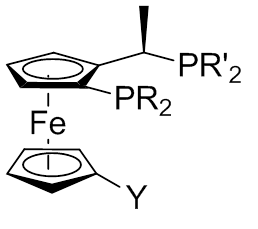
Josiphos Ligand
A Josiphos ligand is a type of chiral diphosphine which has been modified to be substrate-specific; they are widely used for enantioselective synthesis. -U. Blaser, W. Brieden, B. Pugin, F. Spindler, M. Studer and A. Togni, Top. Catal ., 2002, 19, 3. They are named after the technician who made the first one, Josi Puleo. Applications Homogeneous catalysis is often used for enantioselective transformations. The ligands carry chiral information and thus they are modified for individual substrates. Ligands can also influence the chemoselectivity of the catalyst. The Josiphos ligands, often called privileged ligands, are important because of their ability to give high yields in enantioselective synthesis. Josiphos ligands were developed in the 1990s by Antonio Togni in studies on ferrocenyl ligands previously discovered by T. Hayashi (1986). These studies focused of an Au(I)-catalyzed aldol reaction at The Central Research Laboratories of the former Ciba (now Novartis). Diphos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transfer Hydrogenation
In chemistry, transfer hydrogenation is a chemical reaction involving the addition of hydrogen to a compound from a source other than molecular . It is applied in laboratory and industrial organic synthesis to saturate organic compounds and reduce ketones to alcohols, and imines to amines. It avoids the need for high-pressure molecular used in conventional hydrogenation. Transfer hydrogenation usually occurs at mild temperature and pressure conditions using organic or organometallic catalysts, many of which are chiral, allowing efficient asymmetric synthesis. It uses hydrogen donor compounds such as formic acid, isopropanol or dihydroanthracene, dehydrogenating them to , acetone, or anthracene respectively. Often, the donor molecules also function as solvents for the reaction. A large scale application of transfer hydrogenation is coal liquefaction using "donor solvents" such as tetralin. Organometallic catalysts In the area of organic synthesis, a useful family of hydrogen-trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
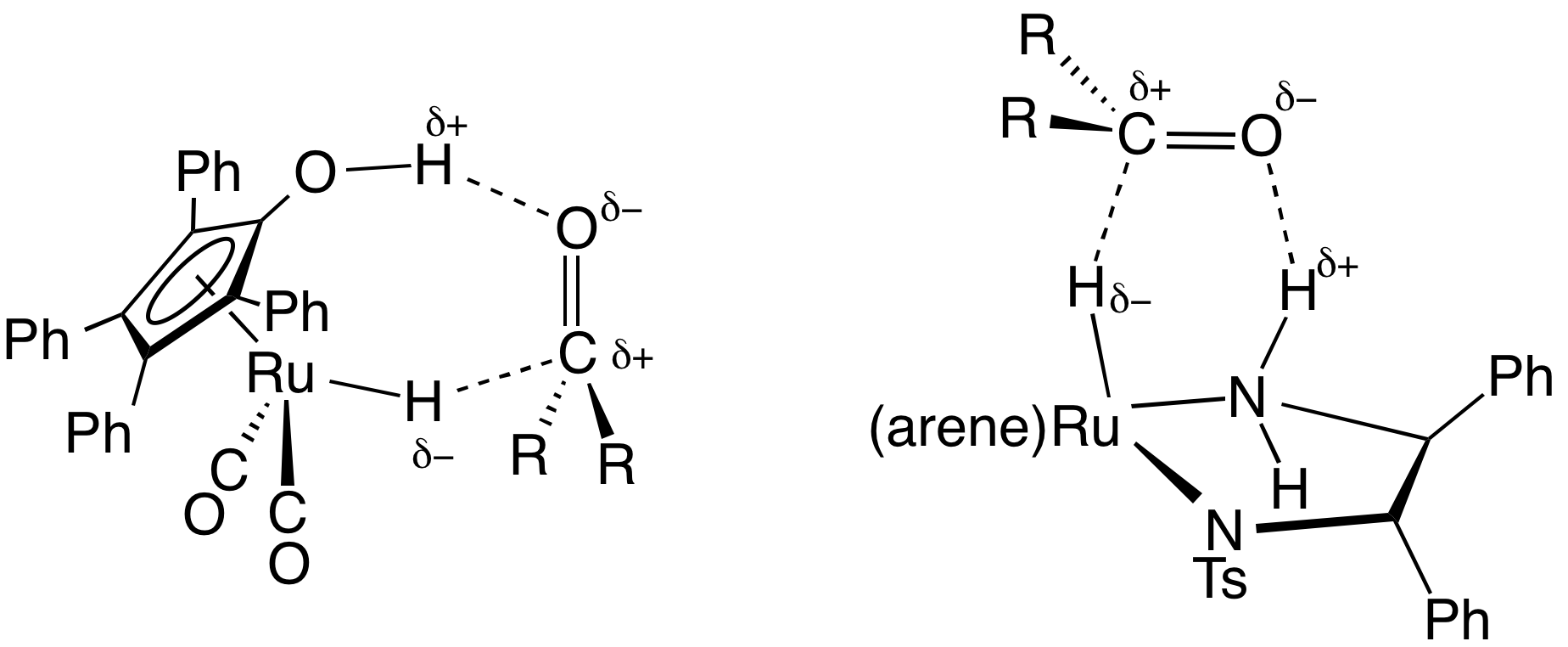
Shvo Catalyst
The Shvo catalyst is an organoruthenium compound that catalyzes the hydrogenation of polar functional groups including aldehydes, ketones and imines. The compound is of academic interest as an early example of a catalyst for transfer hydrogenation that operates by an "outer sphere mechanism". Related derivatives are known where p-tolyl replaces some of the phenyl groups. Shvo's catalyst represents a subset of homogeneous hydrogenation catalysts that involves both metal and ligand in its mechanism. Synthesis and structure The catalyst is named after Youval Shvo, who uncovered it through studies on the effect of diphenylacetylene on the catalytic properties of triruthenium dodecacarbonyl. The reaction of diphenylacetylene and Ru3(CO)12 gives the piano stool complex . Subsequent hydrogenation of this tricarbonyl affords Shvo's catalyst. Y. Blum, D. Reshef, and Y. Shvo. H-transfer catalysis with Ru3(CO)12. Tetrahedron Lett. 22(16) 1981, pp. 1541-1544. Blum, Y.; Shvo, Y. Isr. J. Chem. 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition Metal Complex
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the Periodic Table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central atom are common. These comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |