|
Hydration (other)
Hydration may refer to: * Hydrate, a substance that contains water * Hydration enthalpy, energy released through hydrating a substance * Hydration reaction, a chemical addition reaction where a hydroxyl group and proton are added to a compound * Hydration shell, a type of solvation shell * Hydration system, an apparatus that helps its user drink enough liquid while engaged in physical activity ** Hydration pack, a type of hydration system composed of a carry-on pack used for hydration * Mineral hydration, an inorganic chemical reaction where water is added to the crystal structure of a mineral * Drinking in general, including: ** Oral rehydration therapy, hydration as a health treatment ** Management of dehydration, medical hydration * Tissue hydration, the supply and retention of adequate water in biological tissues * Water of hydration, water that occurs within crystals *Hydration (web development) See also * Dehydration (other) * Solvation {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrate
In chemistry, a hydrate is a substance that contains water or its constituent elements. The chemical state of the water varies widely between different classes of hydrates, some of which were so labeled before their chemical structure was understood. Chemical nature Inorganic chemistry Hydrates are inorganic salts "containing water molecules combined in a definite ratio as an integral part of the crystal" that are either bound to a metal center or that have crystallized with the metal complex. Such hydrates are also said to contain ''water of crystallization'' or ''water of hydration''. If the water is heavy water in which the constituent hydrogen is the isotope deuterium, then the term ''deuterate'' may be used in place of ''hydrate''. A colorful example is cobalt(II) chloride, which turns from blue to red upon hydration, and can therefore be used as a water indicator. The notation "''hydrated compound''⋅''n''", where ''n'' is the number of water molecules per formula un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydration Enthalpy
In chemistry, hydration energy (also hydration enthalpy) is the amount of energy released when one mole of ions undergoes hydration. Hydration energy is one component in the quantitative analysis of solvation. It is a particular special case of water. The value of hydration energies is one of the most challenging aspects of structural prediction. Upon dissolving a salt in water, the cations and anions interact with the positive and negative dipoles of the water. The trade-off of these interactions vs those within the crystalline solid comprises the hydration energy. Examples If the hydration energy is greater than the lattice energy, then the enthalpy of solution is negative (heat is released), otherwise it is positive (heat is absorbed). The hydration energy should not be confused with solvation energy, which is the change in Gibb's free energy (not enthalpy) as solute in the gaseous state is dissolved. If the solvation energy is positive, then the solvation process is enderg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydration Reaction
In chemistry, a hydration reaction is a chemical reaction A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the IUPAC nomenclature for organic transformations, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the pos ... in which a substance combines with water. In organic chemistry, water is added to an unsaturated substrate, which is usually an alkene or an alkyne. This type of reaction is employed industrially to produce ethanol, isopropanol, and butan-2-ol.. Organic chemistry Epoxides to glycol Several million tons of ethylene glycol are produced annually by the hydration of oxirane, a cyclic compound also known as ethylene oxide: : C2H4O + H2O → HO–CH2CH2–OH Acid catalysts are typically used. Alkenes For the hydration of alkenes, the general chemical equation of the reaction is the following: :RRC=CH2 + H2O → RRC(OH)-CH3 A hydroxyl group (OH−) attaches to one carbon of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydration Shell
A solvation shell or solvation sheath is the solvent interface of any chemical compound or biomolecule that constitutes the solute. When the solvent is water it is called a hydration shell or hydration sphere. The number of solvent molecules surrounding each unit of solute is called the hydration number of the solute. A classic example is when water molecules arrange around a metal ion. If the metal ion is a cation, the electronegative oxygen atom of the water molecule would be attracted electrostatically to the positive charge on the metal ion. The result is a solvation shell of water molecules that surround the ion. This shell can be several molecules thick, dependent upon the charge of the ion, its distribution and spatial dimensions. A number of molecules of solvent are involved in the solvation shell around anions and cations from a dissolved salt in a solvent. Metal ions in aqueous solutions form metal aquo complexes. This number can be determined by various methods like c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydration System
A hydration system is an apparatus used in recreation and other sustained outdoor activities. It is intended to help its user carry liquid, to support the physical effort involved in the activity, without the need to use one's hands or take off the pack. Such systems for consumers were first sold to cyclists, and by the 1990s had also found a substantial market among hikers. Familiar commercial models can also be recognized occasionally worn by western military personnel in southwest Asia. In practice, such a system is almost always a commercially manufactured unit that features at least * a flexible bladder of one or a few liters' (quarts') capacity with some means, usually a screwtop, to fill and then reliably seal it, * a light hose to convey the beverage to the user's mouth, and * a bite valve that starts and stops the flow through the hose with minimal effort. Also common are designs that include specific hands-free means to comfortably carry the hydration system. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydration Pack
A hydration pack or drink bag is a type of hydration system built as a backpack or waistpack containing a reservoir or "bladder" commonly made of rubber or flexible plastic. The reservoir contains a capped mouth for filling with liquid and a hose that allows the wearer to drink hands-free. Most hoses end with a "bite valve" that opens when the user bites down on it; the valve may be protected by a dust cover. Some hydration packs are insulated to keep water from freezing or becoming warm. Uses The volume of the reservoir and the pack carrying it can vary widely depending on the purpose of the hydration pack. Some packs are extremely small and minimalist, designed to add as little weight as possible and remain secure while running or cycling, while others are more suited for backpacking and extended hikes, equipped with much larger bladders. However, as water weighs , it is impractical to carry more than a few liters in most situations; typical reservoirs are between 1-3 L even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineral Hydration
In chemistry, mineral hydration is an inorganic chemical reaction which adds water to the crystal structure of a mineral, usually creating a new mineral, usually called a ''hydrate''. In geological terms, the process of mineral hydration is known as ''retrograde alteration'' and is a process occurring in retrograde metamorphism. It commonly accompanies metasomatism and is often a feature of wall rock alteration around ore bodies. Hydration of minerals occurs generally in concert with hydrothermal circulation which may be driven by tectonic or igneous activity. Processes There are two main ways in which minerals hydrate. One is conversion of an oxide to a double hydroxide, as with the hydration of calcium oxide—CaO—to calcium hydroxide—Ca(OH)2, the other is with the incorporation of water molecules directly into the crystalline structure of a new mineral. The later process is exhibited in the hydration of feldspars to clay minerals, garnet to chlorite, or kyanite to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drinking
Drinking is the act of ingesting water or other liquids into the body through the mouth, proboscis, or elsewhere. Humans drink by swallowing, completed by peristalsis in the esophagus. The physiological processes of drinking vary widely among other animals. Most animals drink water to maintain bodily hydration, although many can survive on the water gained from their food. Water is required for many physiological processes. Both inadequate and (less commonly) excessive water intake are associated with health problems. Methods of drinking In humans When a liquid enters a human mouth, the swallowing process is completed by peristalsis which delivers the liquid through the esophagus to the stomach; much of the activity is abetted by gravity. The liquid may be poured from the hands or drinkware may be used as vessels. Drinking can also be performed by acts of inhalation, typically when imbibing hot liquids or drinking from a spoon. Infants employ a method of suction wherein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
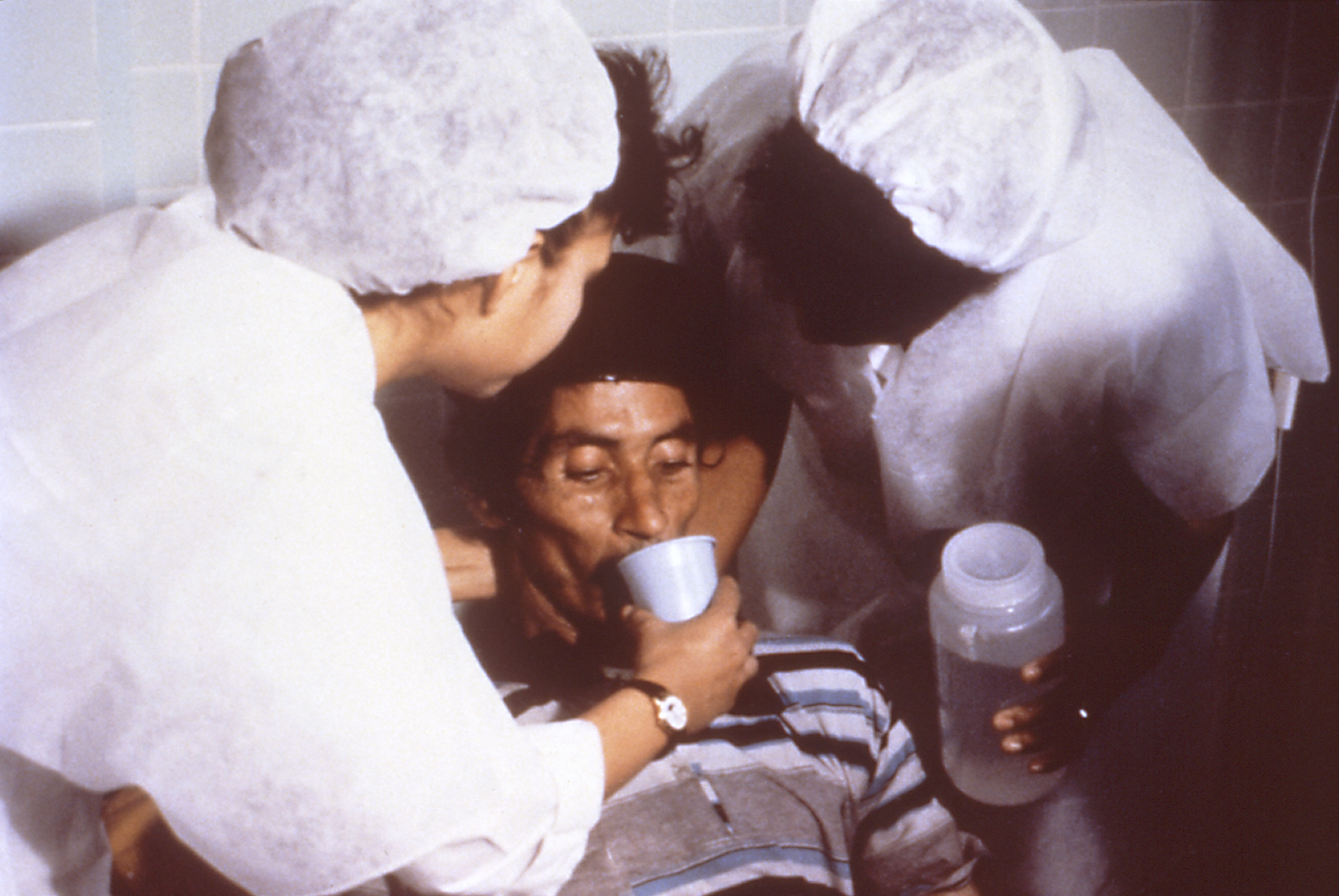
Oral Rehydration Therapy
Oral rehydration therapy (ORT) is a type of fluid replacement used to prevent and treat dehydration, especially due to diarrhea. It involves drinking water with modest amounts of sugar and salts, specifically sodium and potassium. Oral rehydration therapy can also be given by a nasogastric tube. Therapy should routinely include the use of zinc supplements. Use of oral rehydration therapy has been estimated to decrease the risk of death from diarrhea by up to 93%. Side effects may include vomiting, high blood sodium, or high blood potassium. If vomiting occurs, it is recommended that use be paused for 10 minutes and then gradually restarted. The recommended formulation includes sodium chloride, sodium citrate, potassium chloride, and glucose. Glucose may be replaced by sucrose and sodium citrate may be replaced by sodium bicarbonate, if not available. It works as glucose increases the uptake of sodium and thus water by the intestines. A number of other formulations are also ava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Management Of Dehydration
The management of dehydration typically involves the use of oral rehydration solution (ORS). Standard home solutions such as salted rice water, salted yogurt drinks, vegetable and chicken soups with salt can be given. Home solutions such as water in which cereal has been cooked, unsalted soup, green coconut water, weak tea (unsweetened), and unsweetened fresh fruit juices can have from half a teaspoon to full teaspoon of salt (from one-and-a-half to three grams) added per liter. Clean plain water can also be one of several fluids given. There are commercial solutions such as Pedialyte, and relief agencies such as UNICEF widely distribute packets of salts and sugar. The World Health Organization (WHO) describes a homemade ORS with one liter water with one teaspoon salt (or 3 grams) and six teaspoons sugar (or 18 grams) added (approximately the "taste of tears"). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissue Hydration
Tissue hydration is the process of absorbing and retaining water in biological tissues. Plants Land plants maintain adequate tissue hydration by means of an outer waterproof layer. In soft or green tissues, this is usually a waxy cuticle over the outer epidermis. In older, woody tissues, waterproofing chemicals are present in the secondary cell wall that limit or inhibit the flow of water. Vascular plants also possess an internal vascular system that distributes fluids throughout the plant. Some xerophytes, such as cacti and other desert plants, have mucilage in their tissues. This is a sticky substance that holds water within the plant, reducing the rate of dehydration. Some seeds and spores remain dormant until adequate moisture is present, at which time the seed or spore begins to germinate. Animals Animals maintain adequate tissue hydration by means of (1) an outer skin, shell, or cuticle; (2) a fluid-filled coelom cavity; and (3) a circulatory system. Hydration of fat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Of Hydration
In chemistry, water(s) of crystallization or water(s) of hydration are water molecules that are present inside crystals. Water is often incorporated in the formation of crystals from aqueous solutions. In some contexts, water of crystallization is the total mass of water in a substance at a given temperature and is mostly present in a definite (stoichiometric) ratio. Classically, "water of crystallization" refers to water that is found in the crystalline framework of a metal complex or a salt, which is not directly bonded to the metal cation. Upon crystallization from water, or water-containing solvents, many compounds incorporate water molecules in their crystalline frameworks. Water of crystallization can generally be removed by heating a sample but the crystalline properties are often lost. Compared to inorganic salts, proteins crystallize with large amounts of water in the crystal lattice. A water content of 50% is not uncommon for proteins. Applications Knowledge of hyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_chloride.jpg)