|
Hyaluronic Acid
Hyaluronic acid (; abbreviated HA; conjugate base hyaluronate), also called hyaluronan, is an anionic, nonsulfated glycosaminoglycan distributed widely throughout connective, epithelial, and neural tissues. It is unique among glycosaminoglycans as it is non-sulfated, forms in the plasma membrane instead of the Golgi apparatus, and can be very large: human synovial HA averages about 7 million Da per molecule, or about 20,000 disaccharide monomers, while other sources mention 3–4 million Da. The average 70 kg (150 lb) person has roughly 15 grams of hyaluronan in the body, one-third of which is turned over (i.e., degraded and synthesized) per day. As one of the chief components of the extracellular matrix, it contributes significantly to cell proliferation and migration, and is involved in the progression of many malignant tumors. Hyaluronic acid is also a component of the group A streptococcal extracellular capsule, and is believed to play a role in virule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucuronic Acid
Glucuronic acid (from Greek γλεῦκος "''wine, must''" and οὖρον "''urine''") is a uronic acid that was first isolated from urine (hence the name). It is found in many gums such as gum arabic (c. 18%), xanthan, and kombucha tea and is important for the metabolism of microorganisms, plants and animals. Properties Glucuronic acid is a sugar acid derived from glucose, with its sixth carbon atom oxidized to a carboxylic acid. In living beings, this primary oxidation occurs with UDP-α-D-glucose (UDPG), not with the free sugar. Glucuronic acid, like its precursor glucose, can exist as a linear (carboxo-)aldohexose ( 60,000 are too large for renal excretion and will be excreted with bile into the intestine. Neonates are deficient in this conjugating system, making them particularly vulnerable to drugs such as chloramphenicol, which is inactivated by the addition of glucuronic acid, resulting in gray baby syndrome. Bilirubin is excreted in the bile as bilir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Capsule
The bacteria capsule is a large structure common to many bacteria. It is a polysaccharide layer that lies outside the cell envelope, and is thus deemed part of the outer envelope of a bacterial cell. It is a well-organized layer, not easily washed off, and it can be the cause of various diseases. The capsule—which can be found in both gram negative and gram-positive bacteria—is different from the second lipid membrane – bacterial outer membrane, which contains lipopolysaccharides and lipoproteins and is found only in gram-negative bacteria. When the amorphous viscid secretion (that makes up the capsule) diffuses into the surrounding medium and remains as a loose undemarcated secretion, it is known as a slime layer. Capsule and slime layer are sometimes summarized under the term glycocalyx. Composition Most bacterial capsules are composed of polysaccharide, but some species use other materials, such as poly-D-glutamic acid in ''Bacillus anthracis''. Because most caps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Surface Receptor
Cell surface receptors (membrane receptors, transmembrane receptors) are receptors that are embedded in the plasma membrane of cells. They act in cell signaling by receiving (binding to) extracellular molecules. They are specialized integral membrane proteins that allow communication between the cell and the extracellular space. The extracellular molecules may be hormones, neurotransmitters, cytokines, growth factors, cell adhesion molecules, or nutrients; they react with the receptor to induce changes in the metabolism and activity of a cell. In the process of signal transduction, ligand binding affects a cascading chemical change through the cell membrane. Structure and mechanism Many membrane receptors are transmembrane proteins. There are various kinds, including glycoproteins and lipoproteins. Hundreds of different receptors are known and many more have yet to be studied. Transmembrane receptors are typically classified based on their Biomolecular structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided into two layers, the superficial area adjacent to the epidermis called the papillary region and a deep thicker area known as the reticular dermis.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology'' (10th ed.). Saunders. Pages 1, 11–12. . The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis through a basement membrane. Structural components of the dermis are collagen, elastic fibers, and extrafibrillar matrix.Marks, James G; Miller, Jeffery (2006). ''Lookingbill and Marks' Principles of Dermatology'' (4th ed.). Elsevier Inc. Page 8–9. . It also contains mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and thermoreceptors that provide the sense of heat. In addition, hair follicles, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunburn
Sunburn is a form of radiation burn that affects living tissue, such as skin, that results from an overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, usually from the Sun. Common symptoms in humans and animals include: red or reddish skin that is hot to the touch or painful, general fatigue, and mild dizziness. Other symptoms include blistering, peeling skin, swelling, itching, and nausea. Excessive UV radiation is the leading cause of (primarily) non-malignant skin tumors,World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cance"Do sunscreens prevent skin cancer" Press release No. 132, 5 June 2000World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cance"Solar and ultraviolet radiation"IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, Volume 55, November 1997 and in extreme cases can be life-threatening. Sunburn is an inflammatory response in the tissue triggered by direct DNA damage by UV radiation. When the cells' DNA is overl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UVB Radiation
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight, and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack the energy to ionize atoms, it can cause chemical reactions and causes many substances to glow or fluoresce. Consequently, the chemical and biological effects of UV are greater than simple heating effects, and many practical applications of UV radiation derive from its interactions with organic molecules. Short-wave ultraviolet light damages DNA and sterilizes surfaces with which it comes into contact. For h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibroblast
A fibroblast is a type of biological cell that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework ( stroma) for animal tissues, and plays a critical role in wound healing. Fibroblasts are the most common cells of connective tissue in animals. Structure Fibroblasts have a branched cytoplasm surrounding an elliptical, speckled nucleus having two or more nucleoli. Active fibroblasts can be recognized by their abundant rough endoplasmic reticulum. Inactive fibroblasts (called fibrocytes) are smaller, spindle-shaped, and have a reduced amount of rough endoplasmic reticulum. Although disjointed and scattered when they have to cover a large space, fibroblasts, when crowded, often locally align in parallel clusters. Unlike the epithelial cells lining the body structures, fibroblasts do not form flat monolayers and are not restricted by a polarizing attachment to a basal lamina on one side, although they may contribute to basal lamina components in so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
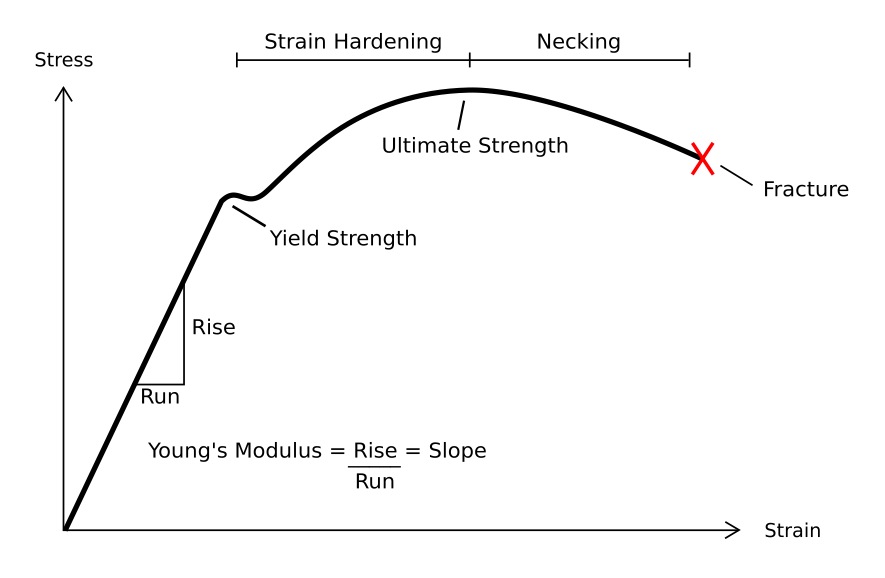
Resilience (materials Science)
In material science, resilience is the ability of a material to absorb energy when it is deformed elastically, and release that energy upon unloading. Proof resilience is defined as the maximum energy that can be absorbed up to the elastic limit, without creating a permanent distortion. The modulus of resilience is defined as the maximum energy that can be absorbed per unit volume without creating a permanent distortion. It can be calculated by integrating the stress–strain curve from zero to the elastic limit. In uniaxial tension, under the assumptions of linear elasticity, : U_= \frac = \frac where ''Ur'' is the modulus of resilience, ''σy'' is the yield strength, ''εy'' is the yield strain, and ''E'' is the Young's modulus. This analysis is not valid for non-linear elastic materials like rubber, for which the approach of area under the curve until elastic limit must be used. Unit of resilience Modulus of resilience (''U''r) is measured in a unit of joule per cubic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HAPLN1
Hyaluronan and proteoglycan link protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HAPLN1'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b .... Interactions HAPLN1 has been shown to interact with Versican. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-5-stub Extracellular matrix proteins Glycoproteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aggrecan
Aggrecan (ACAN), also known as cartilage-specific proteoglycan core protein (CSPCP) or chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ACAN'' gene. This gene is a member of the lectican ( chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan) family. The encoded protein is an integral part of the extracellular matrix in cartilagenous tissue and it withstands compression in cartilage. Aggrecan is a proteoglycan, or a protein modified with large carbohydrates; the human form of the protein is 2316 amino acids long and can be expressed in multiple isoforms due to alternative splicing. Aggrecan was named for its ability to form large aggregates in the cartilage tissue (a large aggregating proteoglycan). Structure Aggrecan is a high molecular weight (1x106 < M < 3x106) proteoglycan. It exhibits a bottlebrush structure, in which chondroitin sulfate and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chondrocyte
Chondrocytes (, from Greek χόνδρος, ''chondros'' = cartilage + κύτος, ''kytos'' = cell) are the only cells found in healthy cartilage. They produce and maintain the cartilaginous matrix, which consists mainly of collagen and proteoglycans. Although the word ''chondroblast'' is commonly used to describe an immature chondrocyte, the term is imprecise, since the progenitor of chondrocytes (which are mesenchymal stem cells) can differentiate into various cell types, including osteoblasts. Development From least- to terminally-differentiated, the chondrocytic lineage is: # Colony-forming unit-fibroblast # Mesenchymal stem cell / marrow stromal cell # Chondrocyte # Hypertrophic chondrocyte Mesenchymal (mesoderm origin) stem cells are undifferentiated, meaning they can differentiate into a variety of generative cells commonly known as osteochondrogenic (or osteogenic, chondrogenic, osteoprogenitor, etc.) cells. When referring to bone, or in this case cartilage, the orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck and the bronchial tubes, and the intervertebral discs. In other taxa, such as chondrichthyans, but also in cyclostomes, it may constitute a much greater proportion of the skeleton. It is not as hard and rigid as bone, but it is much stiffer and much less flexible than muscle. The matrix of cartilage is made up of glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, collagen fibers and, sometimes, elastin. Because of its rigidity, cartilage often serves the purpose of holding tubes open in the body. Examples include the rings of the trachea, such as the cricoid cartilage and carina. Cartilage is composed of specialized cells called chondrocytes that produce a large amount of collagenous extracellular matrix, abundant ground substance that is rich in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)