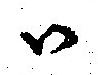|
Horizontal Square Script
Zanabazar's square script is a horizontal Mongolian square script ( mn, Хэвтээ Дөрвөлжин бичиг, ''Khevtee Dörvöljin bichig'' or mn, Хэвтээ Дөрвөлжин Үсэг, ''Khevtee Dörvöljin Üseg''), an abugida developed by the monk and scholar Zanabazar to write Mongolian. It can also be used to write Tibetan and Sanskrit. It was re-discovered in 1801 and the script's applications during the period of its use are not known. It was also largely based on the Tibetan alphabet, read left to right, and employed vowel diacritics above and below the consonant letters. Letters Vowels Consonants Others Unicode "Zanabazar Square" has been included in the Unicode Standard since the release of Unicode version 10.0 in June 2017. The Zanabazar Square block contains 72 characters. The Unicode block for Zanabazar Square is U+11A00–U+11A4F: Reference See also *Mongolian writing systems *ʼPhags-pa script The Phags-pa script is an alphabet de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abugida
An abugida (, from Ge'ez language, Ge'ez: ), sometimes known as alphasyllabary, neosyllabary or pseudo-alphabet, is a segmental Writing systems#Segmental writing system, writing system in which consonant-vowel sequences are written as units; each unit is based on a consonant letter, and vowel notation is secondary. This contrasts with a full alphabet, in which vowels have status equal to consonants, and with an abjad, in which vowel marking is absent, Abjad#Impure abjads, partial, or optional (although in less formal contexts, all three types of script may be termed alphabets). The terms also contrast them with a syllabary, in which the symbols cannot be split into separate consonants and vowels. Related concepts were introduced independently in 1948 by James Germain Février (using the term ) and David Diringer (using the term ''semisyllabary''), then in 1959 by Fred Householder (introducing the term ''pseudo-alphabet''). The Ethiopian Semitic languages, Ethiopic term "abugi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zanabazar Square Vowels
Öndör Gegeen Zanabazar, , , "High Saint Zanabazar"; 1635–1723 (born Eshidorji) was the sixteenth ''Jebtsundamba Khutuktu'' and the first ''Bogd Gegeen'' or supreme spiritual authority, of the Gelugpa (Yellow Hat) lineage of Tibetan Buddhism in Mongolia. The son of a Mongol Tüsheet Khan, Zanabazar was declared spiritual leader of Khalkha Mongols by a convocation of nobles in 1639 when he was just four years old. The 5th Dalai Lama (1617–1682) later recognized him as the reincarnation of the Buddhist scholar Taranatha and bestowed on him the Sanskrit name ''Jñānavajra'' (Sanskrit: ज्ञानवज्र, ''Zanabazar'' in Mongolian) meaning "thunderbolt scepter of wisdom". Over the course of nearly 60 years, Zanabazar advanced the Gelugpa school of Buddhism among the Mongols, supplanting or synthesizing Sakya or "Red Hat" Buddhist traditions that had prevailed in the area, while strongly influencing social and political developments in 17th century Mongolia. His close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ʼPhags-pa Script
The Phags-pa script is an alphabet designed by the Tibetan monk and State Preceptor (later Imperial Preceptor) Drogön Chögyal Phagpa for Kublai Khan, the founder of the Yuan dynasty, as a unified script for the written languages within the Yuan. The actual use of this script was limited to about a hundred years during the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty, and it fell out of use with the advent of the Ming dynasty. It was used to write and transcribe varieties of Chinese, the Tibetic languages, Mongolian, the Uyghur language, Sanskrit, Persian, and other neighboring languages during the Yuan era. For historical linguists, the documentation of its use provides clues about the changes in these languages. Its descendant systems include Horizontal square script, used to write Tibetan and Sanskrit. There is a theory that the Korean Hangul alphabet had a limited influence from Phags-pa (see Origin of Hangul). During the Pax Mongolica the script has even made numerous appearances in west ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicode Consortium
The Unicode Consortium (legally Unicode, Inc.) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization incorporated and based in Mountain View, California. Its primary purpose is to maintain and publish the Unicode Standard which was developed with the intention of replacing existing character encoding schemes which are limited in size and scope, and are incompatible with multilingual environments. The consortium describes its overall purpose as: Unicode's success at unifying character sets has led to its widespread adoption in the internationalization and localization of software. The standard has been implemented in many technologies, including XML, the Java programming language, Swift, and modern operating systems. Voting members include computer software and hardware companies with an interest in text-processing standards, including Adobe, Apple, the Bangladesh Computer Council, Emojipedia, Facebook, Google, IBM, Microsoft, the Omani Ministry of Endowments and Religious Affairs, Monotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zanabazar Square (Unicode Block)
Zanabazar Square is a Unicode block containing characters from the Zanabazar Square script (also known as "Horizontal square script"), which is an abugida developed by the monk and scholar Zanabazar (1635–1723) to write Mongolian, Tibetan and Sanskrit Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late .... Block History The following Unicode-related documents record the purpose and process of defining specific characters in the Zanabazar Square block: References {{reflist Unicode blocks 2017 introductions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicode Standard
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology standard for the consistent encoding, representation, and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems. The standard, which is maintained by the Unicode Consortium, defines as of the current version (15.0) 149,186 characters covering 161 modern and historic scripts, as well as symbols, emoji (including in colors), and non-visual control and formatting codes. Unicode's success at unifying character sets has led to its widespread and predominant use in the internationalization and localization of computer software. The standard has been implemented in many recent technologies, including modern operating systems, XML, and most modern programming languages. The Unicode character repertoire is synchronized with ISO/IEC 10646, each being code-for-code identical with the other. ''The Unicode Standard'', however, includes more than just the base code. Alongside the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consonant Cluster
In linguistics, a consonant cluster, consonant sequence or consonant compound, is a group of consonants which have no intervening vowel. In English, for example, the groups and are consonant clusters in the word ''splits''. In the education field it is variously called a consonant cluster or a consonant blend. Some linguists argue that the term can be properly applied only to those consonant clusters that occur within one syllable. Others claim that the concept is more useful when it includes consonant sequences across syllable boundaries. According to the former definition, the longest consonant clusters in the word ''extra'' would be and , whereas the latter allows , which is phonetically in some accents. Phonotactics Each language has an associated set of phonotactic constraints. Languages' phonotactics differ as to what consonant clusters they permit. Many languages are more restrictive than English in terms of consonant clusters, and some forbid consonant clusters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visarga
Visarga ( sa, विसर्गः, translit=visargaḥ) means "sending forth, discharge". In Sanskrit phonology ('' ''), ' (also called, equivalently, ' by earlier grammarians) is the name of a phone voiceless glottal fricative, , written as: Visarga is an allophone of and in pausa (at the end of an utterance). Since is a common inflectional suffix (of nominative singular, second person singular, etc.), visarga appears frequently in Sanskrit texts. In the traditional order of Sanskrit sounds, visarga and anusvāra appear between vowels and stop consonants. The precise pronunciation of visarga in Vedic texts may vary between Śākhās. Some pronounce a slight echo of the preceding vowel after the aspiration: will be pronounced , and will be pronounced . Visarga is not to be confused with colon. Types The visarga is commonly found in writing, resembling the punctuation mark of colon or as two tiny circles one above the other. This form is retained by most Indian s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anusvara
Anusvara (Sanskrit: ') is a symbol used in many Indic scripts to mark a type of nasal sound, typically transliterated . Depending on its location in the word and the language for which it is used, its exact pronunciation can vary. In the context of ancient Sanskrit, ''anusvara'' is the name of the particular nasal sound itself, regardless of written representation. Sanskrit In Vedic Sanskrit, the anusvāra (lit. "after-sound" or "subordinate sound") was an allophonic (derived) nasal sound. The exact nature of the sound has been subject to debate. The material in the various ancient phonetic treatises points towards different phonetic interpretations, and these discrepancies have historically been attributed to either differences in the description of the same pronunciation or to dialectal or diachronic variation. In a 2013 reappraisal of the evidence, Cardona concludes that these reflect real dialectal differences. The environments in which the anusvara could arise, however, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candrabindu
Chandrabindu (IAST: , in Sanskrit) is a diacritic sign with the form of a dot inside the lower half of a circle. It is used in the Devanagari (ँ), Bengali-Assamese (), Gujarati (ઁ), Odia (ଁ), Telugu (ఁ), Javanese ( ꦀ) and other scripts. It usually means that the previous vowel is nasalized. In Hindi, it is replaced in writing by anusvara when it is written above a consonant that carries a vowel symbol that extends above the top line. In Classical Sanskrit, it seems to occur only over a ''lla'' conjunct consonant, to show that it is pronounced as a nasalized double ''l'', which occurs if ''-nl-'' have become assimilated in sandhi. In Vedic Sanskrit, it is used instead of anusvara to represent the sound anunasika when the next word starts with a vowel. It usually occurs where in earlier times a word ended in ''-ans''. Unicode encodes chandrabindu and chandrabindu-like characters for a variety of scripts: * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virama
Virama ( ्) is a Sanskrit phonological concept to suppress the inherent vowel that otherwise occurs with every consonant letter, commonly used as a generic term for a codepoint in Unicode, representing either # halanta, hasanta or explicit virāma, a diacritic in many Brahmic scripts, including the Devanagari and Bengali–Assamese script, Bengali scripts, or # saṃyuktākṣara (Sanskrit: संयुक्ताक्षर) or implicit virama, a conjunct consonant or ligature. Unicode schemes of scripts writing Mainland Southeast Asia linguistic area, Mainland Southeast Asia languages, such as that of Burmese script and of Tibetan script, generally don't group the two functions together. Names The name is Sanskrit for "cessation, termination, end". As a Sanskrit word, it is used in place of several language-specific terms, such as: }, ''sukun'' , ް◌ , Derives from Arabic "sukun" , - , ''Srog med'' , Lhasa Tibetan, Tibetan , ''Srog med'' , ྄ , Only used when transcrib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zanabazar Square Sign
Öndör Gegeen Zanabazar, , , "High Saint Zanabazar"; 1635–1723 (born Eshidorji) was the sixteenth ''Jebtsundamba Khutuktu'' and the first ''Bogd Gegeen'' or supreme spiritual authority, of the Gelugpa (Yellow Hat) lineage of Tibetan Buddhism in Mongolia. The son of a Mongol Tüsheet Khan, Zanabazar was declared spiritual leader of Khalkha Mongols by a convocation of nobles in 1639 when he was just four years old. The 5th Dalai Lama (1617–1682) later recognized him as the reincarnation of the Buddhist scholar Taranatha and bestowed on him the Sanskrit name ''Jñānavajra'' (Sanskrit: ज्ञानवज्र, ''Zanabazar'' in Mongolian) meaning "thunderbolt scepter of wisdom". Over the course of nearly 60 years, Zanabazar advanced the Gelugpa school of Buddhism among the Mongols, supplanting or synthesizing Sakya or "Red Hat" Buddhist traditions that had prevailed in the area, while strongly influencing social and political developments in 17th century Mongolia. His close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |