|
Homing (biology)
Homing is the inherent ability of an animal to navigate towards an original location (geography), location through unfamiliar areas. This location may be either a home territory, or a breeding spot. Uses Homing abilities can be used to find the way back to home in a wikt:migration, migration. It is often used in reference to going back to a breeding spot seen years before, as in the case of salmon. Homing abilities can also be used to go back to familiar territory when displaced over long distances, such as with the red-bellied newt. True navigation Some animals use true navigation for their homing. This means in familiar areas they will use landmarks such as roads, rivers or mountains when flying, or islands and other landmarks while swimming. However, this only works in familiar territory. Homing pigeons, for example, will often navigate using familiar landmarks, such as roads. Sea turtles will also use landmarks to orient themselves.Avens, L., (2003) "Homing Behavior, Naviga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homing Pigeon
The homing pigeon, also called the mail pigeon or messenger pigeon, is a variety of domestic pigeons (''Columba livia domestica'') derived from the wild rock dove, selective breeding, selectively bred for its ability to find its way home over extremely long distances. The rock dove has an innate homing ability, meaning that it will generally return to its nest using magnetoreception. Flights as long as have been recorded by birds in competitive pigeon racing. Their average flying speed over moderate distances is around and speeds of up to have been observed in top racers for short distances. In 2019 after sixty years a new world record was set in Netherlands for the fastest racing pigeon flight, distance flown 239 kilometers at speed above 143 kilometers per hour. Because of this skill, domesticated pigeons were used to carry messages as messenger pigeons. They are usually referred to as "pigeon post" if used in post service, or "war pigeon" during wars. Until the introducti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth's Magnetic Field
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. The magnetic field is generated by electric currents due to the motion of convection currents of a mixture of molten iron and nickel in Earth's outer core: these convection currents are caused by heat escaping from the core, a natural process called a geodynamo. The magnitude of Earth's magnetic field at its surface ranges from . As an approximation, it is represented by a field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 11° with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were an enormous bar magnet placed at that angle through the center of Earth. The North geomagnetic pole actually represents the South pole of Earth's magnetic field, and conversely the South geomagnetic pole corresponds to the north pole of Earth's magnetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
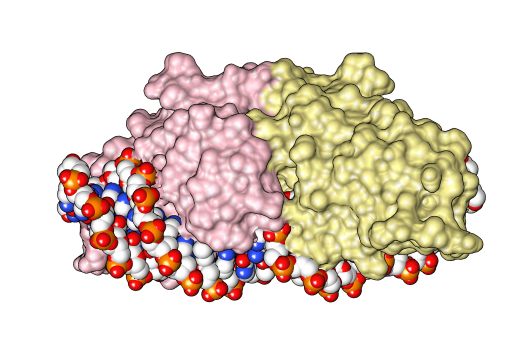
Homing Endonuclease Gene
The homing endonucleases are a collection of endonucleases encoded either as freestanding genes within introns, as fusions with host proteins, or as self-splicing inteins. They catalyze the hydrolysis of genomic DNA within the cells that synthesize them, but do so at very few, or even singular, locations. Repair of the hydrolyzed DNA by the host cell frequently results in the gene encoding the homing endonuclease having been copied into the cleavage site, hence the term 'homing' to describe the movement of these genes. Homing endonucleases can thereby transmit their genes horizontally within a host population, increasing their allele frequency at greater than Mendelian rates. Origin and mechanism Although the origin and function of homing endonucleases is still being researched, the most established hypothesis considers them as selfish genetic elements, similar to transposons, because they facilitate the perpetuation of the genetic elements that encode them independent of prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philopatry
Philopatry is the tendency of an organism to stay in or habitually return to a particular area. The causes of philopatry are numerous, but natal philopatry, where animals return to their birthplace to breed, may be the most common. The term derives from the Greek roots ''philo'', "liking, loving" and ''patra'', "fatherland", although in recent years the term has been applied to more than just the animal's birthplace. Recent usage refers to animals returning to the same area to breed despite not being born there, and migratory species that demonstrate site fidelity: reusing stopovers, staging points, and wintering grounds. Some of the known reasons for organisms to be philopatric would be for mating (reproduction), survival, migration, parental care, resources, etc.. In most species of animals, individuals will benefit from living in groups, because depending on the species, individuals are more vulnerable to predation and more likely to have difficulty finding resources and food. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natal Homing
Natal homing, or natal philopatry, is the homing process by which some adult animals return to their birthplace to reproduce. This process is primarily used by aquatic animals, such as sea turtles and Pacific salmon. Scientists believe that the main cues used by the animals are geomagnetic imprinting and olfactory cues. The benefits of returning to the precise location of an animal's birth may be largely associated with its safety and suitability as a breeding ground. When seabirds, like the Atlantic puffin, return to their natal breeding colony, which are mostly on islands, they are assured of a suitable climate and a sufficient lack of land-based predators. Sea turtles born in any one area differ genetically from turtles born in other areas. The newly hatched young head out to sea and soon find suitable feeding grounds, and it has been shown that it is to these feeding areas that they return rather than to the actual beach on which they started life. Salmon start their lives in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limpet
Limpets are a group of aquatic snails that exhibit a conical shell shape (patelliform) and a strong, muscular foot. Limpets are members of the class Gastropoda, but are polyphyletic, meaning the various groups called "limpets" descended independently from different ancestral gastropods. This general category of conical shell is known as "patelliform" (dish-shaped). All members of the large and ancient marine clade Patellogastropoda are limpets. Within that clade, the members of the Patellidae family in particular are often referred to as "true limpets". Other groups, not in the same family, are also called limpets of one type or another, due to the similarity of their shells' shape. Examples include the Fissurellidae ("keyhole limpet") family, which is part of the Vetigastropoda clade (many other members of the Vetigastropoda do not have the morphology of limpets) and the Siphonariidae ("false limpets"), which use a siphon to pump water over their gills. Behaviour and ecolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olfaction
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste. In humans, it occurs when an odor binds to a receptor within the nasal cavity, transmitting a signal through the olfactory system. Glomeruli aggregate signals from these receptors and transmit them to the olfactory bulb, where the sensory input will start to interact with parts of the brain responsible for smell identification, memory, and emotion. There are many different causes for alteration, lack, or disturbance to a normal sense of smell, and can include damage to the nose or smell receptors, or central problems affecting the brain. Some causes include upper respiratory infections, traumatic brain injury, and neurodegenerative disease. History of study Early scientific study of the sense of smell includes the extensive doctoral dissertation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marbled Newt
The marbled newt (''Triturus marmoratus'') is a mainly terrestrial newt native to western Europe. They are found in the Iberian Peninsula and France, where they typically inhabit mountainous areas. Habitat and distribution The marbled newt is typically found in habitats characterized by hilly and forestry terrain, away from open and exposed areas. Marbled newts live in temporary habitats, such as ponds, that are subject to change depending on the climate conditions of the region. When rainfall is high and the temperature is lower, typically in the fall and winter months, adult marbled newts stay in the ponds. However, these shallow ponds are subject to drought in warmer spring and summer months, which forces the marbled newts to remain on land. Due to this constant change in the habitat conditions, marbled newts have the ability to adapt to different climatic conditions and habitat changes. The characteristics of the marbled newt's habitat have also been found to affect the matu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burrow
An Eastern chipmunk at the entrance of its burrow A burrow is a hole or tunnel excavated into the ground by an animal to construct a space suitable for habitation or temporary refuge, or as a byproduct of locomotion. Burrows provide a form of shelter against predation and exposure to the elements, and can be found in nearly every biome and among various biological interactions. Many animal species are known to form burrows. These species range from small invertebrates, such as the ''Corophium arenarium'', to very large vertebrate species such as the polar bear. Burrows can be constructed into a wide variety of substrates and can range in complexity from a simple tube a few centimeters long to a complex network of interconnecting tunnels and chambers hundreds or thousands of meters in total length; an example of the latter level of complexity, a well-developed burrow, would be a rabbit warren. Vertebrate burrows A large variety of vertebrates construct or use burrows in many t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blesmol
The blesmols, also known as mole-rats, or African mole-rats, are burrowing rodents of the family Bathyergidae. They represent a distinct evolution of a subterranean life among rodents much like the pocket gophers of North America, the tuco-tucos in South America, or the Spalacidae from Eurasia. Distribution Modern blesmols are found strictly in sub-Saharan Africa. Fossil forms are also restricted almost exclusively to Africa, although a few specimens of the Pleistocene species ''Cryptomys asiaticus'' have been found in Israel. Nowak (1999) also reports that †''Gypsorhychus'' has been found in fossil deposits of Mongolia. Anatomy Blesmols are somewhat mole-like animals with cylindrical bodies and short limbs. They range from in length, and from in weight, depending on the species. Blesmols, like many other fossorial mammals, have greatly reduced eyes and ear pinnae, a relatively short tail, loose skin, and (aside from the hairless naked mole rat) velvety fur. Blesmols ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lobster
Lobsters are a family (biology), family (Nephropidae, Synonym (taxonomy), synonym Homaridae) of marine crustaceans. They have long bodies with muscular tails and live in crevices or burrows on the sea floor. Three of their five pairs of legs have claws, including the first pair, which are usually much larger than the others. Highly prized as seafood, lobsters are economically important and are often one of the most profitable commodities in coastal areas they populate. Commercially important species include two species of ''Homarus'' from the northern Atlantic Ocean and scampi (which look more like a shrimp, or a "mini lobster")—the Northern Hemisphere genus ''Nephrops'' and the Southern Hemisphere genus ''Metanephrops''. Distinction Although several other groups of crustaceans have the word "lobster" in their names, the unqualified term "lobster" generally refers to the clawed lobsters of the family Nephropidae. Clawed lobsters are not closely related to spiny lobsters o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird Migration
Bird migration is the regular seasonal movement, often north and south along a flyway, between breeding and wintering grounds. Many species of bird migrate. Migration carries high costs in predation and mortality, including from hunting by humans, and is driven primarily by the availability of food. It occurs mainly in the northern hemisphere, where birds are funneled onto specific routes by natural barriers such as the Mediterranean Sea or the Caribbean Sea. Migration of species such as storks, turtle doves, and swallows was recorded as many as 3,000 years ago by Ancient Greek authors, including Homer and Aristotle, and in the Book of Job. More recently, Johannes Leche began recording dates of arrivals of spring migrants in Finland in 1749, and modern scientific studies have used techniques including bird ringing and satellite tracking to trace migrants. Threats to migratory birds have grown with habitat destruction, especially of stopover and wintering sites, as wel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |