|
Holosticha Antarctica
''Holosticha antarctica'' is a species of littoral ciliates, first found near King George Island. References Further reading *Li, Liqiong, et al. "A redescription of the marine hypotrichous ciliate, Nothoholosticha fasciola (Kahl, 1932) nov. gen., nov. comb.(Ciliophora: Urostylida) with brief notes on its cellular reorganization and SS rRNA gene sequence." European journal of protistology 45.3 (2009): 237–248. *Gong, Jun, et al. "Morphology and infraciliature of Holosticha bradburyae nov. spec.(Ciliophora, Hypotrichida) from the Yellow Sea, China."Hydrobiologia 464.1-3 (2001): 63–69. External links * Species described in 2008 Hypotrichea {{ciliate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryota
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the Three-domain system, three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard (archaea), Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass (ecology), biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated phagotrophs. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAR Supergroup
The SAR supergroup, also just SAR or Harosa, is a clade that includes stramenopiles (heterokonts), alveolates, and Rhizaria. The name is an acronym derived from the first letters of each of these clades; it has been alternatively spelled "RAS". The term "Harosa" (at the subkingdom level) has also been used. The SAR supergroup is a node-based taxon. Note that as a formal taxon, "Sar" has only its first letter capitalized, while the earlier abbreviation, SAR, retains all uppercase letters. Both names refer to the same group of organisms, unless further taxonomic revisions deem otherwise. Members of the SAR supergroup were once included under the separate supergroups Chromalveolata (Chromista and Alveolata) and Rhizaria, until phylogenetic studies confirmed that stramenopiles and alveolates diverged with Rhizaria. This apparently excluded haptophytes and cryptomonads, leading Okamoto ''et al.'' (2009) to propose the clade Hacrobia to accommodate them. Phylogeny Based on a compi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
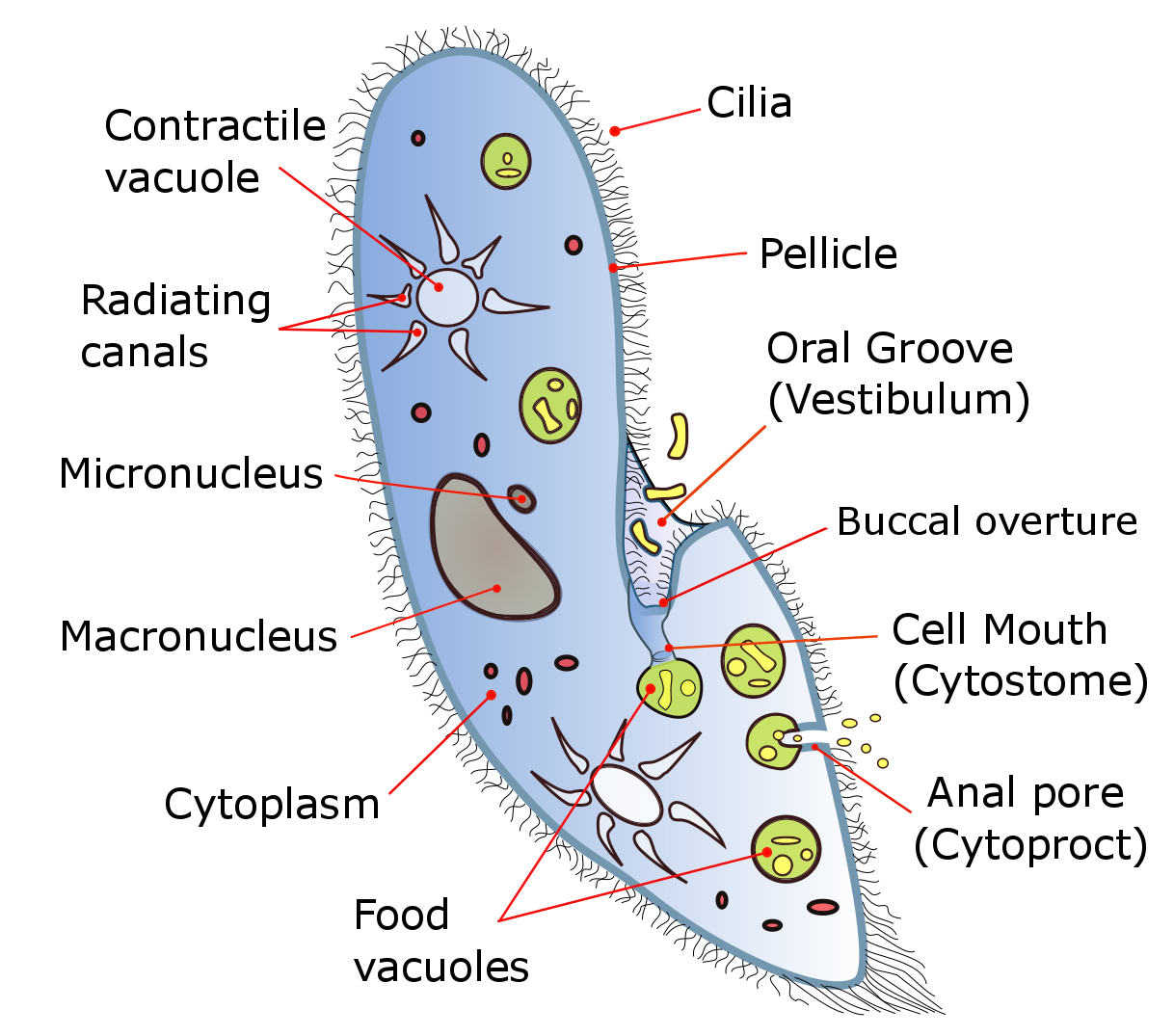
Ciliate
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to flagellum, eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different wikt:undulating, undulating pattern than flagella. Cilia occur in all members of the group (although the peculiar Suctoria only have them for part of their biological life cycle, life cycle) and are variously used in swimming, crawling, attachment, feeding, and sensation. Ciliates are an important group of protists, common almost anywhere there is water—in lakes, ponds, oceans, rivers, and soils. About 4,500 unique free-living species have been described, and the potential number of extant species is estimated at 27,000–40,000. Included in this number are many Ectosymbiosis, ectosymbiotic and endosymbiotic species, as well as some Obligate parasite, obligate and Facultative parasite, opportunistic parasites. Ciliate species r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypotrichia
The hypotrichs are a group of ciliated protozoa, common in fresh water, salt water, soil and moss. Hypotrichs possess compound ciliary organelles called " cirri," which are made up of thick tufts of cilia, sparsely distributed on the ventral surface of the cell. The multiple fused cilia which form a cirrus function together as a unit, enabling the organism to crawl along solid substrates such as submerged debris or sediments. Hypotrichs typically possess a large oral aperture, bordered on one side by a wreath or collar of membranelles (small membranous structures made up of fused cilia), forming an "adoral zone of membranelles," or AZM. Classification In older systems of classification, the term hypotrich comprised all ciliates possessing a relatively flattened body shape, strong cirri restricted to the ventral surface, and a large oral region (peristome) partially surrounded by an "adoral zone of membranelles". From a phylogenetic point of view, this historic grouping--wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urostylida
''Urostylida'' is an order of littoral ciliates. The taxonomy of the order is largely unresolved and still subject to scientific inquiry. Families According to the Catalogue of Life The Catalogue of Life is an online database that provides an index of known species of animals, plants, fungi, and microorganisms. It was created in 2001 as a partnership between the global Species 2000 and the American Integrated Taxonomic Info ..., nine families are accepted within ''Holosticha''. * Bakuellidae * Holostichidae * Kahliellidae * Pseudokeronopsidae * Pseudourostylidae * Psilotrichidae * Rigidothrichidae * Trachelostylidae * Urostylidae References Hypotrichea Eukaryote orders Taxa described in 1979 {{ciliate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holostichidae
Holostichidae is a family of littoral ciliates. Genera According to the Catalogue of Life The Catalogue of Life is an online database that provides an index of known species of animals, plants, fungi, and microorganisms. It was created in 2001 as a partnership between the global Species 2000 and the American Integrated Taxonomic Info ..., 10 genera are accepted within ''Holosticha''. * '' Afrothrix'' * '' Amphisia'' * '' Amphista'' * '' Anteholosticha'' * '' Birojima'' * '' Caudiholosticha'' * '' Holosticha'' * '' Holostichides'' * '' Periholosticha'' * '' Psammomitra'' References Hypotrichea Eukaryote families Taxa described in 1961 {{ciliate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holosticha
''Holosticha'' is a genus of littoral ciliates. Species According to the Catalogue of Life The Catalogue of Life is an online database that provides an index of known species of animals, plants, fungi, and microorganisms. It was created in 2001 as a partnership between the global Species 2000 and the American Integrated Taxonomic Info ..., 77 species are accepted within ''Holosticha''. * '' Holosticha alpestris'' Kahl, 1932 * '' Holosticha antarctica'' Wilbert & Song, 2008 * '' Holosticha apodiademata'' Wilbert & Song, 2008 * '' Holosticha aquarum'' * '' Holosticha arenicola'' Kahl, 1932 * '' Holosticha brachysticha'' Foissner, Agatha & Berger, 2002 * '' Holosticha bradburyae'' Gong, Song, Hu, Ma & Zhu, 2001 * '' Holosticha brevis'' Kahl, 1932 * '' Holosticha corlissi'' * '' Holosticha coronata'' (Vuxanovici, 1963) Buitkamp, 1977 * '' Holosticha coronata'' Gourret & Roeser, 1888 * '' Holosticha crassa'' Claparède & Lachmann, 1858 * '' Holosticha danubialis'' Kaltenbach, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Littoral
The littoral zone or nearshore is the part of a sea, lake, or river that is close to the shore. In coastal ecology, the littoral zone includes the intertidal zone extending from the high water mark (which is rarely inundated), to coastal areas that are permanently underwater, submerged — known as the ''foreshore'' — and the terms are often used interchangeably. However, the geographical meaning of ''littoral zone'' extends well beyond the intertidal zone to include all neritic waters within the bounds of continental shelves. Etymology The word ''littoral'' may be used both as a noun and as an adjective. It derives from the Latin language, Latin noun ''litus, litoris'', meaning "shore". (The doubled ''t'' is a late-medieval innovation, and the word is sometimes seen in the more classical-looking spelling ''litoral''.) Description The term has no single definition. What is regarded as the full extent of the littoral zone, and the way the littoral zone is divided into subregi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King George Island (South Shetland Islands)
King George Island (Argentinian Spanish: Isla 25 de Mayo, Chilean Spanish: Isla Rey Jorge, Russian: Ватерло́о Vaterloo) is the largest of the South Shetland Islands, lying off the coast of Antarctica in the Southern Ocean. The island was named after King George III. Geography King George island has three major bays, Maxwell Bay, Admiralty Bay, and King George Bay. Admiralty Bay contains three fjords, and is protected as an Antarctic Specially Managed Area under the Protocol on Environmental Protection to the Antarctic Treaty. History The island was first claimed for Britain on 16 October 1819, formally annexed by Britain as part of the Falkland Islands Dependencies in 1908, and now as part of the separate British Antarctic Territory. The Island was claimed by Chile in 1940, as part of the Chilean Antarctic Territory. It was also claimed by Argentina in 1943, now as part of Argentine Antarctica, called by the Argentines ''Isla Veinticinco de Mayo'' (25 May) in ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Described In 2008
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes in zoological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |