|
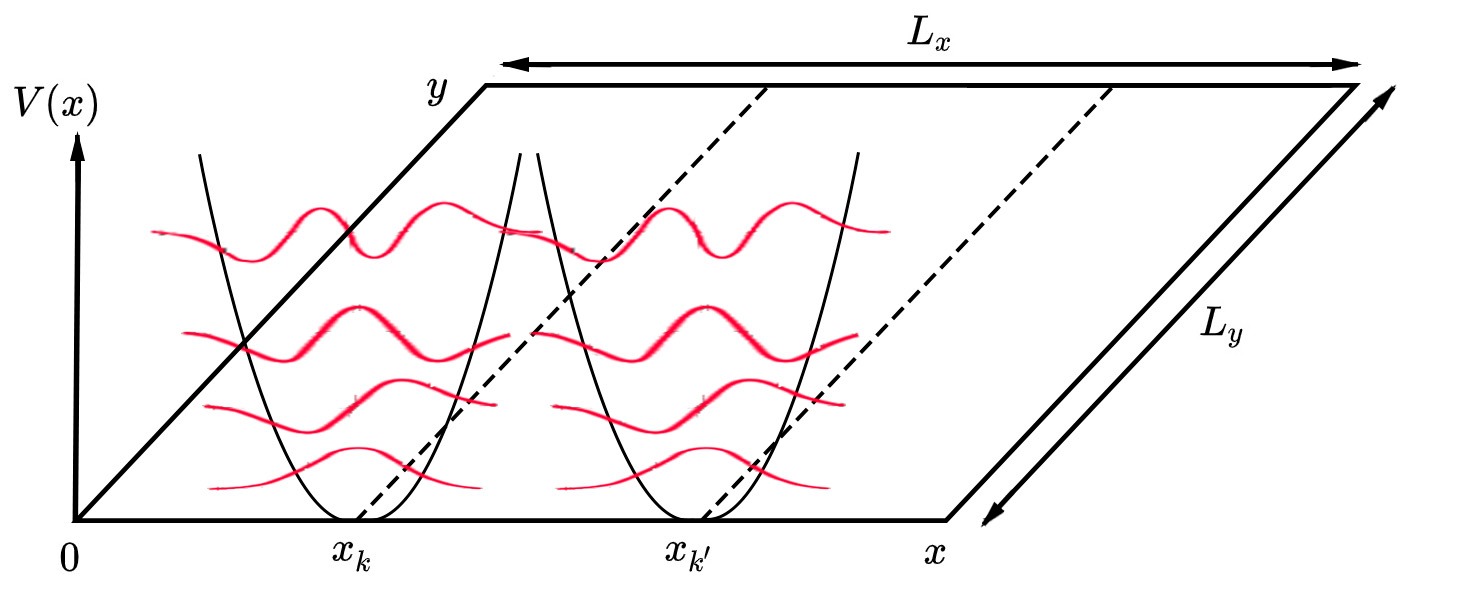
Hofstadter Butterfly
In condensed matter physics, Hofstadter's butterfly is a graph of the spectral properties of non-interacting two-dimensional electrons in a perpendicular magnetic field in a lattice. The fractal, self-similar nature of the spectrum was discovered in the 1976 Ph.D. work of Douglas Hofstadter and is one of the early examples of modern scientific data visualization. The name reflects the fact that, as Hofstadter wrote, "the large gaps n the graphform a very striking pattern somewhat resembling a butterfly." The Hofstadter butterfly plays an important role in the theory of the integer quantum Hall effect and the theory of topological quantum numbers. History The first mathematical description of electrons on a 2D lattice, acted on by a perpendicular homogeneous magnetic field, was studied by Rudolf Peierls and his student R. G. Harper in the 1950s. Hofstadter first described the structure in 1976 in an article on the energy levels of Bloch electrons in perpendicular magnetic fiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recursively
Recursion (adjective: ''recursive'') occurs when a thing is defined in terms of itself or of its type. Recursion is used in a variety of disciplines ranging from linguistics to logic. The most common application of recursion is in mathematics and computer science, where a function being defined is applied within its own definition. While this apparently defines an infinite number of instances (function values), it is often done in such a way that no infinite loop or infinite chain of references ("crock recursion") can occur. Formal definitions In mathematics and computer science, a class of objects or methods exhibits recursive behavior when it can be defined by two properties: * A simple ''base case'' (or cases) — a terminating scenario that does not use recursion to produce an answer * A ''recursive step'' — a set of rules that reduces all successive cases toward the base case. For example, the following is a recursive definition of a person's ''ancestor''. One's anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
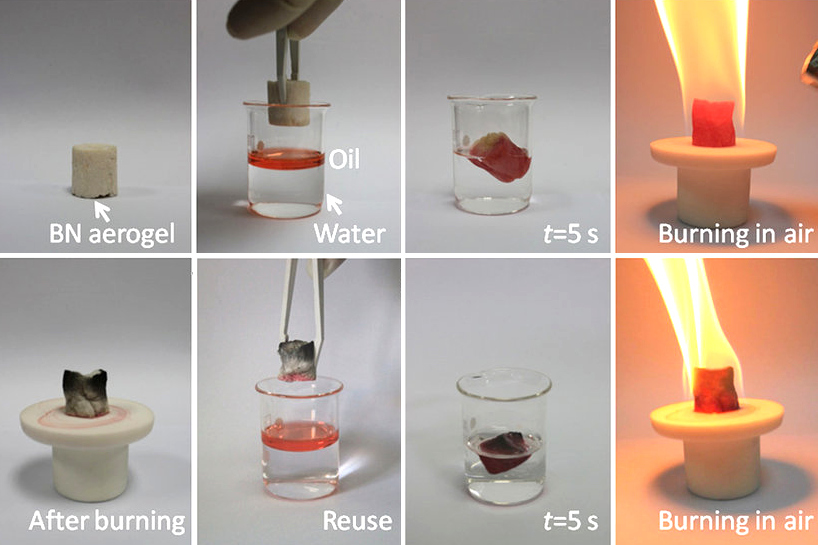
Boron Nitride
Boron nitride is a thermally and chemically resistant refractory compound of boron and nitrogen with the chemical formula BN. It exists in various crystalline forms that are isoelectronic to a similarly structured carbon lattice. The hexagonal form corresponding to graphite is the most stable and soft among BN polymorphs, and is therefore used as a lubricant and an additive to cosmetic products. The cubic ( zincblende aka sphalerite structure) variety analogous to diamond is called c-BN; it is softer than diamond, but its thermal and chemical stability is superior. The rare wurtzite BN modification is similar to lonsdaleite but slightly softer than the cubic form. Because of excellent thermal and chemical stability, boron nitride ceramics are used in high-temperature equipment and metal casting. Boron nitride has potential use in nanotechnology. Structure Boron nitride exists in multiple forms that differ in the arrangement of the boron and nitrogen atoms, giving rise to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphene
Graphene () is an allotrope of carbon consisting of a Single-layer materials, single layer of atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice nanostructure. "Carbon nanostructures for electromagnetic shielding applications", Mohammed Arif Poothanari, Sabu Thomas, et al., ''Industrial Applications of Nanomaterials'', 2019. "Carbon nanostructures include various low-dimensional allotropes of carbon including carbon black (CB), carbon fiber, carbon nanotubes (CNTs), fullerene, and graphene." The name is derived from "graphite" and the suffix -ene, reflecting the fact that the graphite allotrope of carbon contains numerous double bonds. Each atom in a graphene sheet is connected to its three nearest neighbors by a strong σ-bond, and contributes to a valence band one electron that extends over the whole sheet. This is the same type of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-dimensional Electron Gas
A two-dimensional electron gas (2DEG) is a scientific model in solid-state physics. It is an electron gas that is free to move in two dimensions, but tightly confined in the third. This tight confinement leads to quantized energy levels for motion in the third direction, which can then be ignored for most problems. Thus the electrons appear to be a 2D sheet embedded in a 3D world. The analogous construct of holes is called a two-dimensional hole gas (2DHG), and such systems have many useful and interesting properties. Realizations Most 2DEGs are found in transistor-like structures made from semiconductors. The most commonly encountered 2DEG is the layer of electrons found in MOSFETs (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors). When the transistor is in inversion mode, the electrons underneath the gate oxide are confined to the semiconductor-oxide interface, and thus occupy well defined energy levels. For thin-enough potential wells and temperatures not too high, on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klaus Von Klitzing
Klaus von Klitzing (, born 28 June 1943, Schroda) is a German physicist, known for discovery of the integer quantum Hall effect, for which he was awarded the 1985 Nobel Prize in Physics. Education In 1962, Klitzing passed the Abitur at the Artland-Gymnasium in Quakenbrück, Germany, before studying physics at the Braunschweig University of Technology, where he received his diploma in 1969. He continued his studies at the University of Würzburg at the chair of Gottfried Landwehr, completing his PhD thesis entitled ''Galvanomagnetic Properties of Tellurium in Strong Magnetic Fields'' in 1972, and gaining habilitation in 1978. Research and career During his career Klitzing has worked at the Clarendon Laboratory at the University of Oxford and the Grenoble High Magnetic Field Laboratory in France (now LNCMI), where he continued to work until becoming a professor at the Technical University of Munich in 1980. He has been a director of the Max Planck Institute for Solid State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Review Letters
''Physical Review Letters'' (''PRL''), established in 1958, is a peer-reviewed, scientific journal that is published 52 times per year by the American Physical Society. As also confirmed by various measurement standards, which include the '' Journal Citation Reports'' impact factor and the journal ''h''-index proposed by Google Scholar, many physicists and other scientists consider ''Physical Review Letters'' to be one of the most prestigious journals in the field of physics. ''According to Google Scholar, PRL is the journal with the 9th journal h-index among all scientific journals'' ''PRL'' is published as a print journal, and is in electronic format, online and CD-ROM. Its focus is rapid dissemination of significant, or notable, results of fundamental research on all topics related to all fields of physics. This is accomplished by rapid publication of short reports, called "Letters". Papers are published and available electronically one article at a time. When published ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Hall Effect
The quantum Hall effect (or integer quantum Hall effect) is a quantized version of the Hall effect which is observed in two-dimensional electron systems subjected to low temperatures and strong magnetic fields, in which the Hall resistance exhibits steps that take on the quantized values : R_ = \frac = \frac , where is the Hall voltage, is the channel current, is the elementary charge and is Planck's constant. The divisor can take on either integer () or fractional () values. Here, is roughly but not exactly equal to the filling factor of Landau levels. The quantum Hall effect is referred to as the integer or fractional quantum Hall effect depending on whether is an integer or fraction, respectively. The striking feature of the integer quantum Hall effect is the persistence of the quantization (i.e. the Hall plateau) as the electron density is varied. Since the electron density remains constant when the Fermi level is in a clean spectral gap, this situation correspo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chern Class
In mathematics, in particular in algebraic topology, differential geometry and algebraic geometry, the Chern classes are characteristic classes associated with complex vector bundles. They have since found applications in physics, Calabi–Yau manifolds, string theory, Chern–Simons theory, knot theory, Gromov–Witten invariants, topological quantum field theory, the Chern theorem etc. Chern classes were introduced by . Geometric approach Basic idea and motivation Chern classes are characteristic classes. They are topological invariants associated with vector bundles on a smooth manifold. The question of whether two ostensibly different vector bundles are the same can be quite hard to answer. The Chern classes provide a simple test: if the Chern classes of a pair of vector bundles do not agree, then the vector bundles are different. The converse, however, is not true. In topology, differential geometry, and algebraic geometry, it is often important to count ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David J
David John Haskins (born 24 April 1957, Northampton, Northamptonshire, England), better known as David J, is a British alternative rock musician, producer, and writer. He is the bassist for the gothic rock band Bauhaus and for Love and Rockets. He has composed the scores for a number of plays and films, and also wrote and directed his own plays, ''Silver for Gold (The Odyssey of Edie Sedgwick)'', in 2008, which was restaged at REDCAT in Los Angeles in 2011, and ''The Chanteuse and The Devil's Muse'' in 2011. His artwork has been shown in galleries internationally, and he has been a resident DJ at venues such as the Knitting Factory. David J has released a number of singles and solo albums, and in 1990 he released one of the first No. 1 hits on the then nascent Modern Rock Tracks charts, with "I'll Be Your Chauffeur". His most recent single, "The Day That David Bowie Died" entered the UK vinyl singles chart at number 4 in 2016. The track appears on his double album, ''V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gödel, Escher, Bach
''Gödel, Escher, Bach: an Eternal Golden Braid'', also known as ''GEB'', is a 1979 book by Douglas Hofstadter. By exploring common themes in the lives and works of logician Kurt Gödel, artist M. C. Escher, and composer Johann Sebastian Bach, the book expounds concepts fundamental to mathematics, symmetry, and intelligence. Through short stories, illustrations, and analysis, the book discusses how systems can acquire meaningful context despite being made of "meaningless" elements. It also discusses self-reference and formal rules, isomorphism, what it means to communicate, how knowledge can be represented and stored, the methods and limitations of symbolic representation, and even the fundamental notion of "meaning" itself. In response to confusion over the book's theme, Hofstadter emphasized that ''Gödel, Escher, Bach'' is not about the relationships of mathematics, art, and music—but rather about how cognition emerges from hidden neurological mechanisms. One point in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |