|
Histology Of The Vocal Folds
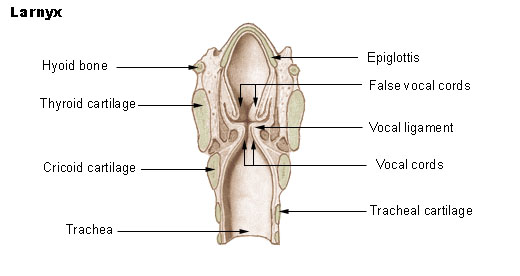
Histology is the study of the minute structure, composition, and function of tissues. Mature human vocal cords are composed of layered structures which are quite different at the histological level. Structure The glottis is defined as the true vocal folds and the space between them. It is composed of an intermembranous portion or anterior glottis, and an intercartilaginous portion or posterior glottis. The border between the anterior and posterior glottises is defined by an imaginary line drawn across the vocal fold at the tip of the vocal process of the arytenoid cartilage. The anterior glottis is the primary structure of vocal fold vibration for phonation and the posterior glottis is the widest opening between the vocal folds for respiration. Thus, voice disorders often involve lesions of the anterior glottis. There are gradual changes in stiffness between the pliable vocal fold and hard, hyaline cartilage of the arytenoid. The vocal processes of the arytenoid cartilages form a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histology
Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope. Although one may divide microscopic anatomy into ''organology'', the study of organs, ''histology'', the study of tissues, and ''cytology'', the study of cells, modern usage places all of these topics under the field of histology. In medicine, histopathology is the branch of histology that includes the microscopic identification and study of diseased tissue. In the field of paleontology, the term paleohistology refers to the histology of fossil organisms. Biological tissues Animal tissue classification There are four basic types of animal tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. All animal tissues are considered to be subtypes of these four principal tissue types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
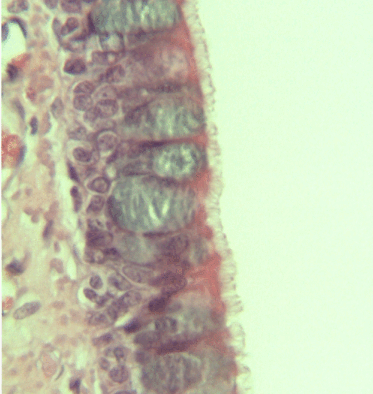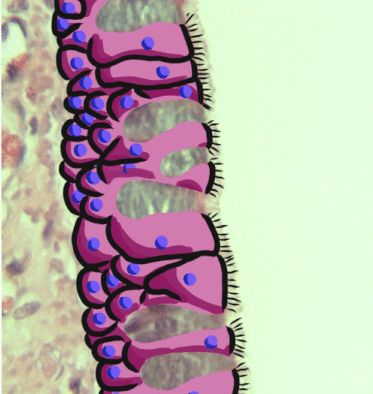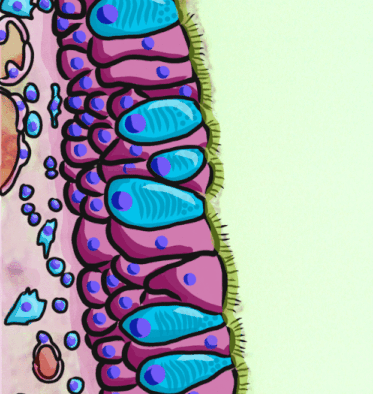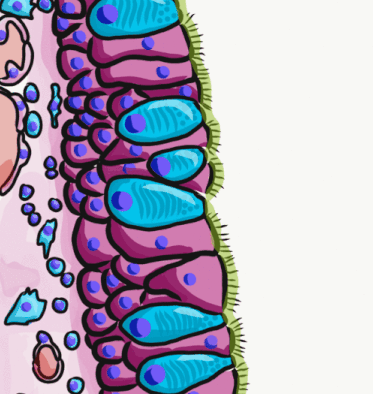
Pseudostratified Epithelium
A pseudostratified epithelium is a type of epithelium that, though comprising only a single layer of cells, has its cell nuclei positioned in a manner suggestive of stratified epithelia. As it rarely occurs as squamous or cuboidal epithelia, it is usually considered synonymous with the term pseudostratified columnar epithelium. The term ''pseudostratified'' is derived from the appearance of this epithelium in the section which conveys the erroneous (''pseudo'' means almost or approaching) impression that there is more than one layer of cells, when in fact this is a true simple epithelium since all the cells rest on the basement membrane. The nuclei of these cells, however, are disposed at different levels, thus creating the illusion of cellular stratification. All cells are not of equal size and not all cells extend to the luminal/apical surface; such cells are capable of cell division providing replacements for cells lost or damaged. Pseudostratified epithelia function in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellular matrix. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either squamous, columnar, or cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to the placement of the nuclei. This sort of tissue is called pseudostratified. All glands are made up of epithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamous Epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellular matrix. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either squamous, columnar, or cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to the placement of the nuclei. This sort of tissue is called pseudostratified. All glands are made up of epithelia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vocal Process
In the human larynx, the vocal process is the anterior angle of the base of the arytenoid cartilage, as it projects horizontally forward and gives attachment to the vocal ligament. The arytenoids are paired cartilages with a medial and a lateral process each. The medial process is called the vocal process because it is the attachment for the vocal ligament. The lateral process is the attachment of one of the major intrinsic muscles of the vocal folds and consequently named the muscular process. As the concave bases of the arytenoid cartilages move on the two convex articular surfaces on the cricoid cartilage (at the cricoarytenoid articulations), the vocal processes are brought closer to each other, which permits the vocal folds to make contact (adduct) and abduct. Just above the vocal process is a shallow depression, the oblong fovea of the arytenoid cartilage. Together they constitute the insertion for the vocalis muscle. Vocal process granulomas are rare and benign lesion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissue Maturation
Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop. Developmental biology also encompasses the biology of regeneration, asexual reproduction, metamorphosis, and the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. Perspectives The main processes involved in the embryonic development of animals are: tissue patterning (via regional specification and patterned cell differentiation); tissue growth; and tissue morphogenesis. * Regional specification refers to the processes that create the spatial patterns in a ball or sheet of initially similar cells. This generally involves the action of cytoplasmic determinants, located within parts of the fertilized egg, and of inductive signals emitted from signaling centers in the embryo. The early stages of regional specification do not generate functional differentiated cells, but cell populations committed to developing to a specific region or part of the organism. These are define ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonation
The term phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, ''phonation'' is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the definition used among those who study laryngeal anatomy and physiology and speech production in general. Phoneticians in other subfields, such as linguistic phonetics, call this process '' voicing'', and use the term ''phonation'' to refer to any oscillatory state of any part of the larynx that modifies the airstream, of which voicing is just one example. Voiceless and supra-glottal phonations are included under this definition. Voicing The phonatory process, or voicing, occurs when air is expelled from the lungs through the glottis, creating a pressure drop across the larynx. When this drop becomes sufficiently large, the vocal folds start to oscillate. The minimum pressure drop required to achieve phonation is called the phonation threshold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extracellular Matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM. The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the Interstitial fluid, interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reinke's Space
Reinke's space is a potential space between the vocal ligament and the overlying mucosa. It is not an empty space, but contains cells, special fibers and extracellular matrix. It plays an important role in the vibration of the vocal cords. Edema of this space is called Reinke's edema Reinke's edema is the swelling of the vocal cords due to fluid (edema) collected within the Reinke's space. First identified by the German anatomist Friedrich B. Reinke in 1895, the Reinke's space is a gelatinous layer of the vocal cord located un .... References Notes {{Reflist Larynx Anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibroblast
A fibroblast is a type of cell (biology), biological cell that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework (Stroma (tissue), stroma) for animal Tissue (biology), tissues, and plays a critical role in wound healing. Fibroblasts are the most common cells of connective tissue in animals. Structure Fibroblasts have a branched cytoplasm surrounding an elliptical, speckled cell nucleus, nucleus having two or more nucleoli. Active fibroblasts can be recognized by their abundant Endoplasmic reticulum#Rough endoplasmic reticulum, rough endoplasmic reticulum. Inactive fibroblasts (called fibrocytes) are smaller, spindle-shaped, and have a reduced amount of rough endoplasmic reticulum. Although disjointed and scattered when they have to cover a large space, fibroblasts, when crowded, often locally align in parallel clusters. Unlike the epithelial cells lining the body structures, fibroblasts do not form flat monolayers and are not restricted by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratum Basale
The ''stratum basale'' (basal layer, sometimes referred to as ''stratum germinativum'') is the deepest layer of the five layers of the epidermis, the external covering of skin in mammals. The ''stratum basale'' is a single layer of columnar or cuboidal basal cells. The cells are attached to each other and to the overlying stratum spinosum cells by desmosomes and hemidesmosomes. The nucleus is large, ovoid and occupies most of the cell. Some basal cells can act like stem cells with the ability to divide and produce new cells, and these are sometimes called basal keratinocyte stem cells. Others serve to anchor the epidermis glabrous skin (hairless), and hyper-proliferative epidermis (from a skin disease).McGrath, J.A.; Eady, R.A.; Pope, F.M. (2004). ''Rook's Textbook of Dermatology'' (Seventh Edition). Blackwell Publishing. Pages 3.7. . They divide to form the keratinocytes of the stratum spinosum, which migrate superficially. Other types of cells found within the ''stratum bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
