|
Himalayan States
The term Himalayan states is used to group countries that straddle the Himalayas. It primarily denotes Bhutan, China, India, Nepal, and Pakistan; some definitions also include Afghanistan and Myanmar. Two countries—Bhutan and Nepal—are located almost entirely within the mountain range, which also covers southern Tibet, the Indian Himalayan Region, and northern Pakistan. The inhabitants of this region are mostly speakers of the Indo-Aryan languages and the Tibeto-Burman languages. Some of the world's major transboundary rivers originate in the territory of the Himalayan states, including the Brahmaputra, the Ganges, the Indus, and the Irrawaddy. See also * Alpine states * Andean states * Baltic states The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, ... References {{r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himalayas With Territorial Boundaries
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over list of highest mountains on Earth, 100 peaks exceeding in elevation lie in the Himalayas. By contrast, the highest peak outside Asia (Aconcagua, in the Andes) is tall. The Himalayas abut or cross Himalayan states, five countries: Bhutan, India, Nepal, China, and Pakistan. The sovereignty of the range in the Kashmir region is disputed among India, Pakistan, and China. The Himalayan range is bordered on the northwest by the Karakoram and Hindu Kush ranges, on the north by the Tibetan Plateau, and on the south by the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Some of the world's major rivers, the Indus River, Indus, the Ganges river, Ganges, and the Yarlung Tsangpo River, Tsangpo–Brahmaputra River, Brahmaputra, rise in the vicinity of the Himalayas, and their com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmaputra River
The Brahmaputra is a trans-boundary river which flows through Tibet, northeast India, and Bangladesh. It is also known as the Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibetan, the Siang/Dihang River in Arunachali, Luit in Assamese, and Jamuna River in Bangla. It is the 9th largest river in the world by discharge, and the 15th longest. With its origin in the Manasarovar Lake region, near Mount Kailash, on the northern side of the Himalayas in Burang County of Tibet where it is known as the Yarlung Tsangpo River, It flows along southern Tibet to break through the Himalayas in great gorges (including the Yarlung Tsangpo Grand Canyon) and into Arunachal Pradesh. It flows southwest through the Assam Valley as the Brahmaputra and south through Bangladesh as the Jamuna (not to be confused with the Yamuna of India). In the vast Ganges Delta, it merges with the Ganges, popularly known as the Padma in Bangladesh, and becomes the Meghna and ultimately empties into the Bay of Bengal. About long, the Bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Asia
Geography of Asia reviews geographical concepts of classifying Asia, the central and eastern part of Eurasia, comprising approximately fifty countries. Geographical characteristics Boundary The land mass of Asia is not the sum of the land masses of each of its regions, which have been defined independently of the whole. For example, the borders of Central Asia and the Middle East depend on who is defining them and for what purpose. These varying definitions are not generally reflected in the map of Asia as a whole; for example, Egypt is typically included in the Middle East, but not in Asia, even though the Middle East is a division of Asia. The demarcation between Asia and Africa is the isthmus of Suez and the Red Sea. The border with Europe starts with the coast of the eastern Mediterranean, even though Turkey in the Near East extends partly into the Aegean Islands and includes Istanbul on the European side of the Bosphorus. On the north the boundary between the con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Bhutan
The Kingdom of Bhutan is a sovereign nation, located towards the eastern extreme of the Himalayas mountain range. It is fairly evenly sandwiched between the sovereign territory of two nations: first, the People's Republic of China on the north and northwest. There are approximately 477 kilometres of border with that nation's Tibet Autonomous Region. The second nation is the Republic of India on the south, southwest, and east; there are approximately 659 kilometres with the states of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, West Bengal, and Sikkim, in clockwise order from the kingdom. Bhutan's total borders amount to 1,139 kilometres. The Republic of Nepal to the west, the India to the south, and the Union of Myanmar to the southeast are other close neighbours; the former two are separated by only very small stretches of Indian territory. Bhutan is a very compact nation, but with just a small bit more length than width. The nation's territory totals an approximate 38,394 square kilometres. Bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
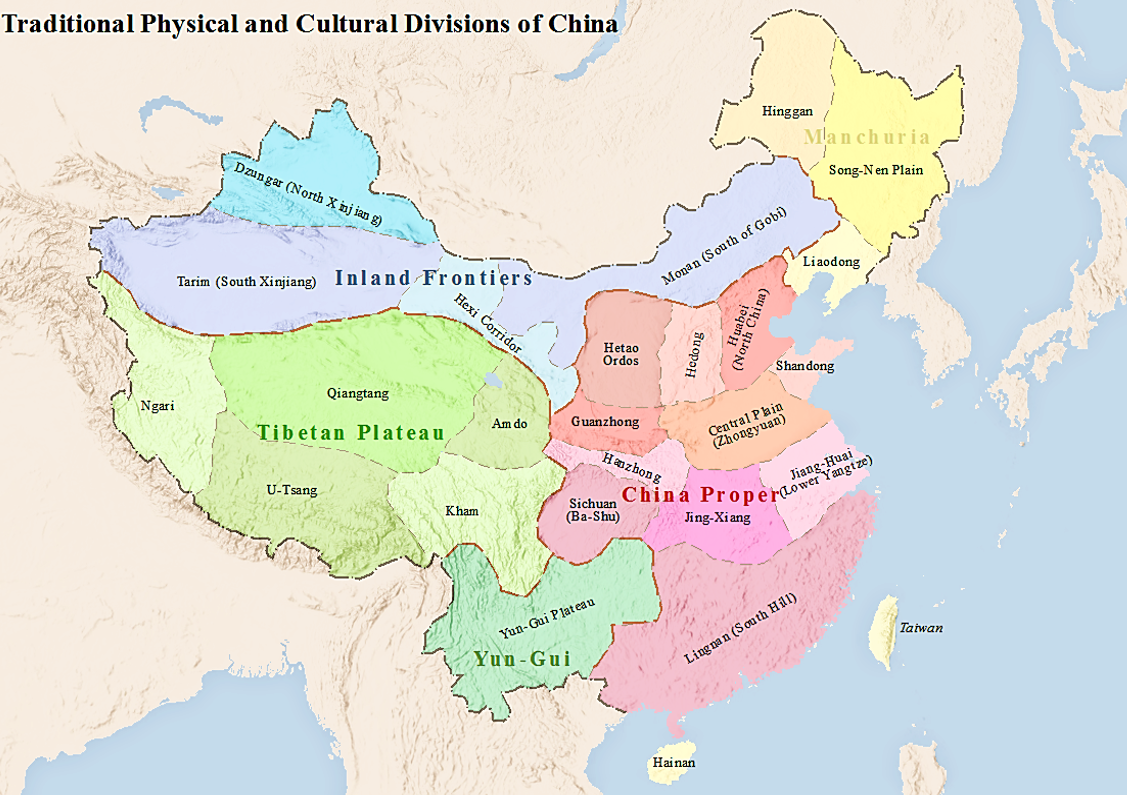
Geography Of China
China has great physical diversity. The eastern plains and southern coasts of the country consist of fertile lowlands and foothills. They are the location of most of China's agricultural output and human population. The southern areas of the country (South of the Yangtze River) consist of hilly and mountainous terrain. The west and north of the country are dominated by sunken basins (such as the Gobi and the Taklamakan), rolling plateaus, and towering massifs. It contains part of the highest tableland on earth, the Tibetan Plateau, and has much lower agricultural potential and population. Traditionally, the Chinese population centered on the Chinese central plain and oriented itself toward its own enormous inland market, developing as an imperial power whose center lay in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River on the northern plains. More recently, the coastline has been used extensively for export-oriented trade, causing the coastal provinces to become the lead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
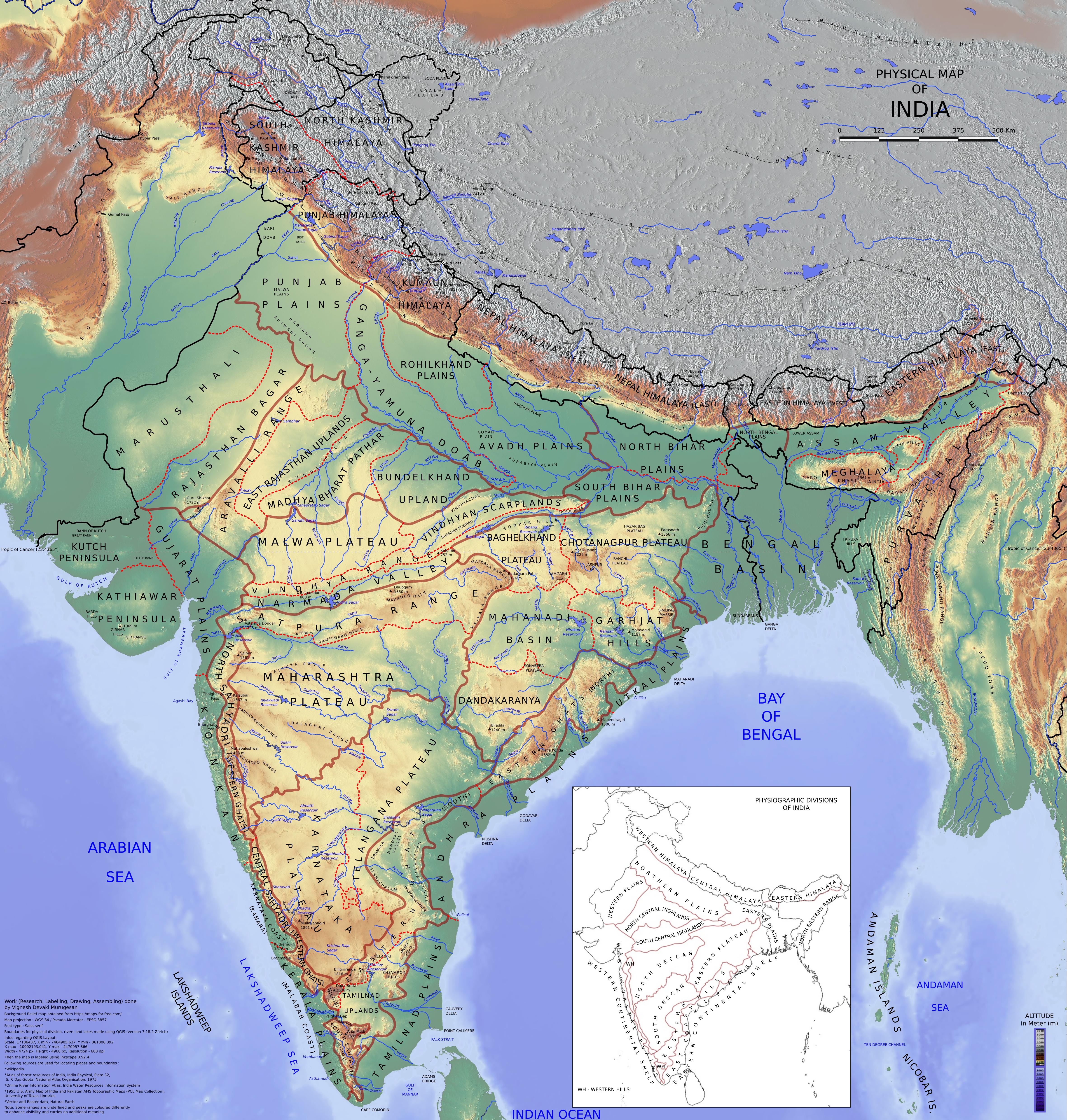
Geography Of India
India is situated north of the equator between 8°4' north (the mainland) to 37°6' north latitude and 68°7' east to 97°25' east longitude. India Yearbook, p. 1 It is the seventh-largest country in the world, with a total area of . Total area excludes disputed territories not under Indian control. India measures from north to south and from east to west. It has a land frontier of and a coastline of . On the south, India projects into and is bounded by the Indian Ocean—in particular, by the Arabian Sea on the west, the Lakshadweep Sea to the southwest, the Bay of Bengal on the east, and the Indian Ocean proper to the south. The Palk Strait and Gulf of Mannar separate India from Sri Lanka to its immediate southeast, and the Maldives are some to the south of India's Lakshadweep Islands across the Eight Degree Channel. India's Andaman and Nicobar Islands, some southeast of the mainland, share maritime borders with Myanmar, Thailand and Indonesia. The southernmost tip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
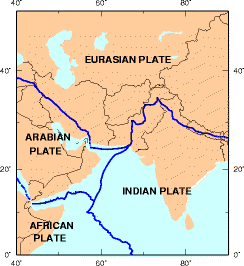
Geography Of Pakistan
The Geography of Pakistan ( ur, ) is a profound blend of landscapes varying from plains to deserts, forests, and plateaus ranging from the coastal areas of the Arabian Sea in the south to the mountains of the Karakoram, Hindukush, Himalayas ranges in the north. Pakistan geologically overlaps both with the Indian and the Eurasian tectonic plates where its Sindh and Punjab provinces lie on the north-western corner of the Indian plate while Balochistan and most of the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa lie within the Eurasian plate which mainly comprises the Iranian Plateau. Pakistan is bordered by India to the east, Afghanistan to the northwest and Iran to the west while China borders the country in the northeast. The nation is geopolitically situated within some of the most controversial regional boundaries which share disputes and have many-a-times escalated military tensions between the nations, e.g., that of Kashmir with India and the Durand Line with Afghanistan. Its western borders in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Nepal
Nepal measures about along its Himalayan axis by across. It has an area of . Nepal is landlocked by China's Tibet Autonomous Region to the north and India on other three sides. West Bengal's narrow ''Siliguri Corridor'' separate Nepal and Bangladesh. To the east are Bhutan and India. Landform regions For a country of its size, Nepal has tremendous geographic diversity. It rises from as low as elevation in the tropical Terai—the northern rim of the Gangetic Plain, through beyond the perpetual snow line to 90 peaks over including Earth's highest ( Mount Everest or ''Sagarmatha''). In addition to the continuum from tropical warmth to cold comparable to polar regions, average annual precipitation varies from as little as in its narrow proportion of the rainshadow north of the Himalayas to as much as on windward slopes, the maximum mainly resting on the magnitude of the South Asian monsoon. Forming south-to-north transects, Nepal can be divided into three belts: Terai, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
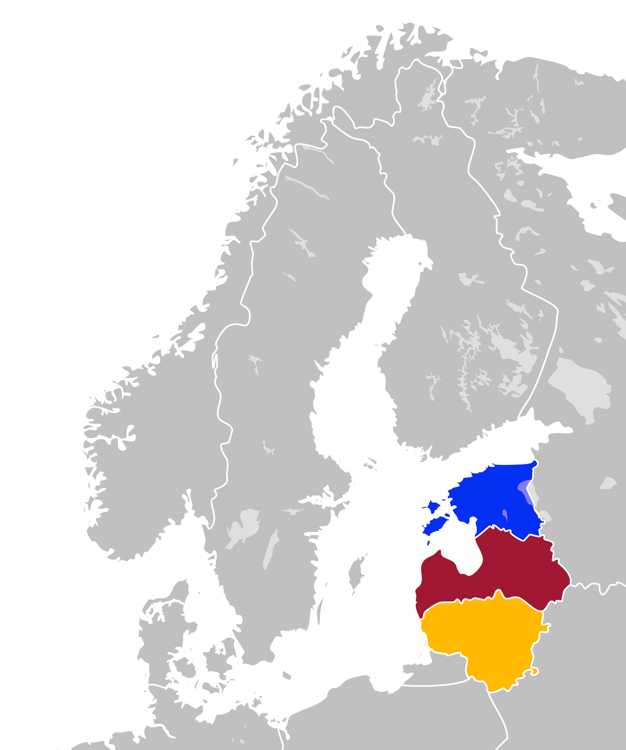
Baltic States
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea are sometimes referred to as the "Baltic nations", less often and in historical circumstances also as the "Baltic republics", the "Baltic lands", or simply the Baltics. All three Baltic countries are classified as high-income economies by the World Bank and maintain a very high Human Development Index. The three governments engage in intergovernmental and parliamentary cooperation. There is also frequent cooperation in foreign and security policy, defence, energy, and transportation. The term "Baltic states" ("countries", "nations", or similar) cannot be used unambiguously in the context of cultural areas, national identity, or language. While the majority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andean States
The Andean states ( es, Estados Andinos) are a group of countries in western South America connected by the Andes mountain range. The "Andean States" is sometimes used to refer to all seven countries that the Andes runs through, regions with a shared culture primarily spread during the times of the Inca Empire (such as the Quechua language and Andean cuisine), or it can be used in a geopolitical sense to designate countries in the region that are members of the Andean Community trade group and have a local (as opposed to the Southern Cone) cultural orientation. The Andes extend through the western part of South America in the following seven countries (arranged from north to south): * (a part of Caribbean South America, not considered an Andean state in geopolitics) * (also a part of Caribbean South America) * * * * (a part of the Southern Cone, generally not considered an Andean state in geopolitics) * (a part of the Southern Cone, often not considered an Andean state i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpine States
The term Alpine states or Alpine countries refers to the territory of eight countries associated with the Alpine region, as defined by the Alpine Convention of 1991: Austria, France, Germany, Italy, Liechtenstein, Monaco, Slovenia, and Switzerland. Territory The territory includes 83 NUTS 3-level local administrative divisions and about 6,200 municipalities. In a narrow sense, the term "Alpine states" could be applied to Austria (28.7% of the total area), Italy (27.2%), and France (21.4%), which represent more than 77% of the Alpine territory and more than three quarters of the Alpine population. However, for larger countries like Italy and France, the share of their territory within the Alpine region only amounts to 17% and 7% respectively. From a strictly national point of view, and with the exception of microstates Liechtenstein and Monaco, the Alps are dominant in only two countries: Austria (65.5% of its territory) and Switzerland (65%). See also * Andean states * Associ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irrawaddy River
The Irrawaddy River ( Ayeyarwady River; , , from Indic ''revatī'', meaning "abounding in riches") is a river that flows from north to south through Myanmar (Burma). It is the country's largest river and most important commercial waterway. Originating from the confluence of the N'mai and Mali rivers, it flows relatively straight North-South before emptying through the Irrawaddy Delta in the Ayeyarwady Region into the Andaman Sea. Its drainage basin of about covers a large part of Burma. After Rudyard Kipling's poem, it is sometimes referred to as ' The Road to Mandalay'. As early as the sixth century, the river was used for trade and transport. Having developed an extensive network of irrigation canals, the river became important to the British Empire after it had colonized Burma. The river is still as vital today, as a considerable amount of (export) goods and traffic moves by river. Rice is produced in the Irrawaddy Delta, irrigated by water from the river. In 2007, Myanmar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)