|
High Energy Density Physics
High-energy-density physics (HEDP) is a new subfield of physics intersecting condensed matter physics, nuclear physics, astrophysics and plasma physics. It has been defined as the physics of matter and radiation at energy densities in excess of about 100 GJ/m^3. High energy density (HED) science includes the study of condensed matter at densities common to the deep interiors of giant planets, and hot plasmas typical of stellar interiors. This multidisciplinary field provides a foundation for understanding a wide variety of astrophysical observations and understanding and ultimately controlling the fusion regime. Specifically, thermonuclear ignition by inertial confinement in the laboratory – as well as the transition from planets to brown dwarfs and stars in nature – takes place via the HED regime. A wide variety of new and emerging experimental capabilities (National Ignition Facility (NIF), Jupiter Laser Facility (JLF), etc.) together with the push towards Exascale Computing he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensed Matter Physics
Condensed matter physics is the field of physics that deals with the macroscopic and microscopic physical properties of matter, especially the solid and liquid phases which arise from electromagnetic forces between atoms. More generally, the subject deals with "condensed" phases of matter: systems of many constituents with strong interactions between them. More exotic condensed phases include the superconducting phase exhibited by certain materials at low temperature, the ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic phases of spins on crystal lattices of atoms, and the Bose–Einstein condensate found in ultracold atomic systems. Condensed matter physicists seek to understand the behavior of these phases by experiments to measure various material properties, and by applying the physical laws of quantum mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics, and other theories to develop mathematical models. The diversity of systems and phenomena available for study makes condensed matter phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electride
An electride is an ionic compound in which an electron is the anion. Solutions of alkali metals in ammonia are electride salts. In the case of sodium, these blue solutions consist of a(NH3)6sup>+ and solvated electrons: :Na + 6 NH3 → a(NH3)6sup>+ + e− The cation a(NH3)6sup>+ is an octahedral coordination complex. Solid salts Addition of a complexant like crown ether or -cryptand.html" ;"title="''2.2.2/nowiki>-cryptand">''2.2.2/nowiki>-cryptand to a solution of a(NH3)6sup>+e− affords a (crown ether)sup>+e− or a(2,2,2-crypt)sup>+e−. Evaporation of these solutions yields a blue-black paramagnetic solid with the formula a(2,2,2-crypt)sup>+e−. Most solid electride salts decompose above 240 K, although a24Al28O64sup>4+(e−)4 is stable at room temperature. In these salts, the electron is delocalized between the cations. Electrides are paramagnetic Paramagnetism is a form of magnetism whereby some materials are weakly attracted by an externally applied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Physics
Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies atomic nuclei and their constituents and interactions, in addition to the study of other forms of nuclear matter. Nuclear physics should not be confused with atomic physics, which studies the atom as a whole, including its electrons. Discoveries in nuclear physics have led to applications in many fields. This includes nuclear power, nuclear weapons, nuclear medicine and magnetic resonance imaging, industrial and agricultural isotopes, ion implantation in materials engineering, and radiocarbon dating in geology and archaeology. Such applications are studied in the field of nuclear engineering. Particle physics evolved out of nuclear physics and the two fields are typically taught in close association. Nuclear astrophysics, the application of nuclear physics to astrophysics, is crucial in explaining the inner workings of stars and the origin of the chemical elements. History The history of nuclear physics as a discipl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Energy Physics
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) and bosons (force-carrying particles). There are three generations of fermions, but ordinary matter is made only from the first fermion generation. The first generation consists of up and down quarks which form protons and neutrons, and electrons and electron neutrinos. The three fundamental interactions known to be mediated by bosons are electromagnetism, the weak interaction, and the strong interaction. Quarks cannot exist on their own but form hadrons. Hadrons that contain an odd number of quarks are called baryons and those that contain an even number are called mesons. Two baryons, the proton and the neutron, make up most of the mass of ordinary matter. Mesons are unstable and the longest-lived last for only a few hundredths of a mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superionic Water
Superionic water, also called superionic ice or ice XVIII is a phase of water that exists at extremely high temperatures and pressures. In superionic water, water molecules break apart and the oxygen ions crystallize into an evenly spaced lattice while the hydrogen ions float around freely within the oxygen lattice.Weird water lurking inside giant planets New Scientist,01 September 2010, Magazine issue 2776. The freely mobile hydrogen ions make superionic water almost as as typical metals, making it a [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallic Hydrogen
Metallic hydrogen is a phase of hydrogen in which it behaves like an electrical conductor. This phase was predicted in 1935 on theoretical grounds by Eugene Wigner and Hillard Bell Huntington. At high pressure and temperatures, metallic hydrogen can exist as a partial liquid rather than a solid, and researchers think it might be present in large quantities in the hot and gravitationally compressed interiors of Jupiter and Saturn, as well as in some exoplanets. Theoretical predictions Hydrogen under pressure Though often placed at the top of the alkali metal column in the periodic table, hydrogen does not, under ordinary conditions, exhibit the properties of an alkali metal. Instead, it forms diatomic molecules, analogous to halogens and some nonmetals in the second period of the periodic table, such as nitrogen and oxygen. Diatomic hydrogen is a gas that, at atmospheric pressure, liquefies and solidifies only at very low temperature (20 degrees and 14 degrees above absolute ze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coulomb Interaction
Coulomb's inverse-square law, or simply Coulomb's law, is an experimental law of physics that quantifies the amount of force between two stationary, electrically charged particles. The electric force between charged bodies at rest is conventionally called ''electrostatic force'' or Coulomb force. Although the law was known earlier, it was first published in 1785 by French physicist Charles-Augustin de Coulomb, hence the name. Coulomb's law was essential to the development of the theory of electromagnetism, maybe even its starting point, as it made it possible to discuss the quantity of electric charge in a meaningful way. The law states that the magnitude of the electrostatic force of attraction or repulsion between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of the magnitudes of charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Coulomb studied the repulsive force between bodies having electrical charges of the same sign: Coulomb also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
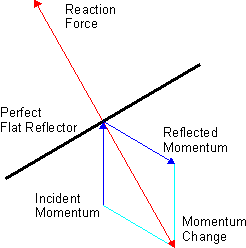
Radiation Pressure
Radiation pressure is the mechanical pressure exerted upon any surface due to the exchange of momentum between the object and the electromagnetic field. This includes the momentum of light or electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength that is absorbed, reflected, or otherwise emitted (e.g. black-body radiation) by matter on any scale (from macroscopic objects to dust particles to gas molecules). The associated force is called the radiation pressure force, or sometimes just the force of light. The forces generated by radiation pressure are generally too small to be noticed under everyday circumstances; however, they are important in some physical processes and technologies. This particularly includes objects in outer space, where it is usually the main force acting on objects besides gravity, and where the net effect of a tiny force may have a large cumulative effect over long periods of time. For example, had the effects of the Sun's radiation pressure on the spacecraft of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrinos
A neutrino ( ; denoted by the Greek letter ) is a fermion (an elementary particle with spin of ) that interacts only via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass is so small ('' -ino'') that it was long thought to be zero. The rest mass of the neutrino is much smaller than that of the other known elementary particles excluding massless particles. The weak force has a very short range, the gravitational interaction is extremely weak due to the very small mass of the neutrino, and neutrinos do not participate in the strong interaction. Thus, neutrinos typically pass through normal matter unimpeded and undetected. Weak interactions create neutrinos in one of three leptonic flavors: electron neutrinos muon neutrinos (), or tau neutrinos (), in association with the corresponding charged lepton. Although neutrinos were long believed to be massless, it is now known that there are three discrete ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degeneracy Pressure
Degenerate matter is a highly dense state of fermionic matter in which the Pauli exclusion principle exerts significant pressure in addition to, or in lieu of, thermal pressure. The description applies to matter composed of electrons, protons, neutrons or other fermions. The term is mainly used in astrophysics to refer to dense stellar objects where gravitational pressure is so extreme that quantum mechanical effects are significant. This type of matter is naturally found in stars in their final evolutionary states, such as white dwarfs and neutron stars, where thermal pressure alone is not enough to avoid gravitational collapse. Degenerate matter is usually modelled as an ideal Fermi gas, an ensemble of non-interacting fermions. In a quantum mechanical description, particles limited to a finite volume may take only a discrete set of energies, called quantum states. The Pauli exclusion principle prevents identical fermions from occupying the same quantum state. At lowest total ener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleon
In physics and chemistry, a nucleon is either a proton or a neutron, considered in its role as a component of an atomic nucleus. The number of nucleons in a nucleus defines the atom's mass number (nucleon number). Until the 1960s, nucleons were thought to be elementary particles, not made up of smaller parts. Now they are known to be composite particles, made of three quarks bound together by the strong interaction. The interaction between two or more nucleons is called internucleon interaction or nuclear force, which is also ultimately caused by the strong interaction. (Before the discovery of quarks, the term "strong interaction" referred to just internucleon interactions.) Nucleons sit at the boundary where particle physics and nuclear physics overlap. Particle physics, particularly quantum chromodynamics, provides the fundamental equations that describe the properties of quarks and of the strong interaction. These equations describe quantitatively how quarks can bind toget ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Star
A neutron star is the collapsed core of a massive supergiant star, which had a total mass of between 10 and 25 solar masses, possibly more if the star was especially metal-rich. Except for black holes and some hypothetical objects (e.g. white holes, quark stars, and strange stars), neutron stars are the smallest and densest currently known class of stellar objects. Neutron stars have a radius on the order of and a mass of about 1.4 solar masses. They result from the supernova explosion of a massive star, combined with gravitational collapse, that compresses the core past white dwarf star density to that of atomic nuclei. Once formed, they no longer actively generate heat, and cool over time; however, they may still evolve further through collision or accretion. Most of the basic models for these objects imply that neutron stars are composed almost entirely of neutrons (subatomic particles with no net electrical charge and with slightly larger mass than protons); the electro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |