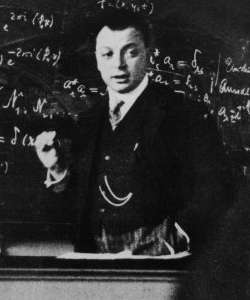|
Hidden Variable Theory
In physics, a hidden-variable theory is a deterministic model which seeks to explain the probabilistic nature of quantum mechanics by introducing additional, possibly inaccessible, variables. The mathematical formulation of quantum mechanics assumes that the state of a system prior to measurement is indeterminate; quantitative bounds on this indeterminacy are expressed by the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. Most hidden-variable theories are attempts to avoid this indeterminacy, but possibly at the expense of requiring that nonlocal interactions be allowed. One notable hidden-variable theory is the de Broglie–Bohm theory. In their 1935 EPR paper, Albert Einstein, Boris Podolsky, and Nathan Rosen argued that quantum entanglement might imply that quantum mechanics is an incomplete description of reality. John Stewart Bell in 1964, in his eponymous theorem proved that correlations between particles under any local hidden variable theory must obey certain constraints. Subse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." It is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics. (...) You will come to see physics as a towering achievement of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell Test
A Bell test, also known as Bell inequality test or Bell experiment, is a real-world physics experiment designed to test the theory of quantum mechanics in relation to Albert Einstein's concept of local realism. Named for John Stewart Bell, the experiments test whether or not the real world satisfies local realism, which requires the presence of some additional local variables (called "hidden" because they are not a feature of quantum theory) to explain the behavior of particles like photons and electrons. The test empirically evaluates the implications of Bell's theorem. , all Bell tests have found that the hypothesis of local hidden variables is inconsistent with the way that physical systems behave. Many types of Bell tests have been performed in physics laboratories, often with the goal of ameliorating problems of experimental design or set-up that could in principle affect the validity of the findings of earlier Bell tests. This is known as "closing loopholes in Bell tests". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolfgang Pauli
Wolfgang Ernst Pauli ( ; ; 25 April 1900 – 15 December 1958) was an Austrian theoretical physicist and a pioneer of quantum mechanics. In 1945, after having been nominated by Albert Einstein, Pauli received the Nobel Prize in Physics "for the discovery of the Exclusion Principle, also called the Pauli exclusion principle, Pauli Principle". The discovery involved Spin (physics), spin theory, which is the basis of a theory of the Matter#Structure, structure of matter. To preserve the conservation of energy in beta decay, he posited the existence of a small neutral particle, dubbed the neutrino by Enrico Fermi. The neutrino was detected in 1956. Early life Pauli was born in Vienna to a chemist, (''né'' Wolf Pascheles, 1869–1955), and his wife, Bertha Camilla Schütz; his sister was Hertha Pauli, a writer and actress. Pauli's middle name was given in honor of his Godparent, godfather, physicist Ernst Mach. Pauli's paternal grandparents were from prominent Jewish families of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilot Wave Theory
In theoretical physics, the pilot wave theory, also known as Bohmian mechanics, was the first known example of a hidden-variable theory, presented by Louis de Broglie in 1927. Its more modern version, the de Broglie–Bohm theory, interprets quantum mechanics as a deterministic theory, and avoids issues such as wave function collapse, and the paradox of Schrödinger's cat by being inherently nonlocal. The de Broglie–Bohm pilot wave theory is one of several interpretations of (non-relativistic) quantum mechanics. History Louis de Broglie's early results on the pilot wave theory were presented in his thesis (1924) in the context of atomic orbitals where the waves are stationary. Early attempts to develop a general formulation for the dynamics of these guiding waves in terms of a relativistic wave equation were unsuccessful until in 1926 Schrödinger developed his non-relativistic wave equation. He further suggested that since the equation described waves in configuration s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis De Broglie
Louis Victor Pierre Raymond, 7th Duc de Broglie (15 August 1892 – 19 March 1987) was a French theoretical physicist and aristocrat known for his contributions to quantum theory. In his 1924 PhD thesis, he postulated the wave nature of electrons and suggested that all matter has wave properties. This concept is known as the de Broglie hypothesis, an example of wave-particle duality, and forms a central part of the theory of quantum mechanics. De Broglie won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1929, after the wave-like behaviour of matter was first experimentally demonstrated in 1927. The wave-like behaviour of particles discovered by de Broglie was used by Erwin Schrödinger in his formulation of wave mechanics. De Broglie presented an alternative interpretation of these mechanics call the pilot-wave concept at the 1927 Solvay Conferences then abandoned it. In 1952, David Bohm developed a new form of the concept which became known as the de Broglie–Bohm theory. De Broglie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
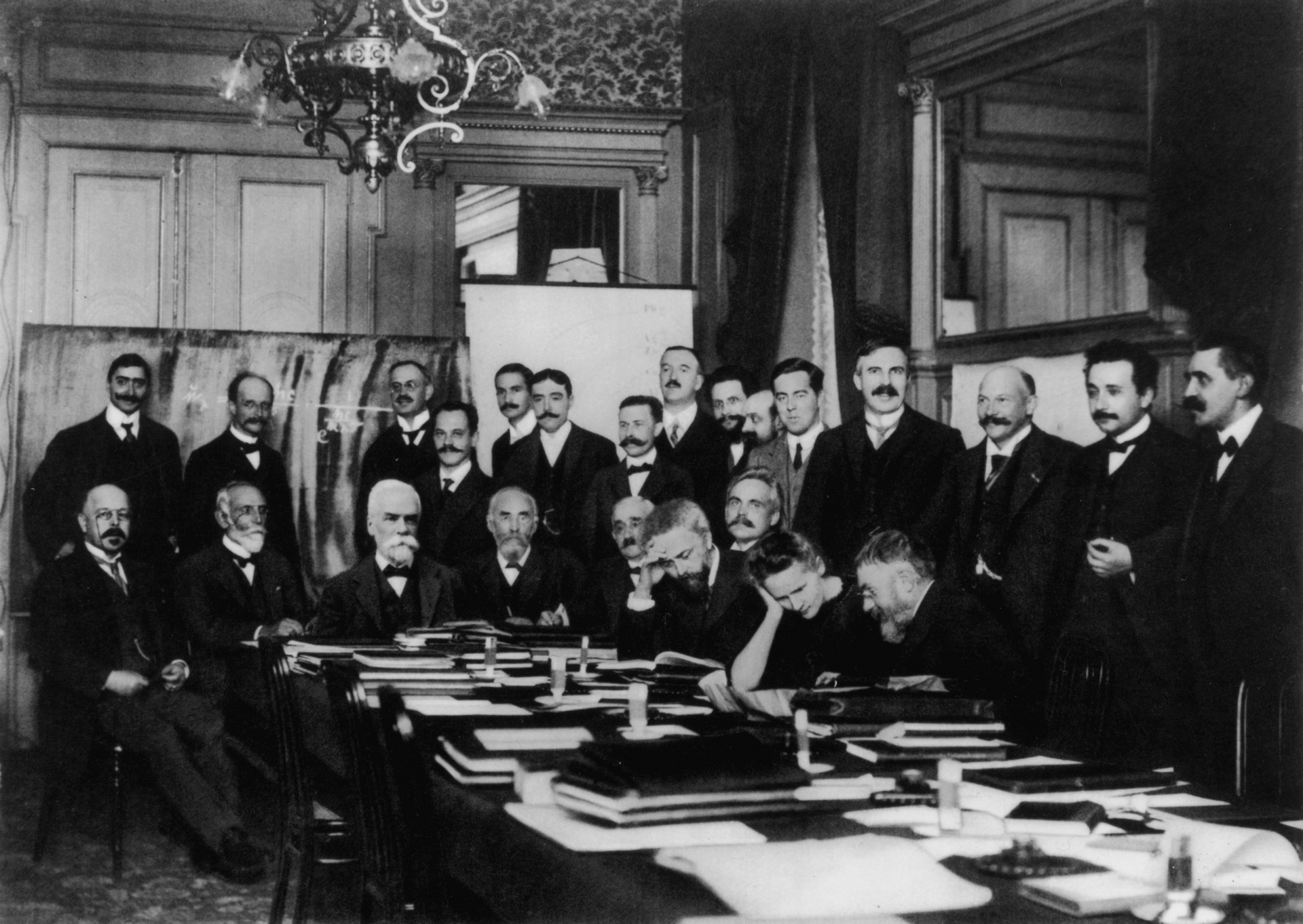
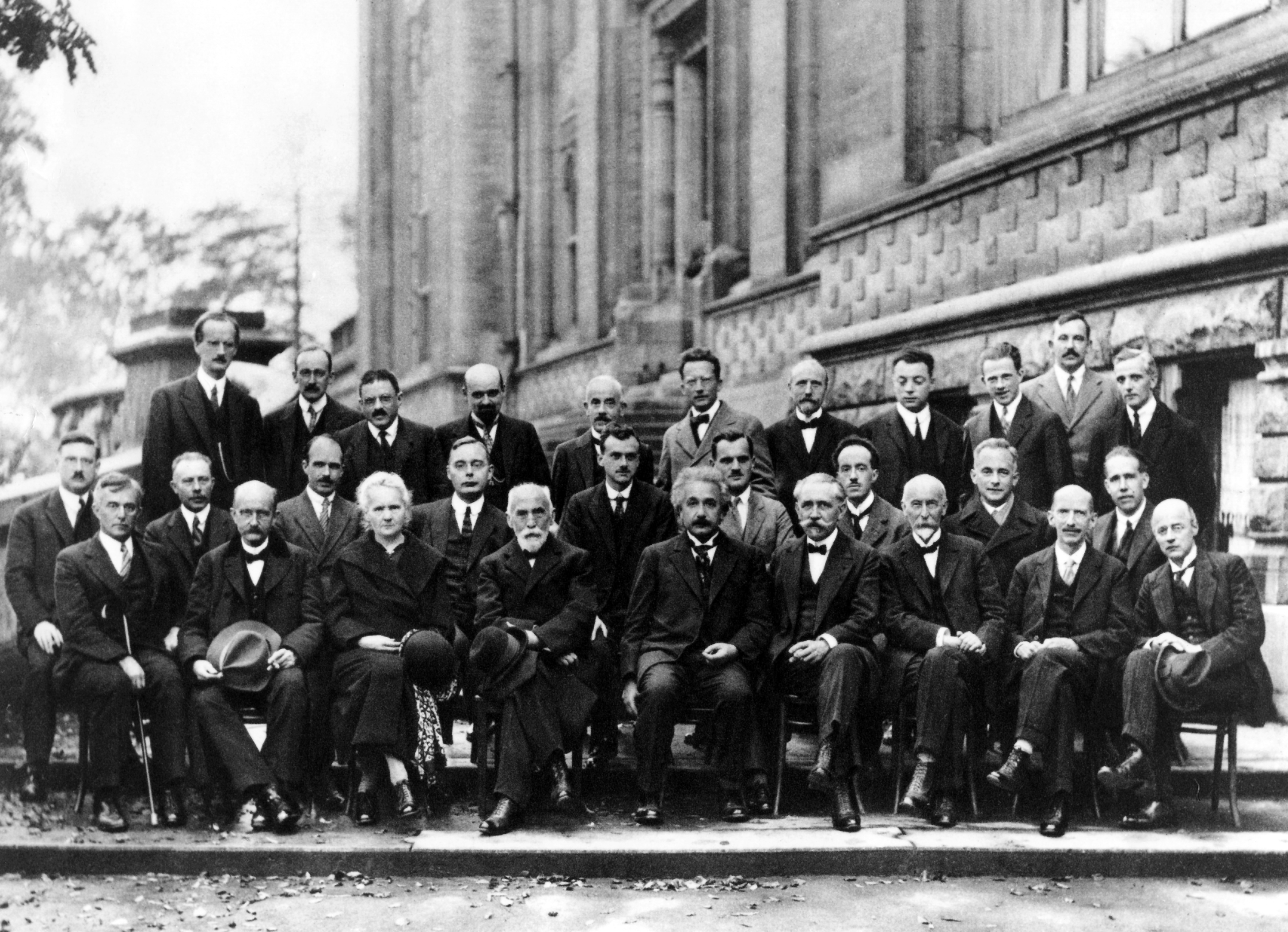
Solvay Conference
The Solvay Conferences () have been devoted to preeminent unsolved problems in both physics and chemistry. They began with the historic invitation-only 1911 Solvay Conference on Physics, considered a turning point in the world of physics, and are ongoing. Since the success of 1911, they have been organised by the International Solvay Institutes for Physics and Chemistry, founded by the Belgian industrialist Ernest Solvay in 1912 and 1913, and located in Brussels. The institutes coordinate conferences, workshops, seminars, and colloquia. Recent Solvay Conferences entail a three year cycle: the Solvay Conference on Physics followed by a gap year, followed by the Solvay Conference on Chemistry. The 1st Solvay Conference on Biology titled "The organisation and dynamics of biological computation" took place in April 2024. Notable conferences First conference Hendrik Lorentz was chairman of the first Solvay Conference on Physics, held in Brussels from 30 October to 3 November ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussian Academy Of Sciences
The Royal Prussian Academy of Sciences () was an academy established in Berlin, Germany on 11 July 1700, four years after the Prussian Academy of Arts, or "Arts Academy," to which "Berlin Academy" may also refer. In the 18th century, when French was the language of science and culture, it was a French-language institution. Origins Prince-elector Frederick III of Brandenburg, Germany founded the Academy under the name of ''Kurfürstlich Brandenburgische Societät der Wissenschaften'' ("Electoral-Brandenburger Society of Sciences") upon the advice of Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, who was appointed president. Unlike other Academies, the Prussian Academy was not directly funded out of the state treasury. Frederick granted it the monopoly on producing and selling calendars in Brandenburg, a suggestion from Leibniz. As Frederick was crowned "King in Prussia" in 1701, creating the Kingdom of Prussia, the Academy was renamed ''Königlich Preußische Sozietät der Wissenschaften'' ("Royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solvay Congress
The Solvay Conferences () have been devoted to preeminent unsolved problems in both physics and chemistry. They began with the historic invitation-only 1911 Solvay Conference on Physics, considered a turning point in the world of physics, and are ongoing. Since the success of 1911, they have been organised by the International Solvay Institutes for Physics and Chemistry, founded by the Belgian industrialist Ernest Solvay in 1912 and 1913, and located in Brussels. The institutes coordinate conferences, workshops, seminars, and colloquia. Recent Solvay Conferences entail a three year cycle: the Solvay Conference on Physics followed by a gap year, followed by the Solvay Conference on Chemistry. The 1st Solvay Conference on Biology titled "The organisation and dynamics of biological computation" took place in April 2024. Notable conferences First conference Hendrik Lorentz was chairman of the first Solvay Conference on Physics, held in Brussels from 30 October to 3 November 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niels Bohr
Niels Henrik David Bohr (, ; ; 7 October 1885 – 18 November 1962) was a Danish theoretical physicist who made foundational contributions to understanding atomic structure and old quantum theory, quantum theory, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922. Bohr was also a philosopher and a promoter of scientific research. Bohr developed the Bohr model of the atom, in which he proposed that energy levels of electrons are discrete and that the electrons revolve in stable orbits around the atomic nucleus but can jump from one energy level (or orbit) to another. Although the Bohr model has been supplanted by other models, its underlying principles remain valid. He conceived the principle of Complementarity (physics), complementarity: that items could be separately analysed in terms of contradictory properties, like behaving as a Wave–particle duality, wave or a stream of particles. The notion of complementarity dominated Bohr's thinking in both science and philoso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erwin Schrödinger
Erwin Rudolf Josef Alexander Schrödinger ( ; ; 12 August 1887 – 4 January 1961), sometimes written as or , was an Austrian-Irish theoretical physicist who developed fundamental results in quantum field theory, quantum theory. In particular, he is recognized for postulating the Schrödinger equation, an equation that provides a way to calculate the wave function of a system and how it changes dynamically in time. Schrödinger coined the term "quantum entanglement" in 1935. In addition, he wrote many works on various aspects of physics: statistical mechanics and thermodynamics, physics of dielectrics, color theory, electrodynamics, general relativity, and cosmology, and he made several attempts to construct a unified field theory. In his book ''What Is Life?'' Schrödinger addressed the problems of genetics, looking at the phenomenon of life from the point of view of physics. He also paid great attention to the philosophical aspects of science, ancient, and oriental philoso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavefunction
In quantum physics, a wave function (or wavefunction) is a mathematical description of the quantum state of an isolated quantum system. The most common symbols for a wave function are the Greek letters and (lower-case and capital psi (letter), psi, respectively). Wave functions are complex number, complex-valued. For example, a wave function might assign a complex number to each point in a region of space. The Born rule provides the means to turn these complex probability amplitudes into actual probabilities. In one common form, it says that the squared modulus of a wave function that depends upon position is the probability density function, probability density of measurement in quantum mechanics, measuring a particle as being at a given place. The integral of a wavefunction's squared modulus over all the system's degrees of freedom must be equal to 1, a condition called ''normalization''. Since the wave function is complex-valued, only its relative phase and relative magnitud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Born
Max Born (; 11 December 1882 – 5 January 1970) was a German-British theoretical physicist who was instrumental in the development of quantum mechanics. He also made contributions to solid-state physics and optics, and supervised the work of a number of notable physicists in the 1920s and 1930s. Born shared the 1954 Nobel Prize in Physics with Walther Bothe "for his fundamental research in quantum mechanics, especially in the statistical interpretation of the wave function". Born entered the University of Göttingen in 1904, where he met the three renowned mathematicians Felix Klein, David Hilbert, and Hermann Minkowski. He wrote his PhD thesis on the subject of the stability of elastic wires and tapes, winning the university's Philosophy Faculty Prize. In 1905, he began researching special relativity with Minkowski, and subsequently wrote his habilitation thesis on the Thomson model of the atom. A chance meeting with Fritz Haber in Berlin in 1918 led to discussion of how an io ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |