|
Hexyl Alcohol
Hexanol may refer to any of the following isomer In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formulae – that is, same number of atoms of each element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism is existence or possibility of isomers. Iso ...ic organic compounds with the formula C6H13OH: : See also * Cyclohexanol * Amyl alcohol {{Chemistry index Fatty alcohols ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johnson & Johnson
Johnson & Johnson (J&J) is an American multinational corporation founded in 1886 that develops medical devices, pharmaceuticals, and consumer packaged goods. Its common stock is a component of the Dow Jones Industrial Average and the company is ranked No. 36 on the 2021 Fortune 500 list of the largest United States corporations by total revenue. Johnson & Johnson is one of the List of public corporations by market capitalization, world's most valuable companies, and is one of only two U.S.-based companies that has a prime credit rating of AAA, higher than that of the United States government. Johnson & Johnson is headquartered in New Brunswick, New Jersey, the consumer division being located in Skillman, New Jersey. The corporation includes some 250 subsidiary companies with operations in 60 countries and products sold in over 175 countries. Johnson & Johnson had worldwide sales of $93.8billion during calendar year 2021. Johnson & Johnson's brands include numerous household na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-Methyl-2-pentanol
2-Methyl-2-pentanol (IUPAC name: 2-methylpentan-2-ol) is an organic chemical compound. It can be added to a gas chromatograph to help distinguish between branched compounds, especially alcohols. Its presence in urine can be used to test for exposure to 2-methylpentane. As with many other short-chain alcohols, 2-methyl-2-pentanol can produce intoxication and sedative effects similar to those of ethanol Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ..., though it is more irritating to mucous membranes and generally more toxic to the body. See also * 2-Methyl-2-butanol * 3-Methyl-3-pentanol References Hexanols Tertiary alcohols {{alcohol-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2,2-Dimethyl-1-butanol
2,2-Dimethyl-1-butanol is an organic chemical compound; it is one of the isomeric hexanols. Its main use is as a solvent A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for .... References Hexanols Primary alcohols {{alcohol-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Formula Of 2,2-dimethyl-1-butanol
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as biological organisms, minerals and chemicals. Abstract structures include data structures in computer science and musical form. Types of structure include a hierarchy (a cascade of one-to-many relationships), a network featuring many-to-many links, or a lattice featuring connections between components that are neighbors in space. Load-bearing Buildings, aircraft, skeletons, anthills, beaver dams, bridges and salt domes are all examples of load-bearing structures. The results of construction are divided into buildings and non-building structures, and make up the infrastructure of a human society. Built structures are broadly divided by their varying design approaches and standards, into categories including building structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
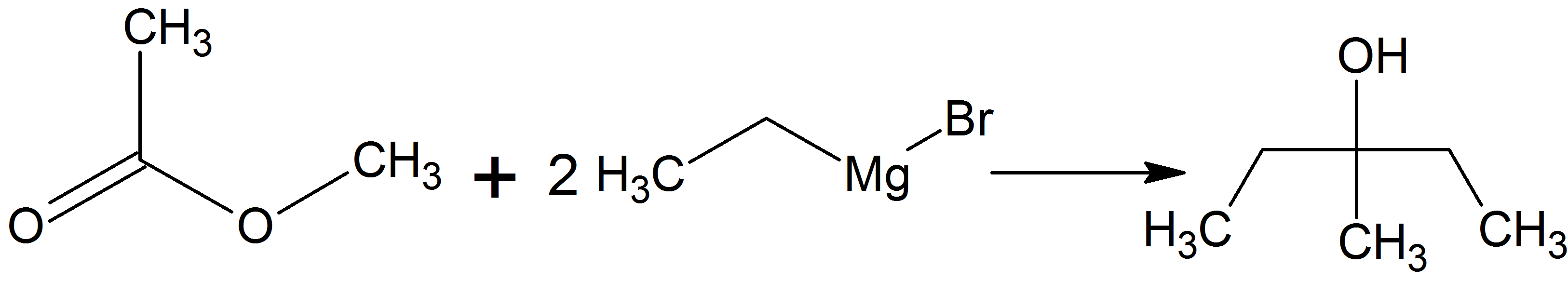
3-Methyl-3-pentanol
3-Methyl-3-pentanol (IUPAC name: 3-methylpentan-3-ol) is an organic chemical compound and a tertiary hexanol. It is used in the synthesis of the tranquilizer emylcamate, and has similar sedative and anticonvulsant actions itself. Synthesis It can be prepared by reacting ethylmagnesium bromide with methyl acetate in the so-called Grignard reaction using dried diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran as solvent. It can be prepared also by reacting ethylmagnesium bromide with butanone Butanone, also known as methyl ethyl ketone (MEK), is an organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH2CH3. This colourless liquid ketone has a sharp, sweet odor reminiscent of acetone. It is produced industrially on a large scale, but occurs in ... in the same conditions already mentioned. References Tertiary alcohols Hexanols {{alcohol-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-methyl-3-pentanol
3-Methyl-3-pentanol (IUPAC name: 3-methylpentan-3-ol) is an organic chemical compound and a tertiary hexanol. It is used in the synthesis of the tranquilizer emylcamate, and has similar sedative and anticonvulsant actions itself. Synthesis It can be prepared by reacting ethylmagnesium bromide with methyl acetate in the so-called Grignard reaction using dried diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran as solvent. It can be prepared also by reacting ethylmagnesium bromide with butanone Butanone, also known as methyl ethyl ketone (MEK), is an organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH2CH3. This colourless liquid ketone has a sharp, sweet odor reminiscent of acetone. It is produced industrially on a large scale, but occurs in ... in the same conditions already mentioned. References Tertiary alcohols Hexanols {{alcohol-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-Methyl-2-pentanol
4-Methyl-2-pentanol (IUPAC name: 4-methylpentan-2-ol) or methyl isobutyl carbinol (MIBC) is an organic chemical compound used primarily as a frother in mineral flotation and in the production of lubricant oil additives such as Zinc dithiophosphate. It is also used as a solvent, in organic synthesis, and in the manufacture of brake fluid and as a precursor to some plasticizer A plasticizer ( UK: plasticiser) is a substance that is added to a material to make it softer and more flexible, to increase its plasticity, to decrease its viscosity, and/or to decrease friction during its handling in manufacture. Plasticiz ...s. It is an acetone derivative in liquid state, with limited solubility in water but generally miscible with most organic solvents. References Hexanols {{mining-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |