|
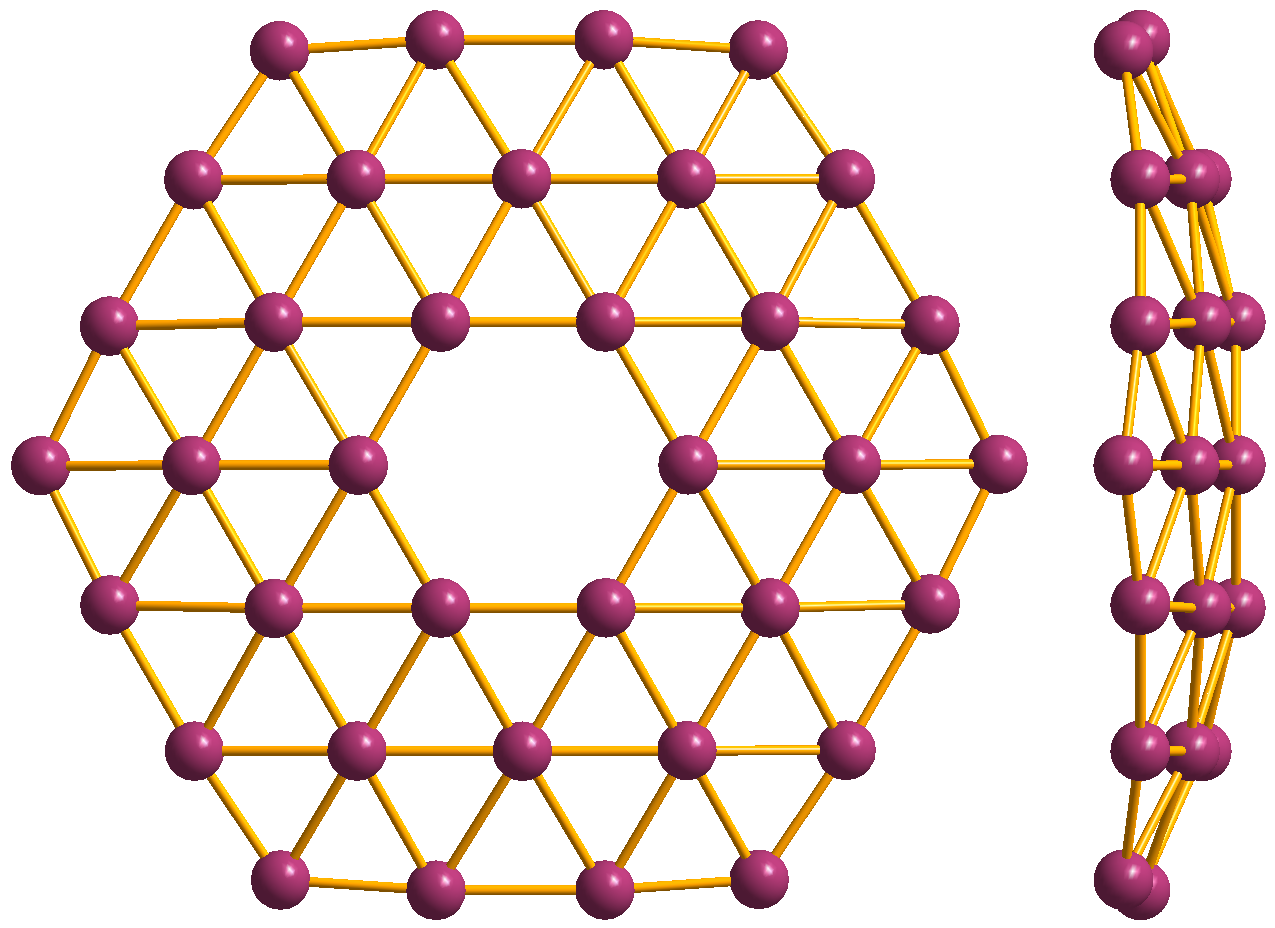
Hexagonal Bilayer Silica
Two-dimensional silica (2D silica) is a layered polymorph of silicon dioxide. Two varieties of 2D silica, both of hexagonal crystal symmetry, have been grown so far on various metal substrates. One is based on SiO4 tetrahedra, which are covalently bonded to the substrate. The second comprises graphene-like fully saturated sheets, which interact with the substrate via weak van der Waals bonds. One sheet of the second 2D silica variety is also called hexagonal bilayer silica (HBS); it can have either ordered or disordered (amorphous) structure. 2D silica has potential applications in electronics as the thinnest gate dielectric. It can also be used for isolation of graphene sheets from the substrate. 2D silica is a wide band gap semiconductor, whose band gap and geometry can be engineered by external electric field. It was shown to be a member of the auxetics Auxetics are structures or materials that have a negative Poisson's ratio. When stretched, they become thicker perpend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphene Vs 2D Silica-2
Graphene () is an allotrope of carbon consisting of a Single-layer materials, single layer of atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice nanostructure. "Carbon nanostructures for electromagnetic shielding applications", Mohammed Arif Poothanari, Sabu Thomas, et al., ''Industrial Applications of Nanomaterials'', 2019. "Carbon nanostructures include various low-dimensional allotropes of carbon including carbon black (CB), carbon fiber, carbon nanotubes (CNTs), fullerene, and graphene." The name is derived from "graphite" and the suffix -ene, reflecting the fact that the graphite allotrope of carbon contains numerous double bonds. Each atom in a graphene sheet is connected to its three nearest neighbors by a strong σ-bond, and contributes to a valence band one electron that extends over the whole sheet. This is the same type of b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defects In 2D Silica And Graphene
A defect is a physical, functional, or aesthetic attribute of a product or service that exhibits that the product or service failed to meet one of the desired specifications. Defect, defects or defected may also refer to: Examples * Angular defect, failure of some angles to add up to the expected amount of 360° or 180°, when such angles in the Euclidean plane would * Birth defect, a condition present at birth * Crystallographic defect, defects in the crystal lattice of solid materials *Latent defect, a fault in a property which could not have been discovered by a reasonably thorough inspection before completion or acquisition. * Product defect, a characteristic of a product which hinders its usability ** Software bug, a failure of computer software to meet requirements * Social defect, a sociological disorder Music * Defected Records, a music label * The Defects, a Northern-Irish punk rock band Other uses * Defect, the action of defection, abandoning allegiance to one country ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amorphous 2D Silica TEM-2
In condensed matter physics and materials science, an amorphous solid (or non-crystalline solid, glassy solid) is a solid that lacks the long-range order that is characteristic of a crystal. Etymology The term comes from the Greek ''a'' ("without"), and ''morphé'' ("shape, form"). In some older articles and books, the term was used synonymously with glass. Today, "glassy solid" or "amorphous solid" is considered the overarching concept. Polymers are often amorphous. Structure Amorphous materials have an internal structure comprising interconnected structural blocks that can be similar to the basic structural units found in the corresponding crystalline phase of the same compound. Unlike crystalline materials, however, no long-range order exists. Localized order in amorphous materials can be categorized as short or medium range order. By convention, short range order extends only to the nearest neighbor shell, typically only 1-2 atomic spacings. Medium range order is then de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymorphism (materials Science)
In materials science, polymorphism describes the existence of a solid material in more than one form or crystal structure. Polymorphism is a form of isomerism. Any crystalline material can exhibit the phenomenon. Allotropy refers to polymorphism for chemical elements. Polymorphism is of practical relevance to pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, pigments, dyestuffs, foods, and explosives. According to IUPAC, a polymorphic transition is "A reversible transition of a solid crystalline phase at a certain temperature and pressure (the inversion point) to another phase of the same chemical composition with a different crystal structure." According to McCrone, polymorphs are "different in crystal structure but identical in the liquid or vapor states." Materials with two polymorphs are called dimorphic, with three polymorphs, trimorphic, etc. Examples Many compounds exhibit polymorphism. It has been claimed that "every compound has different polymorphic forms, and that, in general, the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Dioxide
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and most abundant families of materials, existing as a compound of several minerals and as a synthetic product. Notable examples include fused quartz, fumed silica, silica gel, opal and aerogels. It is used in structural materials, microelectronics (as an electrical insulator), and as components in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Structure In the majority of silicates, the silicon atom shows tetrahedral coordination, with four oxygen atoms surrounding a central Si atomsee 3-D Unit Cell. Thus, SiO2 forms 3-dimensional network solids in which each silicon atom is covalently bonded in a tetrahedral manner to 4 oxygen atoms. In contrast, CO2 is a linear molecule. The starkly different structures of the dioxid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covalent Bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is known as covalent bonding. For many molecules, the sharing of electrons allows each atom to attain the equivalent of a full valence shell, corresponding to a stable electronic configuration. In organic chemistry, covalent bonding is much more common than ionic bonding. Covalent bonding also includes many kinds of interactions, including σ-bonding, π-bonding, metal-to-metal bonding, agostic interactions, bent bonds, three-center two-electron bonds and three-center four-electron bonds. The term ''covalent bond'' dates from 1939. The prefix ''co-'' means ''jointly, associated in action, partnered to a lesser degree, '' etc.; thus a "co-valent bond", in essence, means that the atoms share " valence", such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphene
Graphene () is an allotrope of carbon consisting of a single layer of atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice nanostructure. "Carbon nanostructures for electromagnetic shielding applications", Mohammed Arif Poothanari, Sabu Thomas, et al., ''Industrial Applications of Nanomaterials'', 2019. "Carbon nanostructures include various low-dimensional allotropes of carbon including carbon black (CB), carbon fiber, carbon nanotubes (CNTs), fullerene, and graphene." The name is derived from "graphite" and the suffix -ene, reflecting the fact that the allotrope of carbon contains numerous double bonds. Each atom in a graphene sheet is connecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van Der Waals Bond
In molecular physics, the van der Waals force is a distance-dependent interaction between atoms or molecules. Unlike ionic or covalent bonds, these attractions do not result from a chemical electronic bond; they are comparatively weak and therefore more susceptible to disturbance. The van der Waals force quickly vanishes at longer distances between interacting molecules. Named after Dutch physicist Johannes Diderik van der Waals, the van der Waals force plays a fundamental role in fields as diverse as supramolecular chemistry, structural biology, polymer science, nanotechnology, surface science, and condensed matter physics. It also underlies many properties of organic compounds and molecular solids, including their solubility in polar and non-polar media. If no other force is present, the distance between atoms at which the force becomes repulsive rather than attractive as the atoms approach one another is called the van der Waals contact distance; this phenomenon results f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gate Dielectric
A gate dielectric is a dielectric used between the gate and substrate of a field-effect transistor (such as a MOSFET). In state-of-the-art processes, the gate dielectric is subject to many constraints, including: * Electrically clean interface to the substrate (low density of quantum states for electrons) * High capacitance, to increase the FET transconductance * High thickness, to avoid dielectric breakdown and leakage by quantum tunneling. The capacitance and thickness constraints are almost directly opposed to each other. For silicon-substrate FETs, the gate dielectric is almost always silicon dioxide (called "gate oxide"), since thermal oxide has a very clean interface. However, the semiconductor industry is interested in finding alternative materials with higher dielectric constants, which would allow higher capacitance with the same thickness. History The earliest gate dielectric used in a field-effect transistor was silicon dioxide (SiO2). The silicon and silicondioxid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auxetics
Auxetics are structures or materials that have a negative Poisson's ratio. When stretched, they become thicker perpendicular to the applied force. This occurs due to their particular internal structure and the way this deforms when the sample is uniaxially loaded. Auxetics can be single molecules, crystals, or a particular structure of macroscopic matter. Such materials and structures are expected to have mechanical properties such as high energy absorption and fracture resistance. Auxetics may be useful in applications such as body armor, packing material, knee and elbow pads, robust shock absorbing material, and sponge mops. History The term ''auxetic'' derives from the Greek word () which means 'that which tends to increase' and has its root in the word (), meaning 'increase' (noun). This terminology was coined by Professor Ken Evans of the University of Exeter.. One of the first artificially produced auxetic materials, the RFS structure (diamond-fold structure), was inve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-dimensional Nanomaterials
In materials science, the term single-layer materials or 2D materials refers to crystalline solids consisting of a single layer of atoms. These materials are promising for some applications but remain the focus of research. Single-layer materials derived from single elements generally carry the -ene suffix in their names, e.g. graphene. Single-layer materials that are compounds of two or more elements have -ane or -ide suffixes. 2D materials can generally be categorized as either 2D allotropes of various elements or as compounds (consisting of two or more covalently bonding elements). It is predicted that there are hundreds of stable single-layer materials. The atomic structure and calculated basic properties of these and many other potentially synthesisable single-layer materials, can be found in computational databases. 2D materials can be produced using mainly two approaches: top-down exfoliation and bottom-up synthesis. The exfoliation methods include sonication, mechanical, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Dioxide
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and most abundant families of materials, existing as a compound of several minerals and as a synthetic product. Notable examples include fused quartz, fumed silica, silica gel, opal and aerogels. It is used in structural materials, microelectronics (as an electrical insulator), and as components in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Structure In the majority of silicates, the silicon atom shows tetrahedral coordination, with four oxygen atoms surrounding a central Si atomsee 3-D Unit Cell. Thus, SiO2 forms 3-dimensional network solids in which each silicon atom is covalently bonded in a tetrahedral manner to 4 oxygen atoms. In contrast, CO2 is a linear molecule. The starkly different structures of the dioxid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |