|
Hersey–Blanchard Situational Theory
Situational Leadership Theory, or the Situational Leadership Model, is a model created by Paul Hersey and Ken Blanchard, developed while working on ''Management of Organizational Behavior''.Hersey, P. and Blanchard, K. H. (1969). ''Management of Organizational Behavior – Utilizing Human Resources''. New Jersey/Prentice Hall. The theory was first introduced in 1969 as "life cycle theory of leadership". During the mid-1970s, ''life cycle theory of leadership'' was renamed "Situational Leadership Theory."Hersey, P. and Blanchard, K. H. (1977). ''Management of Organizational Behavior 3rd Edition– Utilizing Human Resources''. New Jersey/Prentice Hall. Situational Leadership emerged as one of a related group of two-factor theories of leadership, many of which originated in research done at Ohio State University in the 1960s. These two-factor theories hold that possibilities in leadership style are composed of combinations of two main variables: task behavior and relationship behavior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Hersey
Paul Hersey (January 26, 1931 - December 18, 2012) was a behavioral scientist and entrepreneur. He was best known for conceiving Situational Leadership. Hersey published ''Management of Organization Behavior'', which is now in its ninth edition. Hersey taught about training and development in leadership, management, and selling. He was also a consultant to industrial, government, and military organizations. Hersey was born in 1931 to Ralph Emerson Hersey and Beatrice Bromell. He was a Distinguished Professor of Leadership Studies at Nova Southeastern University. He had been a faculty member of Northern Illinois University, California State University, Chico, University of Arkansas, and Ohio University. He also served in the roles of Chairman of the Department of Management and Dean of the School of Business. Hersey had also served as Project Director for the Industrial Relations Center of the University of Chicago, Training Director at Kaiser Aluminum & Chemical Company, and Dep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ken Blanchard
Kenneth Hartley Blanchard (born May 6, 1939) is an American author, business consultant and motivational speaker. His writing career includes 60+ published books, most of which are co-authored books. His most successful book, ''The One Minute Manager'', has sold over 15 million copies and been translated into many languages. Blanchard is also the Chief Spiritual Officer of The Ken Blanchard Companies, an international management training and consulting firm that he and his wife, Marjorie Blanchard, co-founded in 1979 in San Diego, California. Blanchard is known for the quote "None of us is as smart as all of us." Education Blanchard attended New Rochelle High School, and graduated in 1957. He completed a BA degree in government and philosophy at Cornell University in 1961, an MA degree in sociology and counseling at Colgate University in 1963 and a PhD degree in education administration and leadership at Cornell University in 1967. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Managerial Grid Model
The managerial grid model or managerial grid theory (1964) is a style leadership model developed by Robert R. Blake and Jane Mouton. This model originally identified five different leadership styles based on the ''concern for people'' and the ''concern for production''. The optimal leadership style in this model is based on Theory Y. The grid theory has continued to evolve and develop. The theory was updated with two additional leadership styles and with a new element, resilience. In 1999, the grid managerial seminar began using a new text, The Power to Change. The model is represented as a grid with ''concern for production'' as the x-axis and ''concern for people'' as the y-axis; each axis ranges from 1 (Low) to 9 (High). The resulting leadership styles are as follows: * The indifferent (previously called impoverished) style (1,1): evade and elude. In this style, managers have low concern for both people and production. Managers use this style to preserve job and job seni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William James Reddin
William James Reddin also known as Bill Reddin (May 10, 1930 – June 20, 1999) was a British-born management behavioralist, theorist, writer, and consultant. His published works examined and explained how managers in profit and non-profit organizations behaved under certain situations and conditions. The focus of his work was to understand to what extent managers were effective in their role and successful in managing situations to have the right impact on the organization's objectives. Through extensive research Reddin concluded that there is no ideal management style. He put forward that there was only one realistic and unambiguous definition of managerial effectiveness, the extent to which a manager or leader achieves the output requirements of the position. This is the manager's or leader's only job: to be effective. Reddin was often quoted as saying both in his writings, to his clients and to his students, that there is no ideal style of managing; and there is no one way t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leadership And The One Minute Manager
Leadership, both as a research area and as a practical skill, encompasses the ability of an individual, group or organization to "lead", influence or guide other individuals, teams, or entire organizations. The word "leadership" often gets viewed as a contested term. Specialist literature debates various viewpoints on the concept, sometimes contrasting Eastern and Western approaches to leadership, and also (within the West) North American versus European approaches. U.S. academic environments define leadership as "a process of social influence in which a person can enlist the aid and support of others in the accomplishment of a common and ethical task". Basically, leadership can be defined as an influential power-relationship in which the power of one party (the "leader") promotes movement/change in others (the "followers"). Some have challenged the more traditional managerial views of leadership (which portray leadership as something possessed or owned by one individual due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leadership Style
A leadership style is a leader's method of providing direction, implementing plans, and motivating people. Various authors have proposed identifying many different leadership styles as exhibited by leaders in the political, business or other fields. Studies on leadership style are conducted in the military field, expressing an approach that stresses a holistic view of leadership, including how a leader's physical presence determines how others perceive that leader. The factors of physical presence in this context include military bearing, physical fitness, confidence, and resilience. A leader's conceptual abilities include agility, judgment, innovation, interpersonal tact, and domain knowledge. Leaders are characterized as individuals who have differential influence over the setting of goals, logistics for coordination, monitoring of effort, and rewards and punishment of group members. Domain knowledge encompasses tactical and technical knowledge as well as cultural and geopolitica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behavior
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions and mannerisms made by individuals, organisms, systems or artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or organisms as well as the inanimate physical environment. It is the computed response of the system or organism to various stimuli or inputs, whether internal or external, conscious or subconscious, overt or covert, and voluntary or involuntary. Taking a behavior informatics perspective, a behavior consists of actor, operation, interactions, and their properties. This can be represented as a behavior vector. Models Biology Although disagreement exists as to how to precisely define behavior in a biological context, one common interpretation based on a meta-analysis of scientific literature states that "behavior is the internally coordinated responses (actions or inactions) of whole living organisms (individuals or groups) to internal and/or external sti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contingency Theory
A contingency theory is an organizational theory that claims that there is no best way to organize a corporation, to lead a company, or to make decisions. Instead, the optimal course of action is contingent (dependent) upon the internal and external situation. Contingent leaders are flexible in choosing and adapting to succinct strategies to suit change in situation at a particular period in time in the running of the organization. History The contingency approach to leadership was influenced by two earlier research programs endeavoring to pinpoint effective leadership behavior. During the 1950s, researchers at Ohio State University administered extensive questionnaires measuring a range of possible leader behaviors in various organizational contexts. Although multiple sets of leadership behaviors were originally identified based on these questionnaires, two types of behaviors proved to be especially typical of effective leaders: ''(1) consideration'' leader behaviors that inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
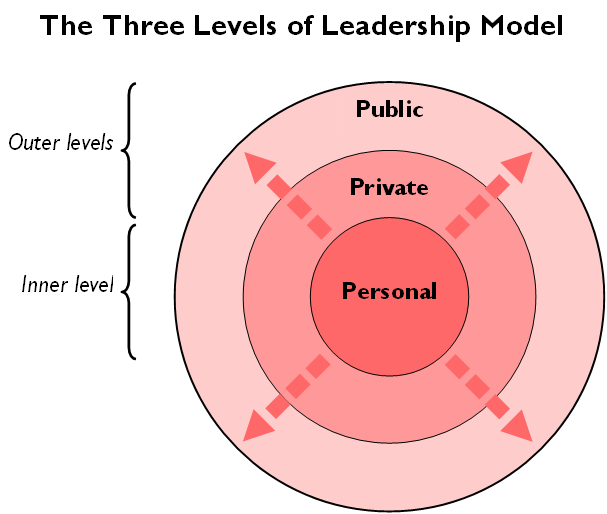
Three Levels Of Leadership Model
The Three Levels of Leadership is a leadership model formulated in 2011 by James Scouller. Designed as a practical tool for developing a person's leadership presence, knowhow and skill, it aims to summarize what leaders have to do, not only to bring leadership to their group or organization, but also to develop themselves technically and psychologically as leaders. It has been classified as an " integrated psychological" theory of leadership. It is sometimes known as the 3P model of leadership (the three Ps standing for Public, Private and Personal leadership). The Three Levels of Leadership model attempts to combine the strengths of older leadership theories (i.e. traits, behavioral/styles, situational, functional) while addressing their limitations and, at the same time, offering a foundation for leaders wanting to apply the philosophies of servant leadership and "authentic leadership". Limitations of older leadership theories In reviewing the older leadership theories, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trait Leadership
Trait leadership is defined as integrated patterns of personal characteristics that reflect a range of individual differences and foster consistent leader effectiveness across a variety of group and organizational situations (Zaccaro, Kemp, & Bader, 2004; Zaccaro 2007). The theory of trait leadership is developed from early leadership research which focused primarily on finding a group of heritable attributes that differentiate leaders from nonleaders. Leader effectiveness refers to the amount of influence a leader has on individual or group performance, followers’ satisfaction, and overall effectiveness (Derue, Nahrgang, Wellman, & Humphrey, 2011; de Vries 2012). Many scholars have argued that leadership is unique to only a select number of individuals and that these individuals possess certain immutable traits that cannot be developed (Galton, 1869). Although this perspective has been criticized immensely over the past century, scholars still continue to study the effects of pers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |