|
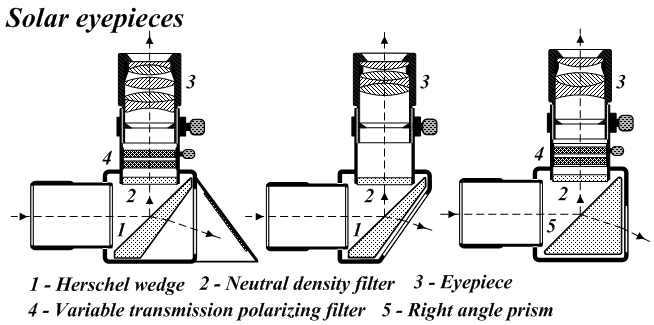
Herschel Wedge
A Herschel wedge or Herschel prism is an optical prism used in solar observation to refract most of the light out of the optical path, allowing safe visual observation. It was first proposed and used by astronomer John Herschel in the 1830s. Overview The prism in a Herschel wedge has a trapezoidal cross section. The surface of the prism facing the light acts as a standard diagonal mirror, reflecting a small portion of the incoming light at 90 degrees into the eyepiece. The trapezoidal prism shape refracts the remainder of the light gathered by the telescope's objective away at an angle. The Herschel wedge reflects about 4.6% of the light that passes through one of the prism faces that is flat to 1/10 of the wavelength of the light. The remaining ~95.4% of the light and heat goes into the prism and exits through the other face and out the back door of the housing; thus, the excess light and heat is disposed of and not used for observing. While they decrease the intensity of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Telescope
A solar telescope is a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun. Solar telescopes usually detect light with wavelengths in, or not far outside, the visible spectrum. Obsolete names for Sun telescopes include heliograph and photoheliograph. Professional solar telescopes Solar telescopes need optics large enough to achieve the best possible diffraction limit but less so for the associated light-collecting power of other astronomical telescopes. However, recently newer narrower filters and higher framerates have also driven solar telescopes towards photon-starved operations. Both the Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope as well as the proposed European Solar Telescope (EST) have larger apertures not only to increase the resolution, but also to increase the light-collecting power. Because solar telescopes operate during the day, seeing is generally worse than for night-time telescopes, because the ground around the telescope is heated which causes turbulence and degrades ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refraction
In physics, refraction is the redirection of a wave as it passes from one medium to another. The redirection can be caused by the wave's change in speed or by a change in the medium. Refraction of light is the most commonly observed phenomenon, but other waves such as sound waves and water waves also experience refraction. How much a wave is refracted is determined by the change in wave speed and the initial direction of wave propagation relative to the direction of change in speed. For light, refraction follows Snell's law, which states that, for a given pair of media, the ratio of the sines of the angle of incidence ''θ1'' and angle of refraction ''θ2'' is equal to the ratio of phase velocities (''v''1 / ''v''2) in the two media, or equivalently, to the refractive indices (''n''2 / ''n''1) of the two media. :\frac =\frac=\frac Optical prisms and lenses use refraction to redirect light, as does the human eye. The refractive index of materials varies with the wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Herschel
Sir John Frederick William Herschel, 1st Baronet (; 7 March 1792 – 11 May 1871) was an English polymath active as a mathematician, astronomer, chemist, inventor, experimental photographer who invented the blueprint and did botanical work. Herschel originated the use of the Julian day system in astronomy. He named seven moons of Saturn and four moons of Uranus – the seventh planet, discovered by his father Sir William Herschel. He made many contributions to the science of photography, and investigated colour blindness and the chemical power of ultraviolet rays. His ''Preliminary Discourse'' (1831), which advocated an inductive approach to scientific experiment and theory-building, was an important contribution to the philosophy of science. Early life and work on astronomy Herschel was born in Slough, Buckinghamshire, the son of Mary Baldwin and astronomer William Herschel. He was the nephew of astronomer Caroline Herschel. He studied shortly at Eton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star Diagonal
A star diagonal, erecting lens or diagonal mirror is an angled mirror or prism used in telescopes that allows viewing from a direction that is perpendicular to the usual eyepiece axis. It allows more convenient and comfortable viewing when the telescope is pointed at, or near the zenith (i.e. directly overhead). Also, the resulting image is right side up, but is reversed from left to right. Types of diagonals Star diagonals are available in 0.965", 1.25", and 2" diameters. The 2" diagonals allow longer-focal length, low-power 2" barrel eyepieces for a wider field of view. Star diagonals come in all price ranges, from as low as a few dollars up to hundreds of dollars. Mirror (reflective) diagonals These diagonals (often called star diagonals) use a mirror set at a 45° angle inside the diagonal to turn the telescope's image at a 90° angle to the rear cell. Mirror diagonals produce an image in the eyepiece that is correctly oriented vertically, but is reversed left-to-right hori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Objective (optics)
In optical engineering, the objective is the optical element that gathers light from the object being observed and focuses the light rays to produce a real image. Objectives can be a single lens or mirror, or combinations of several optical elements. They are used in microscopes, binoculars, telescopes, cameras, slide projectors, CD players and many other optical instruments. Objectives are also called object lenses, object glasses, or objective glasses. Microscope objectives The objective lens of a microscope is the one at the bottom near the sample. At its simplest, it is a very high-powered magnifying glass, with very short focal length. This is brought very close to the specimen being examined so that the light from the specimen comes to a focus inside the microscope tube. The objective itself is usually a cylinder containing one or more lenses that are typically made of glass; its function is to collect light from the sample. Magnification One of the most important prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflecting Telescope
A reflecting telescope (also called a reflector) is a telescope that uses a single or a combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century by Isaac Newton as an alternative to the refracting telescope which, at that time, was a design that suffered from severe chromatic aberration. Although reflecting telescopes produce other types of optical aberrations, it is a design that allows for very large diameter objectives. Almost all of the major telescopes used in astronomy research are reflectors. Many variant forms are in use and some employ extra optical elements to improve image quality or place the image in a mechanically advantageous position. Since reflecting telescopes use mirrors, the design is sometimes referred to as a catoptric telescope. From the time of Newton to the 1800s, the mirror itself was made of metal usually speculum metal. This type included Newton's first designs and even the larges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutral Density Filter
In photography and optics, a neutral-density filter, or ND filter, is a filter that reduces or modifies the intensity of all wavelengths, or colors, of light equally, giving no changes in hue of color rendition. It can be a colorless (clear) or grey filter, and is denoted by Wratten number 96. The purpose of a standard photographic neutral-density filter is to reduce the amount of light entering the lens. Doing so allows the photographer to select combinations of aperture, exposure time and sensor sensitivity that would otherwise produce overexposed pictures. This is done to achieve effects such as a shallower depth of field or motion blur of a subject in a wider range of situations and atmospheric conditions. For example, one might wish to photograph a waterfall at a slow shutter speed to create a deliberate motion-blur effect. The photographer might determine that to obtain the desired effect, a shutter speed of ten seconds was needed. On a very bright day, there might be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Telescope Parts And Construction
Hardware Accessories * Finderscope * Iron sight * Reflector (reflex) sight * Cheshire collimator: A simple tool to collimate a telescope Control * Clock drive * GoTo Mechanical construction * Mirror support cell * Serrurier truss *Silvering Mounts * Telescope mount - Types include: ** Altazimuth mount ** Equatorial mount *** Equatorial platform **** Poncet Platform *** Fork mount *** German equatorial mount *** Springfield mount Optics Mirrors and lenses are the critical light-bending components of a telescope. * Objective: The first lens or curved mirror that collects and focuses the incoming light. **Primary lens: The objective of a refracting telescope. ** Primary mirror: The objective of a reflecting telescope. *Corrector plate: A full aperture negative lens placed before a primary mirror designed to correct the optical aberrations of the mirror. ** Schmidt corrector plate: An aspheric-shaped corrector plate used in the Schmidt telescope. ** Meniscus corrector: A m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Instruments
Astronomical instruments include: *Alidade *Armillary sphere * Astrarium *Astrolabe *Astronomical clock *the Antikythera mechanism, an astronomical clock *Blink comparator *Bolometer *the Canterbury Astrolabe Quadrant *Celatone *Celestial sphere *Charge-coupled device * Computers *CMOS sensor *Coronagraph * Cosmolabe *Dioptra * Equatorial ring * Equatorium *Gnomon *Inclinometer *Interferometer * Kamal *Meridian circle * Microchannel plate detector * Mural instrument * Nebra sky disk *Nocturnal * Octant *Optical spectrometer, a.k.a., Spectrograph *Orrery *Photographic plate *Photometer *Planisphere *the Prague astronomical clock * Quadrant *Reticle * Radio plate *Retroreflector * Scaphe *Sextant *Starshade *Space telescope *Spectrometers *Sundial *Telescope * Torquetum * Triquetrum *Zenith telescope See also *Astronomy * Outline of astronomy * Surveying instrument *Measurement instrument {{DEFAULTSORT:Astronomical instruments Instruments Instrument may refer to: Science a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Imaging
Astrophotography, also known as astronomical imaging, is the photography or imaging of astronomical objects, celestial events, or areas of the night sky. The first photograph of an astronomical object (the Moon) was taken in 1840, but it was not until the late 19th century that advances in technology allowed for detailed stellar photography. Besides being able to record the details of extended objects such as the Moon, Sun, and planets, modern astrophotography has the ability to image objects invisible to the human eye such as dim stars, nebulae, and galaxies. This is done by long time exposure since both film and digital cameras can accumulate and sum photons over these long periods of time. Photography using extended exposure-times revolutionized the field of professional astronomical research, recording hundreds of thousands of new stars, and nebulae invisible to the human eye. Specialized and ever-larger optical telescopes were constructed as essentially big cameras t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Telescopes
A solar telescope is a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun. Solar telescopes usually detect light with wavelengths in, or not far outside, the visible spectrum. Obsolete names for Sun telescopes include heliograph and photoheliograph. Professional solar telescopes Solar telescopes need optics large enough to achieve the best possible diffraction limit but less so for the associated light-collecting power of other astronomical telescopes. However, recently newer narrower filters and higher framerates have also driven solar telescopes towards photon-starved operations. Both the Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope as well as the proposed European Solar Telescope (EST) have larger apertures not only to increase the resolution, but also to increase the light-collecting power. Because solar telescopes operate during the day, seeing is generally worse than for night-time telescopes, because the ground around the telescope is heated which causes turbulence and degrades the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |